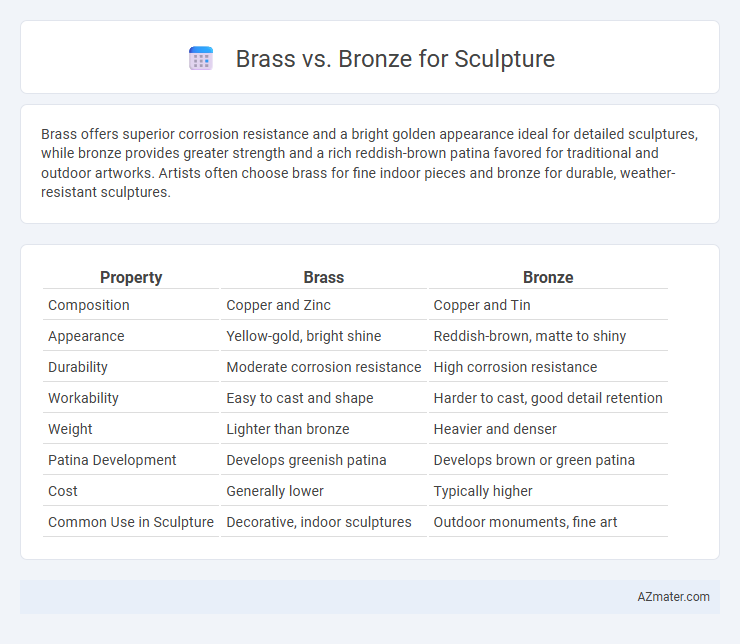
Brass offers superior corrosion resistance and a bright golden appearance ideal for detailed sculptures, while bronze provides greater strength and a rich reddish-brown patina favored for traditional and outdoor artworks. Artists often choose brass for fine indoor pieces and bronze for durable, weather-resistant sculptures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brass | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Zinc | Copper and Tin |
| Appearance | Yellow-gold, bright shine | Reddish-brown, matte to shiny |
| Durability | Moderate corrosion resistance | High corrosion resistance |
| Workability | Easy to cast and shape | Harder to cast, good detail retention |
| Weight | Lighter than bronze | Heavier and denser |
| Patina Development | Develops greenish patina | Develops brown or green patina |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Common Use in Sculpture | Decorative, indoor sculptures | Outdoor monuments, fine art |
Introduction: Brass vs Bronze in Sculpture
Brass and bronze are two popular metal alloys widely used in sculpture due to their durability and aesthetic qualities. Brass, composed primarily of copper and zinc, is known for its bright gold-like appearance and malleability, making it ideal for detailed work. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, offers superior strength and a rich, warm patina that enhances the depth and character of sculptures over time.
Historical Use of Brass and Bronze in Art
Brass and bronze have been pivotal in sculpture throughout history, with bronze dominating ancient and classical art due to its durability and fine detail capabilities, exemplified by iconic works like the Greek Riace Warriors and Roman busts. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, gained prominence in the Renaissance and Baroque periods for decorative and architectural sculptures, prized for its golden hue and resistance to corrosion. The distinct metallurgical properties of bronze made it favorable for casting intricate statues and complex forms, while brass was often chosen for ornamental and functional art pieces in historical European and Asian contexts.
Composition and Material Differences
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, offering a bright yellowish appearance and higher malleability, making it ideal for detailed sculpting. Bronze consists mainly of copper and tin, known for its superior strength, corrosion resistance, and warm reddish-brown tone, which enhances patina development over time. The differing metal compositions affect not only the sculpture's color and texture but also its durability and suitability for various artistic techniques.
Visual Appearance and Finish
Brass offers a bright, golden-yellow hue that enhances sculptures with a warm, reflective surface, making details more pronounced and visually striking. Bronze presents a deeper, reddish-brown color that ages to a rich patina, providing an antique and timeless finish favored in classical and traditional sculptures. Both metals allow for smooth polishing, but bronze's natural oxidation creates unique textures that add character and depth to the artwork over time.
Durability and Longevity
Bronze sculptures exhibit superior durability and longevity due to their high resistance to corrosion and environmental wear, making them ideal for outdoor installations. Brass, while visually appealing with its golden hue, tends to tarnish and is more susceptible to corrosion over time, especially in humid or salty environments. The robust patina that develops on bronze enhances its protective qualities, ensuring the sculpture maintains structural integrity and aesthetic appeal for centuries.
Workability and Casting Properties
Brass offers excellent workability due to its malleability and lower melting point around 900-940degC, making it easier to shape and cast with detailed precision. Bronze, typically composed of copper and tin, has a higher melting point of approximately 950-1050degC and provides superior fluidity, resulting in finer surface textures and intricate detail retention in sculptures. Both alloys are favored in casting, but bronze's superior strength and corrosion resistance make it ideal for outdoor sculptures, while brass's ease of machining suits complex interior pieces.
Cost Comparison: Brass vs Bronze
Brass typically costs less than bronze due to its higher zinc content and simpler alloy composition, making it a budget-friendly choice for sculptures. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, tends to be more expensive but offers superior durability and a richer patina over time. Artists and sculptors weigh the initial cost against the long-term value and aesthetic qualities when choosing between brass and bronze for their work.
Popular Sculpture Applications
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is favored in popular sculpture applications for its bright gold-like appearance and excellent malleability, making it ideal for intricate designs and decorative statues. Bronze, comprised primarily of copper and tin, is highly valued for its durability and ability to capture fine detail, commonly used in large public monuments, historical sculptures, and outdoor installations due to its resistance to corrosion. Both materials offer distinct aesthetic and functional advantages, with bronze preferred for longevity and brass chosen for its vibrant color and ease of casting.
Conservation and Maintenance
Brass sculptures require regular cleaning and careful polishing to prevent tarnishing and corrosion due to their high copper and zinc content, with protective coatings often applied to extend longevity. Bronze, composed primarily of copper and tin, develops a protective patina over time that helps resist corrosion but still benefits from occasional maintenance such as waxing to preserve surface integrity. Both metals demand controlled environmental conditions to minimize oxidation and prolong the sculpture's aesthetic and structural stability.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Sculpture
Selecting the right alloy for your sculpture depends on factors such as durability, workability, and aesthetics. Brass, composed primarily of copper and zinc, offers a bright gold-like finish and is easier to cast and polish, making it ideal for detailed work and indoor sculptures. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, provides superior strength, corrosion resistance, and a classic warm brown patina, making it a preferred choice for outdoor sculptures and large-scale projects.
Infographic: Brass vs Bronze for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com