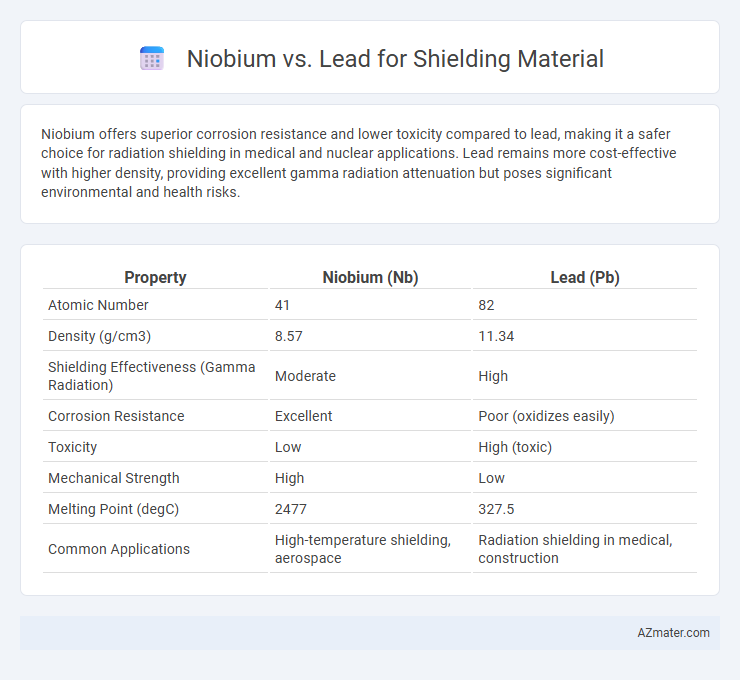
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and lower toxicity compared to lead, making it a safer choice for radiation shielding in medical and nuclear applications. Lead remains more cost-effective with higher density, providing excellent gamma radiation attenuation but poses significant environmental and health risks.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Lead (Pb) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 41 | 82 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.57 | 11.34 |
| Shielding Effectiveness (Gamma Radiation) | Moderate | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Poor (oxidizes easily) |
| Toxicity | Low | High (toxic) |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Low |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2477 | 327.5 |
| Common Applications | High-temperature shielding, aerospace | Radiation shielding in medical, construction |
Introduction to Radiation Shielding Materials
Radiation shielding materials are critical for protecting human health and sensitive equipment from harmful ionizing radiation by absorbing or deflecting particles and waves. Niobium, a transition metal with high density and excellent corrosion resistance, offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it effective for shielding high-energy radiation, especially in aerospace and nuclear applications. Lead remains the most commonly used shielding material due to its high atomic number and density, providing cost-effective attenuation of gamma rays and x-rays, although its toxicity and weight pose significant drawbacks in modern uses.
Overview of Niobium as a Shielding Material
Niobium offers exceptional radiation shielding properties due to its high density (8.57 g/cm3) and excellent neutron absorption cross-section, making it a valuable alternative to traditional materials like lead. Its superior mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and non-toxic nature allow niobium to provide safer and more durable shielding solutions in medical, nuclear, and aerospace applications. Niobium's ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions further enhances its effectiveness as a protective barrier against ionizing radiation.
Overview of Lead as a Shielding Material
Lead is a dense metal widely used for radiation shielding due to its high atomic number (Z=82) and effective attenuation of gamma rays and X-rays. Its malleability and ease of fabrication allow for customizable shield designs in medical, industrial, and nuclear applications. Despite its effectiveness, lead's toxicity necessitates careful handling and disposal to minimize environmental and health risks.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and a higher melting point (2477degC) compared to lead (327.5degC), making it more durable under extreme conditions. Its lower density (8.57 g/cm3) results in lighter shielding solutions, while lead's density (11.34 g/cm3) provides greater mass-based radiation attenuation. Chemically, niobium's stability and non-toxicity enhance safety and longevity in shielding applications, contrasting with lead's toxicity and environmental hazards.
Radiation Attenuation Efficiency: Niobium vs Lead
Niobium offers moderate radiation attenuation efficiency due to its atomic number (41) and density (8.57 g/cm3), making it less effective than lead, which has a higher atomic number (82) and density (11.34 g/cm3). Lead remains the industry standard for radiation shielding because its greater atomic number enhances photoelectric absorption, significantly reducing gamma and X-ray penetration. However, niobium's mechanical strength and corrosion resistance provide benefits in specialized environments despite its lower attenuation performance.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
Niobium offers superior safety over lead as a shielding material due to its non-toxic nature and biocompatibility, eliminating health hazards associated with lead exposure such as neurotoxicity and heavy metal poisoning. Lead, while effective in radiation shielding, poses significant risks including chronic lead poisoning, contamination, and environmental persistence, requiring stringent handling and disposal protocols. Selecting niobium enhances long-term safety in medical and industrial applications by minimizing toxicological impacts and regulatory constraints.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Niobium exhibits superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to lead, making it a preferred choice for long-term shielding applications. Its resistance to oxidation and chemical degradation ensures stable performance in harsh environments, unlike lead, which is prone to corrosion and structural weakening over time. Niobium's strength-to-weight ratio also enhances its longevity as a shielding material in demanding industrial and medical settings.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Niobium offers superior radiation shielding properties but comes at a significantly higher cost due to its rarity and complex extraction process. Lead remains the most cost-effective and widely available shielding material despite its toxicity and environmental concerns. The abundant supply and lower market price of lead make it the preferred choice for most industrial and medical shielding applications.
Practical Applications and Industry Use
Niobium excels in electromagnetic shielding due to its high magnetic permeability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and nuclear applications. Lead remains widely used for radiation shielding in medical and industrial settings because of its high density and relatively low cost. Niobium's lighter weight and durability offer advantages in environments requiring reduced structural weight and long-term performance.
Future Prospects in Shielding Technology
Niobium offers promising future prospects in shielding technology due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance compared to lead. Advances in nanostructured niobium composites enhance radiation absorption efficiency, making it a viable alternative for both medical and nuclear applications. Ongoing research into eco-friendly and sustainable materials further supports niobium's role in next-generation shielding solutions, reducing environmental hazards linked to lead usage.
Infographic: Niobium vs Lead for Shielding Material
 azmater.com
azmater.com