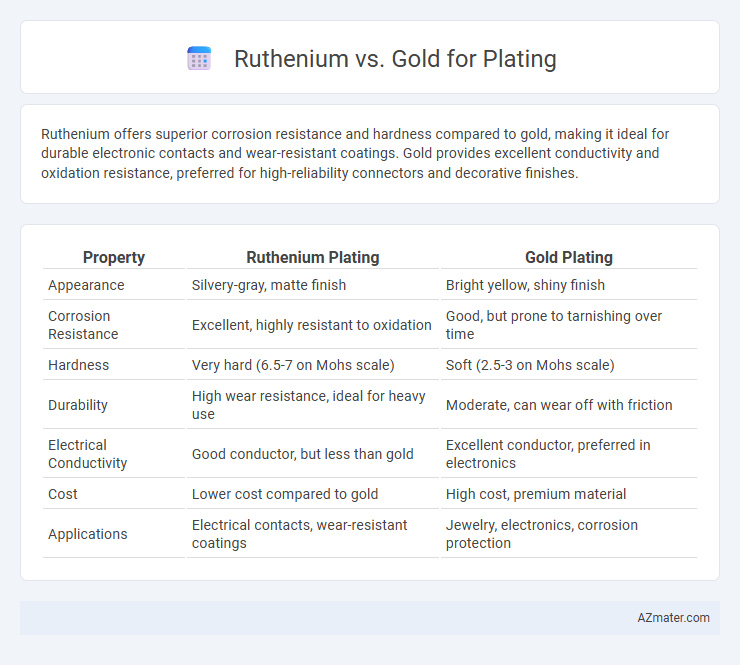
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness compared to gold, making it ideal for durable electronic contacts and wear-resistant coatings. Gold provides excellent conductivity and oxidation resistance, preferred for high-reliability connectors and decorative finishes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium Plating | Gold Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Silvery-gray, matte finish | Bright yellow, shiny finish |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to oxidation | Good, but prone to tarnishing over time |
| Hardness | Very hard (6.5-7 on Mohs scale) | Soft (2.5-3 on Mohs scale) |
| Durability | High wear resistance, ideal for heavy use | Moderate, can wear off with friction |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good conductor, but less than gold | Excellent conductor, preferred in electronics |
| Cost | Lower cost compared to gold | High cost, premium material |
| Applications | Electrical contacts, wear-resistant coatings | Jewelry, electronics, corrosion protection |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Ruthenium vs Gold
Ruthenium and gold are both used in metal plating for enhancing corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity in electronics and jewelry. Ruthenium offers superior hardness and wear resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and scratch resistance. Gold plating provides excellent conductivity and an attractive, tarnish-resistant finish favored in decorative and high-performance electronic components.
Chemical and Physical Properties Compared
Ruthenium offers higher hardness and superior corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for wear-resistant plating applications. Gold exhibits excellent electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance but is softer, leading to less durability under mechanical stress. Both metals provide excellent chemical stability, but ruthenium's greater hardness and higher melting point enhance its performance in harsh environments.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Ruthenium offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting protection against corrosion and abrasion. Ruthenium's hardness is significantly higher than gold, which is relatively soft and prone to scratching and deformation under frequent use. Its resistance to tarnishing ensures that ruthenium plating maintains its appearance and structural integrity in demanding environments far better than gold.
Aesthetic Differences: Color and Finish
Ruthenium plating offers a dark, gunmetal gray to black finish that provides a modern, sleek aesthetic distinct from gold's classic, warm yellow luster. While gold plating displays a bright, reflective shine often associated with elegance and luxury, ruthenium's matte or semi-gloss finish enhances contrast and depth, ideal for contemporary jewelry and high-tech applications. The choice between the two depends on the desired visual impact: gold for traditional richness and timeless appeal, ruthenium for bold, sophisticated, and unique surface design.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Ruthenium plating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for environments exposed to harsh chemicals and high wear. Gold plating, while excellent for its conductivity and tarnish resistance, is more prone to abrasion and corrosion over time. Ruthenium's hardness and chemical inertness enhance the longevity of plated items, particularly in industrial and electronic applications.
Cost Analysis: Ruthenium vs Gold Plating
Ruthenium plating offers a significantly lower material cost compared to gold, with ruthenium priced at approximately $300 per ounce versus gold's market value exceeding $2,000 per ounce. The cost advantage of ruthenium makes it an economical choice for electronic contacts and decorative finishes without sacrificing corrosion resistance or durability. Despite higher initial equipment expenses for ruthenium plating, the long-term savings on precious metal consumption make it more cost-effective than traditional gold plating in high-volume applications.
Popular Applications in Jewelry and Electronics
Ruthenium plating offers exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and a dark, matte finish favored in modern jewelry designs and high-performance electronic contacts. Gold plating remains the industry standard for its superior conductivity, tarnish resistance, and lustrous appearance, making it ideal for decorative jewelry and reliable connectors in electronics. Jewelry manufacturers choose ruthenium for its durability and unique aesthetic, while electronics benefit from gold's excellent electrical conductivity and stability in circuit boards and connectors.
Hypoallergenic Qualities and Skin Safety
Ruthenium plating offers superior hypoallergenic qualities compared to gold, making it a preferred choice for individuals with sensitive skin or metal allergies. Unlike gold, which can contain nickel or other allergens in alloys, ruthenium is a platinum-group metal known for its inertness and resistance to tarnishing, reducing the risk of skin irritation. This enhanced skin safety profile makes ruthenium plating ideal for jewelry and wearable tech components intended for prolonged skin contact.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ruthenium plating offers a more environmentally sustainable alternative to gold due to its lower mining impact and higher abundance in the Earth's crust, reducing resource depletion. Unlike gold, ruthenium requires less energy-intensive extraction processes and generates fewer toxic byproducts, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. The use of ruthenium in plating supports eco-friendlier practices in electronics and jewelry industries by promoting resource efficiency and reducing hazardous waste.
Choosing the Right Plating: Factors to Consider
When choosing between ruthenium and gold plating, consider factors like corrosion resistance, conductivity, and cost. Ruthenium offers superior wear resistance and hardness, making it ideal for high-durability applications, while gold excels in conductivity and is highly resistant to oxidation. The decision depends on specific use cases such as electronic contacts, jewelry, or decorative finishes, balancing performance requirements with budget constraints.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Gold for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com