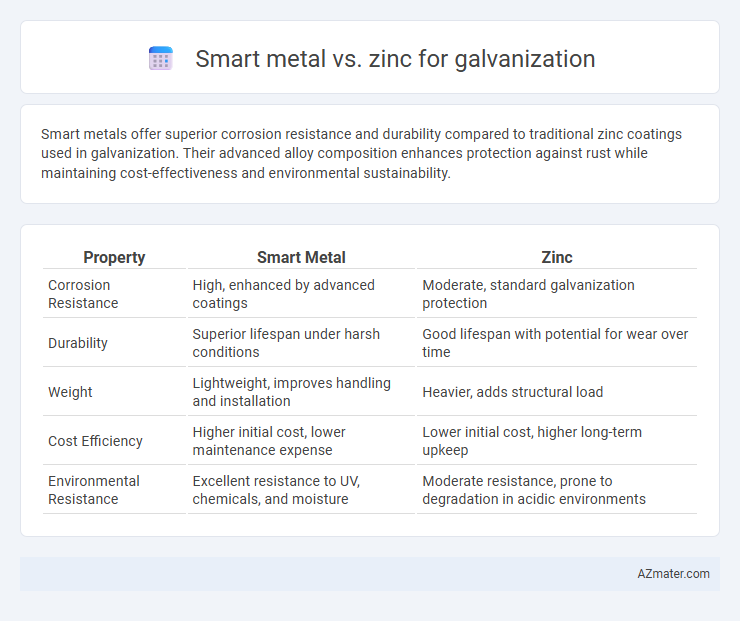
Smart metals offer superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to traditional zinc coatings used in galvanization. Their advanced alloy composition enhances protection against rust while maintaining cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Metal | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High, enhanced by advanced coatings | Moderate, standard galvanization protection |
| Durability | Superior lifespan under harsh conditions | Good lifespan with potential for wear over time |
| Weight | Lightweight, improves handling and installation | Heavier, adds structural load |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance expense | Lower initial cost, higher long-term upkeep |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent resistance to UV, chemicals, and moisture | Moderate resistance, prone to degradation in acidic environments |
Introduction to Galvanization: Importance and Methods
Galvanization is a critical process for enhancing metal durability by applying a protective zinc coating that prevents rust and corrosion. Smart metal technology integrates advanced zinc alloys and coating techniques to improve adhesion, corrosion resistance, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional zinc galvanization. These innovations extend the lifespan of galvanized products in industrial and construction applications, optimizing both performance and cost-efficiency.
What is Smart Metal?
Smart Metal is an advanced galvanization technology that enhances corrosion resistance by incorporating nanostructured zinc alloys, providing superior durability compared to traditional zinc coatings. Unlike conventional zinc galvanization, Smart Metal forms a more uniform and tightly adherent protective layer, reducing oxidation and extending the lifespan of steel structures. This innovative method improves mechanical strength and environmental resistance, making it ideal for automotive, construction, and industrial applications where long-term protection is critical.
What is Zinc Galvanization?
Zinc galvanization is a process that involves applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rusting and corrosion. This method forms a barrier that protects the base metal while also providing sacrificial protection, as zinc corrodes before the underlying metal. Compared to other smart metal coatings, zinc galvanization offers cost-effective durability and long-lasting corrosion resistance in various industrial applications.
Key Differences: Smart Metal vs Zinc Galvanization
Smart metal galvanization utilizes advanced alloy coatings offering superior corrosion resistance, flexibility, and longer lifespan compared to traditional zinc galvanization. Zinc galvanization relies on a sacrificial zinc layer to protect steel from rust through galvanic action but may suffer degradation in harsh environments. Smart metal coatings integrate elements like aluminum and magnesium, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs significantly over zinc-only galvanization.
Corrosion Resistance: Smart Metal vs Zinc
Smart metal coatings exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional zinc galvanization due to advanced alloy compositions and nano-engineered surface treatments that provide enhanced barrier properties and self-healing capabilities. Zinc coatings offer sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially, but they can degrade quicker in harsh environments, especially with exposure to chloride or acidic conditions, reducing long-term durability. Smart metal solutions extend service life by resisting pitting and uniform corrosion, making them ideal for demanding industrial and marine applications.
Cost Comparison: Smart Metal and Zinc Galvanization
Smart metal galvanization generally offers a lower overall cost compared to traditional zinc galvanization due to reduced material consumption and longer-lasting corrosion resistance. Zinc galvanization requires thicker coatings and frequent maintenance, increasing lifecycle expenses despite its widespread availability. Choosing smart metal can optimize budget efficiency in industrial and infrastructure projects by minimizing reapplication and material costs.
Environmental Impact of Smart Metal and Zinc
Smart metals used in galvanization often incorporate advanced coatings that reduce environmental pollutants by minimizing toxic runoff compared to traditional zinc coatings. Zinc galvanization, although effective in corrosion resistance, can contribute to soil and water contamination through zinc leaching, posing risks to aquatic ecosystems. The biodegradability and recyclability of smart metal coatings enhance their sustainability profile, making them a preferable choice for eco-friendly metal protection.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Smart metal alloys designed for galvanization exhibit superior durability compared to traditional zinc coatings due to their enhanced corrosion resistance and self-healing properties. Zinc, while effective as a sacrificial anode to protect steel, tends to degrade over time under harsh environmental conditions, limiting its longevity. Studies show smart metal coatings can extend the lifespan of galvanized structures by up to 50%, making them a more resilient choice for long-term protection.
Industrial Applications: Choosing Between Smart Metal and Zinc
Smart metal offers enhanced corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to traditional zinc coatings, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. Zinc remains cost-effective and widely used for general galvanization needs, providing reliable protection against rust in less extreme conditions. Selecting between smart metal and zinc depends on budget constraints, environmental exposure, and required durability in industrial settings.
Future Trends in Galvanization Technology
Smart metal coatings are emerging as a revolutionary alternative to traditional zinc for galvanization, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and self-healing properties through embedded nanomaterials and sensors. Future trends in galvanization technology emphasize the integration of smart coatings with IoT-enabled monitoring systems to provide real-time data on metal integrity and environmental exposure. This advancement promises to extend the lifespan of galvanized structures while reducing maintenance costs and environmental impact.
Infographic: Smart metal vs Zinc for Galvanization
 azmater.com
azmater.com