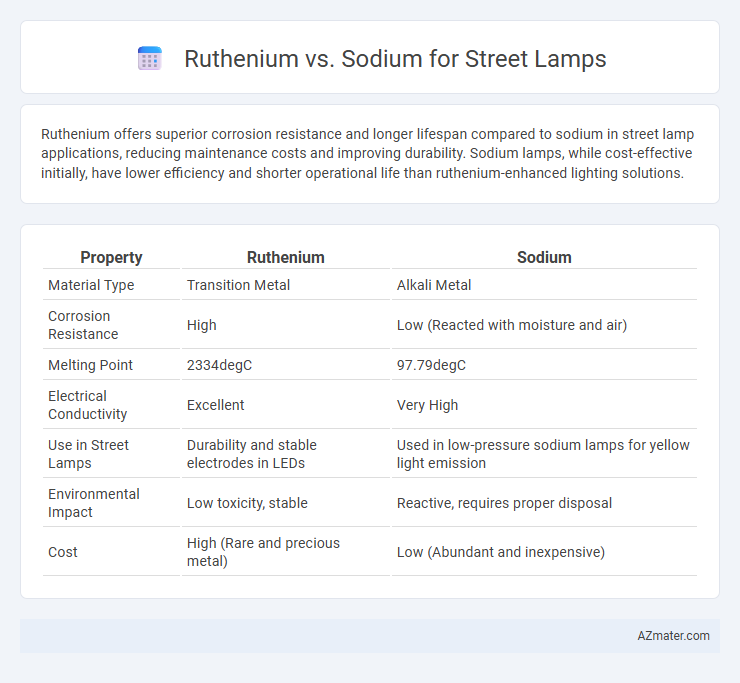
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to sodium in street lamp applications, reducing maintenance costs and improving durability. Sodium lamps, while cost-effective initially, have lower efficiency and shorter operational life than ruthenium-enhanced lighting solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium | Sodium |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Transition Metal | Alkali Metal |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Low (Reacted with moisture and air) |
| Melting Point | 2334degC | 97.79degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent | Very High |
| Use in Street Lamps | Durability and stable electrodes in LEDs | Used in low-pressure sodium lamps for yellow light emission |
| Environmental Impact | Low toxicity, stable | Reactive, requires proper disposal |
| Cost | High (Rare and precious metal) | Low (Abundant and inexpensive) |
Introduction to Ruthenium and Sodium in Street Lighting
Ruthenium, a rare transition metal, is primarily used in specialized lighting applications due to its excellent durability and resistance to corrosion, though it is not commonly employed in standard street lamps. Sodium, especially in the form of low-pressure and high-pressure sodium lamps, dominates street lighting because of its high luminous efficacy and long operational life, providing bright, energy-efficient illumination with characteristic yellow-orange light. The choice between ruthenium and sodium focuses on cost-effectiveness and performance, with sodium being the preferred material for widespread urban and highway lighting solutions.
Chemical Properties: Ruthenium vs Sodium
Ruthenium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and high melting point, making it durable for street lamp components exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Sodium, highly reactive and with a low melting point, poses challenges due to its vulnerability to oxidation and difficulty in handling safely. The chemical stability of ruthenium under varying temperatures and atmospheric exposure makes it a preferred choice over sodium for long-lasting street lighting applications.
Light Emission Characteristics
Ruthenium-based street lamps exhibit a stable and intense blue-white light emission with high color rendering index (CRI), enhancing visibility and object recognition at night. Sodium lamps, especially low-pressure variants, produce a monochromatic yellow-orange light with limited color rendering, which can hinder accurate color perception. The spectral efficiency of ruthenium allows better energy utilization and visibility in urban lighting compared to the narrow spectral output of sodium lamps.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Ruthenium-based street lamps exhibit higher energy efficiency than sodium lamps due to their improved luminous efficacy, providing more light output per watt of energy consumed. Ruthenium alloys in LED technology enable longer lifespan and reduced energy loss compared to traditional high-pressure sodium lamps that consume more power for equivalent brightness. This shift towards ruthenium-enhanced lighting systems results in significant reductions in energy consumption and maintenance costs for municipal street lighting.
Durability and Lifespan of Ruthenium and Sodium Lamps
Ruthenium-based street lamps exhibit superior durability due to their resistance to corrosion and high thermal stability, resulting in a longer operational lifespan often exceeding 20,000 hours. Sodium lamps, particularly high-pressure sodium lamps, typically offer lifespans ranging from 12,000 to 24,000 hours but are more susceptible to lumen depreciation over time. The enhanced longevity and robust material properties of Ruthenium enable reduced maintenance frequency and improved performance reliability in outdoor lighting applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Ruthenium-based street lamps significantly reduce environmental impact by offering higher energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to sodium lamps, which emit more light pollution and consume more power. Ruthenium lamps produce less hazardous waste due to their minimal use of toxic elements, whereas sodium lamps release sodium vapor that can be harmful to ecosystems. Safety concerns also favor ruthenium, as its lower operating temperatures reduce fire risks and exposure to harmful chemicals, unlike high-pressure sodium lamps that pose greater ignition and chemical hazards.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Ruthenium-based street lamps typically involve higher installation costs due to specialized materials and technology, whereas sodium lamps benefit from lower upfront expenses and widespread availability, making them more cost-effective initially. Maintenance costs for ruthenium lamps are generally reduced because of their longer lifespan and higher durability, while sodium lamps require more frequent replacements and repairs, increasing life-cycle expenses. Overall, sodium lamps offer lower initial investment, but ruthenium lamps can yield savings over time through decreased maintenance and energy efficiency.
Color Rendering Index and Visibility
Ruthenium-enhanced street lamps typically offer a higher Color Rendering Index (CRI) than sodium lamps, resulting in more accurate and vivid color perception under nighttime conditions. Sodium lamps, especially low-pressure variants, have a lower CRI and emit a monochromatic yellow light, which reduces visibility and color differentiation for pedestrians and drivers. Enhanced CRI with ruthenium allows better recognition of objects and contributes to improved safety and overall visibility in urban street lighting.
Practical Applications in Urban Street Lighting
Ruthenium-based coatings enhance urban street lighting by improving the efficiency and lifespan of LED lamps through superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. Sodium vapor lamps, historically favored for their high luminous efficacy and warm yellow glow, are less energy-efficient and have shorter operational lifespans compared to modern ruthenium-enhanced LED solutions. These properties position ruthenium as a critical component in advancing sustainable, low-maintenance street lighting systems that reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs in urban environments.
Future Trends and Innovations in Street Lamp Technology
Ruthenium-enhanced street lamps are gaining attention for their superior energy efficiency and longer lifespan compared to traditional sodium vapor lamps, which dominate current street lighting due to their cost-effectiveness. Future trends emphasize integrating ruthenium-based electrocatalysts in LED systems to achieve higher luminous efficacy and reduced environmental impact. Innovations include smart street lamps with sensor-driven adaptive brightness and Ruthenium-infused materials that enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs in urban infrastructure.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Sodium for Street Lamp
 azmater.com
azmater.com