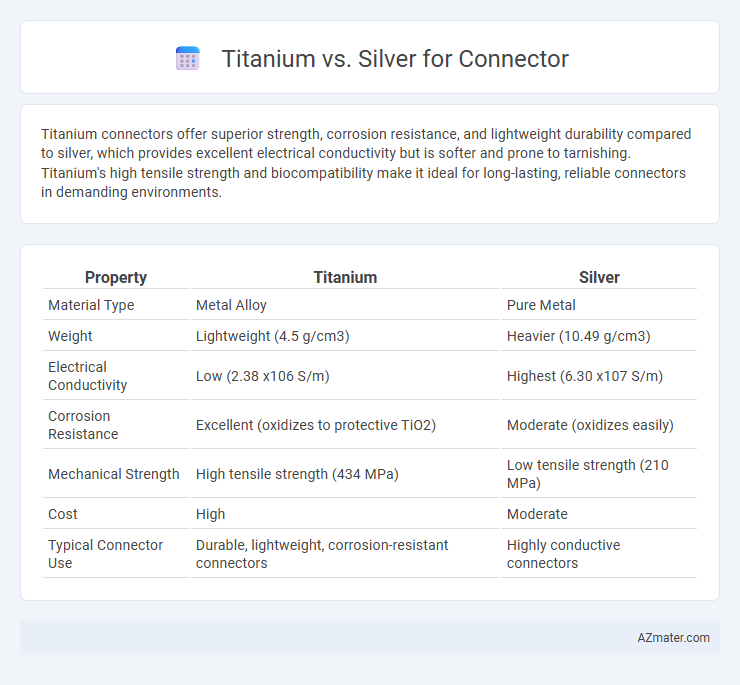
Titanium connectors offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight durability compared to silver, which provides excellent electrical conductivity but is softer and prone to tarnishing. Titanium's high tensile strength and biocompatibility make it ideal for long-lasting, reliable connectors in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Metal Alloy | Pure Metal |
| Weight | Lightweight (4.5 g/cm3) | Heavier (10.49 g/cm3) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (2.38 x106 S/m) | Highest (6.30 x107 S/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (oxidizes to protective TiO2) | Moderate (oxidizes easily) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength (434 MPa) | Low tensile strength (210 MPa) |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Typical Connector Use | Durable, lightweight, corrosion-resistant connectors | Highly conductive connectors |
Overview: Titanium vs Silver Connectors
Titanium connectors offer exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for demanding industrial and aerospace applications. Silver connectors are prized for their superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance but are softer and more prone to tarnishing. Choosing between titanium and silver connectors depends on whether mechanical durability or electrical efficiency is the primary requirement.
Material Properties Comparison
Titanium connectors offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance compared to silver, making them ideal for harsh environments and long-term durability. Silver connectors provide excellent electrical conductivity, outperforming titanium in conductivity but are more prone to oxidation and mechanical wear. The choice between titanium and silver connectors depends on the balance between mechanical robustness and electrical performance requirements.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Titanium exhibits significantly lower electrical conductivity compared to silver, with silver boasting the highest conductivity among all metals at approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, while titanium's conductivity is around 2.4 x 10^6 S/m. This vast difference makes silver connectors ideal for applications requiring minimal resistance and efficient signal transmission. Titanium connectors, though less conductive, offer superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for harsh environments where conductivity is a secondary concern.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Titanium connectors exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to the formation of a stable oxide layer that protects against oxidation and harsh environmental conditions, outperforming silver in longevity. Silver connectors, while highly conductive, are more prone to tarnishing and corrosion, especially in sulfur-rich or acidic environments, which can degrade performance over time. Titanium's exceptional durability and resistance to wear make it ideal for applications requiring long-term reliability and minimal maintenance.
Weight and Mechanical Strength
Titanium connectors offer superior mechanical strength with a tensile strength of approximately 434 MPa, making them significantly stronger than silver connectors, which have a tensile strength around 170 MPa. Despite its high strength, titanium is remarkably lightweight, with a density of 4.51 g/cm3, compared to silver's much heavier density of 10.49 g/cm3, providing a strength-to-weight advantage ideal for high-performance applications. This combination makes titanium connectors optimal for environments where durability and weight savings are critical, outperforming silver in both mechanical resilience and weight efficiency.
Cost and Availability
Titanium connectors typically cost more than silver due to the higher expense of raw materials and more complex manufacturing processes. Silver is generally more abundant and easier to source, making silver connectors more readily available and affordable for mass production. Despite the higher cost, titanium offers superior strength and corrosion resistance, often justifying its premium in specialized applications.
Applications in Different Industries
Titanium connectors are favored in aerospace, medical devices, and marine industries due to their exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio, and biocompatibility. Silver connectors are widely used in electronics, telecommunications, and high-frequency applications because of superior electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance. Choosing between titanium and silver connectors depends on industry-specific requirements like durability in harsh environments or optimal electrical efficiency.
Ease of Fabrication and Maintenance
Titanium connectors offer superior corrosion resistance and strength, but their hardness makes machining and fabrication more challenging compared to silver connectors. Silver connectors excel in ease of fabrication due to their excellent malleability and conductivity, enabling precise shaping and soldering with minimal effort. Maintenance of titanium connectors is minimal due to their resistance to tarnish and wear, while silver connectors require regular polishing and cleaning to prevent oxidation and maintain conductivity.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Titanium connectors exhibit superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to silver, making them ideal for harsh environments with extreme temperatures and chemical exposure. Silver connectors, while offering excellent electrical conductivity, are prone to tarnishing and degradation when exposed to moisture or corrosive elements. The enhanced durability and oxidation resistance of titanium ensure longer service life and reliability in demanding industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Connectors
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for connectors in harsh or high-stress environments. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity but is prone to tarnishing and mechanical wear, which can affect long-term performance. Selecting between titanium and silver connectors depends on balancing conductivity requirements with durability and environmental factors.
Infographic: Titanium vs Silver for Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com