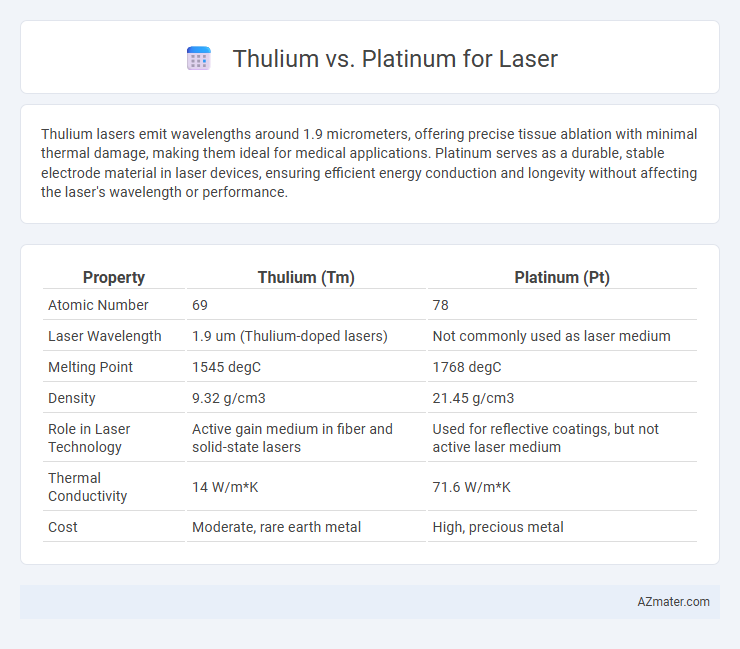
Thulium lasers emit wavelengths around 1.9 micrometers, offering precise tissue ablation with minimal thermal damage, making them ideal for medical applications. Platinum serves as a durable, stable electrode material in laser devices, ensuring efficient energy conduction and longevity without affecting the laser's wavelength or performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thulium (Tm) | Platinum (Pt) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 69 | 78 |
| Laser Wavelength | 1.9 um (Thulium-doped lasers) | Not commonly used as laser medium |
| Melting Point | 1545 degC | 1768 degC |
| Density | 9.32 g/cm3 | 21.45 g/cm3 |
| Role in Laser Technology | Active gain medium in fiber and solid-state lasers | Used for reflective coatings, but not active laser medium |
| Thermal Conductivity | 14 W/m*K | 71.6 W/m*K |
| Cost | Moderate, rare earth metal | High, precious metal |
Introduction to Thulium and Platinum Lasers
Thulium lasers operate primarily at a wavelength of around 2 micrometers, offering superior water absorption and precise tissue interaction, making them ideal for urological and soft tissue surgeries. Platinum-based lasers, often used in combination with other elements, provide robust stability and enhanced thermal conductivity, optimizing power output for industrial and medical laser applications. Both Thulium and Platinum lasers emphasize accuracy and control, but Thulium lasers excel in minimally invasive procedures due to their specific wavelength targeting soft tissues.
Core Differences Between Thulium and Platinum Lasers
Thulium lasers operate at a wavelength around 1940 nm, offering high water absorption ideal for precise soft tissue ablation with minimal thermal damage, whereas platinum itself is not a laser source but a metal often used as a coating or electrode in laser devices. Thulium laser systems excel in urological and dermatological procedures due to their controlled penetration depth and efficient energy delivery, while platinum's role is primarily conductive and catalytic in laser apparatus. The core difference lies in thulium being an active laser medium emitting infrared light, contrasting with platinum's function as a supporting material enhancing the laser device's performance or durability.
Wavelength Comparison: Thulium vs Platinum
Thulium lasers operate primarily around the 1940 nm wavelength, ideal for precise tissue ablation due to its strong absorption in water, making them highly effective in medical applications. Platinum-based laser systems, though less common, can be engineered to emit in various wavelengths depending on the dopants used, but generally do not match the specific absorption efficiency of thulium lasers at this wavelength. The distinct wavelength profile of thulium lasers provides superior control and minimized collateral damage compared to platinum lasers, enhancing their suitability for delicate surgical procedures.
Key Applications in Medical and Industrial Fields
Thulium lasers, operating primarily at a wavelength of around 1940 nm, are ideal for medical applications such as soft tissue surgery, dermatology, and laser lithotripsy due to their strong water absorption and precise cutting capabilities. Platinum-based lasers, although less common, offer excellent durability and stability for industrial uses like precision cutting, welding, and surface modification, benefiting from platinum's high melting point and resistance to corrosion. The choice between thulium and platinum lasers hinges on the specific application requirements, balancing wavelength efficiency for biological tissues versus material robustness for demanding industrial environments.
Efficiency and Performance Metrics
Thulium lasers exhibit higher efficiency in mid-infrared wavelength emissions around 2 microns, offering superior tissue absorption, which enhances precision in medical and industrial applications compared to platinum-based lasers. Platinum typically serves as a catalytic material or electrode but is less common as an active lasing medium, resulting in lower overall laser performance metrics such as output power and beam quality. The 1.9-2.1 micron wavelength range of thulium lasers supports optimized energy transfer, reduced thermal damage, and improved cutting or ablation efficacy relative to platinum-utilizing systems.
Safety Considerations for Each Laser Type
Thulium lasers operate at a wavelength around 2 microns, offering high water absorption which results in precise tissue ablation with minimal collateral damage, enhancing safety in soft tissue procedures. Platinum-based lasers, less common and typically used in specialized industrial applications, present challenges in controlling laser-tissue interactions due to their varied emission spectra, requiring stringent safeguards to prevent tissue overheating and unintended injury. Safety protocols for thulium lasers emphasize eye and skin protection with appropriate eyewear, while platinum-based laser systems demand comprehensive monitoring of power output and cooling mechanisms to mitigate risks associated with thermal damage.
Cost Analysis: Thulium vs Platinum Lasers
Thulium lasers generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to platinum lasers, making them more accessible for medical and industrial applications. The operational expenses for thulium lasers are also reduced due to their longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements. In contrast, platinum lasers, while more expensive initially, provide higher durability and performance efficiency that may justify the investment in high-precision environments.
Maintenance and Longevity of Laser Systems
Thulium lasers offer lower maintenance requirements due to their solid-state design and reduced cooling demands, resulting in longer operational lifespans compared to platinum-based fiber lasers. Platinum components in fiber lasers may require more frequent replacement or calibration due to sensitivity to environmental conditions and higher thermal load. Choosing thulium laser systems can enhance durability and reduce overall maintenance costs, making them a reliable choice for long-term industrial applications.
Recent Advancements in Thulium and Platinum Lasers
Recent advancements in thulium lasers have improved their efficiency and wavelength tunability, making them ideal for precise medical and industrial applications, particularly in soft tissue surgery and dermatology. Platinum lasers, while less common, have seen enhanced stability and power output in niche high-precision manufacturing processes and spectroscopy. Innovations in diode-pumping and cooling systems have significantly increased the operational lifespan and energy efficiency of both thulium and platinum laser technologies.
Choosing the Right Laser: Thulium or Platinum?
Thulium lasers offer precise tissue ablation with minimal thermal damage, making them ideal for delicate medical procedures such as urology and dermatology. Platinum-based lasers are known for their high durability and stable output, suitable for industrial applications requiring consistent power and longevity. Selecting between Thulium and Platinum lasers depends on the specific application needs: Thulium excels in medical precision, while Platinum is preferred for robust, high-performance industrial use.
Infographic: Thulium vs Platinum for Laser
 azmater.com
azmater.com