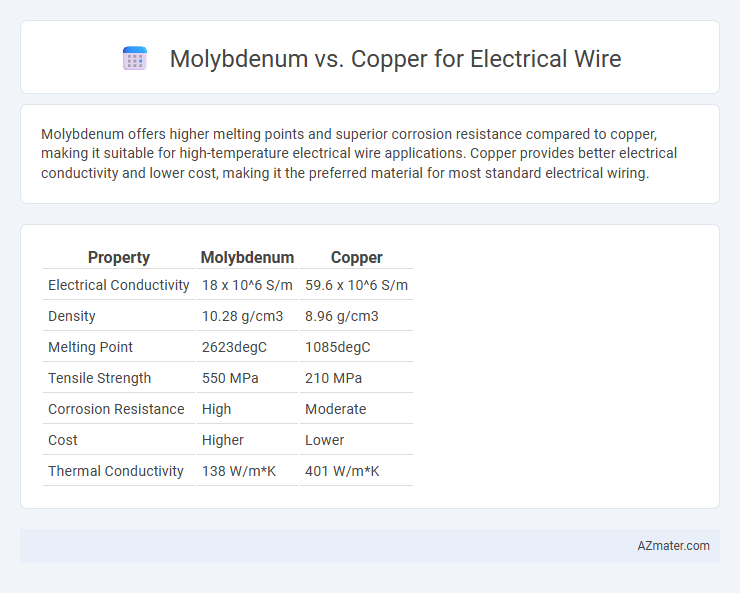
Molybdenum offers higher melting points and superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it suitable for high-temperature electrical wire applications. Copper provides better electrical conductivity and lower cost, making it the preferred material for most standard electrical wiring.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Molybdenum | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 18 x 10^6 S/m | 59.6 x 10^6 S/m |
| Density | 10.28 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2623degC | 1085degC |
| Tensile Strength | 550 MPa | 210 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m*K | 401 W/m*K |
Introduction to Electrical Wire Materials
Molybdenum and copper are key materials for electrical wire applications, distinguished by their conductivity and mechanical properties. Copper boasts an electrical conductivity of approximately 59.6 million Siemens per meter (MS/m), making it the industry standard for wiring due to its excellent conductivity and ductility. Molybdenum, with a conductivity of about 18 MS/m and superior high-temperature stability, is primarily used in specialized high-performance electrical components where durability under extreme conditions is critical.
Overview of Molybdenum and Copper
Molybdenum is a refractory metal known for its high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and strength at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for specialized electrical applications requiring durability and heat resistance. Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ductility, which makes it the standard choice for general electrical wiring due to efficient current flow and ease of installation. While copper dominates in conventional wire manufacturing, molybdenum is favored in niche environments where temperature stability and mechanical strength outweigh pure conductivity.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity at approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring where minimal resistance and efficient current flow are critical. Molybdenum, with a lower conductivity of about 1.88 x 10^7 S/m, offers durability and high melting point advantages but falls short in conductivity for typical electrical wiring applications. The substantial conductivity difference impacts energy efficiency, heat generation, and performance in electrical circuits, favoring copper for most conventional wiring needs.
Thermal Conductivity and Performance
Molybdenum exhibits a thermal conductivity of approximately 138 W/m*K, which is significantly lower than copper's thermal conductivity at around 401 W/m*K, affecting heat dissipation in electrical wiring. Copper's superior thermal conductivity enhances electrical performance by efficiently transferring heat and reducing resistance, making it the preferred choice for standard wiring applications. In high-temperature environments, molybdenum's higher melting point and stability offer performance advantages despite its lower thermal conductivity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Molybdenum offers superior mechanical strength and higher tensile strength compared to copper, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Copper exhibits excellent ductility and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance in standard electrical wiring but with lower mechanical resilience than molybdenum. The choice between molybdenum and copper depends on the specific need for strength versus conductivity and environmental durability.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Molybdenum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, making it highly effective in harsh or high-temperature environments where oxidation and chemical exposure are concerns. Copper, while excellent for conductivity, is prone to oxidation and tarnishing, which can reduce wire lifespan in corrosive settings. The enhanced corrosion resistance of molybdenum significantly improves the longevity and reliability of electrical wiring in demanding industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: Molybdenum vs Copper
Molybdenum offers a higher melting point and superior corrosion resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to copper, which remains the industry standard for electrical wiring due to its affordability and excellent electrical conductivity. Copper's widespread availability and established extraction methods contribute to its lower price per kilogram, making it a more cost-effective choice for bulk electrical applications. While molybdenum may reduce maintenance expenses in harsh environments, the initial investment for molybdenum wiring is substantially greater, limiting its cost competitiveness in general electrical infrastructure projects.
Applications in Electrical Industries
Molybdenum's superior high-temperature stability and corrosion resistance make it ideal for specialized electrical applications such as vacuum tube anodes and filament supports in high-power devices. Copper remains the industry standard due to its exceptional electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, widely used in power cables, wiring harnesses, and electronic circuits. Electrical industries prioritize copper for general wiring, while molybdenum serves niche roles where durability under extreme conditions is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Molybdenum offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity compared to copper, potentially reducing the frequency of wire replacement and waste generation. Copper mining and refining typically result in higher greenhouse gas emissions and more significant environmental degradation due to habitat disruption and toxic waste. Sustainability efforts favor molybdenum for its lower lifecycle environmental footprint and better recyclability in high-performance electrical applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Molybdenum offers exceptional strength and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for specialized electrical wiring in extreme environments. Copper provides superior electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, making it the preferred choice for standard electrical wiring applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing conductivity requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Molybdenum vs Copper for Electrical Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com