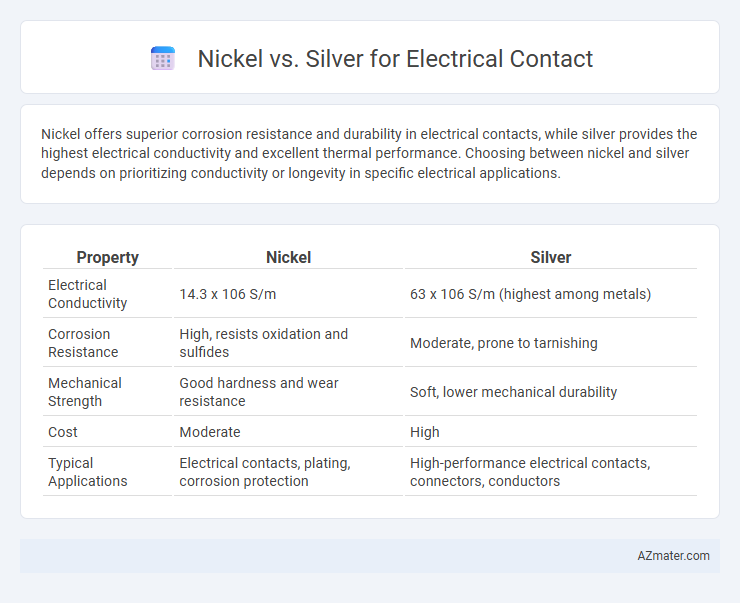
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability in electrical contacts, while silver provides the highest electrical conductivity and excellent thermal performance. Choosing between nickel and silver depends on prioritizing conductivity or longevity in specific electrical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 14.3 x 106 S/m | 63 x 106 S/m (highest among metals) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, resists oxidation and sulfides | Moderate, prone to tarnishing |
| Mechanical Strength | Good hardness and wear resistance | Soft, lower mechanical durability |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Electrical contacts, plating, corrosion protection | High-performance electrical contacts, connectors, conductors |
Introduction to Electrical Contact Materials
Nickel and silver are widely used materials for electrical contacts due to their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Silver offers the highest electrical conductivity among metals, making it ideal for low-resistance contacts, while nickel provides superior mechanical strength and oxidation resistance, enhancing durability in harsh environments. Selection between nickel and silver contacts depends on balancing conductivity requirements with environmental factors and mechanical wear.
Overview of Nickel and Silver Properties
Nickel exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point of 1455degC, and strong mechanical strength, making it durable for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Silver boasts the highest electrical conductivity among metals at approximately 6.30x10^7 S/m, coupled with superior thermal conductivity and excellent oxidation resistance under normal conditions. While silver provides optimal electrical performance, nickel outperforms in wear resistance and longevity in demanding applications.
Electrical Conductivity: Nickel vs Silver
Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among all metals, approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m, making it the superior choice for electrical contacts where minimal resistance is critical. Nickel, with a significantly lower conductivity around 14 x 10^6 S/m, is less efficient in conducting electricity but offers enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical durability. Silver's conductivity advantage supports faster electron flow, reducing energy loss and heat generation in electrical contact applications.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Nickel exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to silver in electrical contacts, particularly in harsh environments with high humidity or exposure to sulfur compounds. While silver offers excellent electrical conductivity, it tarnishes easily due to silver sulfide formation, leading to increased contact resistance over time. Nickel's passive oxide layer provides robust protection against oxidation and corrosion, ensuring longer-lasting and more reliable electrical performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nickel offers superior mechanical strength compared to silver, making it more resistant to deformation and wear under electrical contact stress. Silver, while providing excellent electrical conductivity, is softer and more prone to surface damage and erosion, reducing long-term durability in harsh environments. The enhanced durability of nickel contacts ensures stable performance and lower maintenance requirements in high-load or abrasive conditions.
Contact Reliability and Performance
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains stable electrical conductivity under high-temperature and harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting contact reliability in electrical applications. Silver, while exhibiting the highest electrical conductivity among metals, is prone to oxidation and sulfide buildup that can degrade contact performance over time if not properly protected. Combining silver plating over nickel substrates often balances excellent conductivity with robust durability, optimizing both contact reliability and electrical performance in demanding conditions.
Cost Analysis: Nickel vs Silver
Nickel offers a lower cost alternative to silver for electrical contacts, with its price typically ranging from $18 to $20 per kilogram compared to silver's $700+ per kilogram, greatly reducing material expenses. While silver provides superior conductivity and corrosion resistance essential for high-performance applications, nickel's durability and corrosion resistance at a fraction of the cost make it ideal for cost-sensitive or industrial environments. The total cost of ownership often favors nickel when considering long-term maintenance and replacement in less demanding electrical contacts.
Applications in Electrical Industry
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and high hardness, making it ideal for electrical contacts in harsh environments such as aerospace and industrial machinery. Silver provides excellent electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, preferred in high-performance switches, connectors, and circuit breakers. The electrical industry often uses silver in low-voltage applications, while nickel is favored for durability and protection against oxidation in heavy-duty contacts.
Environmental and Maintenance Considerations
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability in electrical contacts, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and environmental waste compared to silver. Silver provides excellent conductivity but tarnishes quickly, leading to higher maintenance needs and potential environmental contamination from cleaning agents. Choosing nickel-plated contacts enhances long-term reliability and minimizes ecological impact through reduced material degradation and maintenance interventions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Nickel offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability for electrical contacts, making it ideal for harsh environments, while silver provides superior electrical conductivity and low contact resistance, essential for high-performance applications. The choice depends on balancing conductivity needs with environmental exposure and cost considerations. Silver is preferred for optimal electrical performance, whereas nickel suits applications requiring robustness and longevity.
Infographic: Nickel vs Silver for Electrical contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com