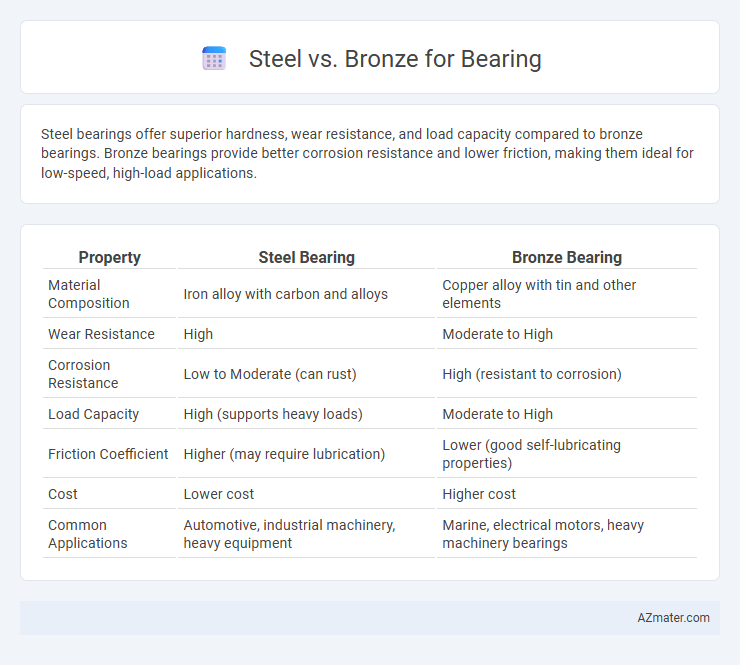
Steel bearings offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and load capacity compared to bronze bearings. Bronze bearings provide better corrosion resistance and lower friction, making them ideal for low-speed, high-load applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Steel Bearing | Bronze Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Iron alloy with carbon and alloys | Copper alloy with tin and other elements |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to Moderate (can rust) | High (resistant to corrosion) |
| Load Capacity | High (supports heavy loads) | Moderate to High |
| Friction Coefficient | Higher (may require lubrication) | Lower (good self-lubricating properties) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Applications | Automotive, industrial machinery, heavy equipment | Marine, electrical motors, heavy machinery bearings |
Introduction to Bearing Materials
Steel bearings offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to deformation under high loads, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Bronze bearings provide excellent corrosion resistance, good wear properties, and self-lubricating capabilities, which are beneficial for lower-speed or marine environments. The choice between steel and bronze depends on operating conditions, load requirements, and environmental factors affecting bearing performance.
Key Characteristics of Steel Bearings
Steel bearings exhibit superior hardness, wear resistance, and load-bearing capacity compared to bronze bearings, making them ideal for high-stress applications. Their precision manufacturing enables lower friction coefficients and higher rotational accuracy, enhancing overall performance and service life. Steel bearings also offer better corrosion resistance when alloyed or treated, which extends durability in demanding environments.
Key Characteristics of Bronze Bearings
Bronze bearings exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments where steel bearings may fail. Their low friction properties and good load-carrying capacity enhance performance in applications requiring smooth operation and durability. Bronze's inherent lubricity reduces wear and extends service life, especially in conditions lacking continuous lubrication.
Load Capacity: Steel vs Bronze
Steel bearings offer higher load capacity compared to bronze due to their superior tensile strength and hardness, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Bronze bearings, while exhibiting good load-bearing capabilities, typically perform better in moderate load environments with better resistance to wear and corrosion. The choice between steel and bronze bearings largely depends on the specific load requirements and operating conditions of the machinery.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Steel bearings exhibit superior wear resistance due to their high tensile strength and hardness, making them ideal for heavy load and high-speed applications. Bronze bearings provide excellent durability with self-lubricating properties that reduce friction and wear in low to moderate load conditions. The choice between steel and bronze depends on the specific operational environment, with steel favored for extreme stress and bronze preferred for corrosion resistance and quieter performance.
Lubrication Needs and Maintenance
Steel bearings require consistent lubrication with high-quality oils or greases to reduce friction and prevent wear, especially under high load and speed conditions. Bronze bearings often feature self-lubricating properties due to embedded lubricants or porous structures that retain oil, lowering maintenance frequency. Regular inspection and timely lubrication are essential for steel bearings, while bronze bearings typically demand less frequent maintenance but still need monitoring to avoid lubricant depletion.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Steel bearings generally exhibit superior mechanical strength but are more prone to corrosion without protective coatings or stainless variants, especially in humid or marine environments. Bronze bearings naturally offer better corrosion resistance due to their copper content, making them ideal for applications exposed to water or corrosive substances. Selecting bronze over steel significantly enhances bearing lifespan in corrosive settings, reducing maintenance frequency and operational downtime.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Steel bearings generally offer lower cost and higher availability due to widespread production and abundant raw materials, making them ideal for large-scale industrial applications. Bronze bearings, while more expensive, provide excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, but their availability is limited by higher material costs and less common manufacturing. Selecting between steel and bronze bearings depends heavily on budget constraints and supply chain reliability, with steel often preferred for cost efficiency and bronze for specialized performance needs.
Typical Applications of Steel and Bronze Bearings
Steel bearings are typically used in high-load and high-speed applications such as automotive engines, industrial machinery, and aerospace components due to their superior strength, durability, and wear resistance. Bronze bearings excel in environments requiring excellent corrosion resistance and low friction, making them ideal for marine equipment, agricultural machinery, and electrical motors. Both materials offer distinct advantages: steel for heavy-duty performance and bronze for enhanced lubrication and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the Right Bearing Material
Selecting the right bearing material depends on factors like load capacity, wear resistance, and operating environment. Steel bearings offer high strength, durability, and excellent load-bearing capabilities, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications with high-speed and temperature conditions. Bronze bearings provide superior corrosion resistance and self-lubricating properties, which are beneficial for low-speed, low-load, or marine environments.
Infographic: Steel vs Bronze for Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com