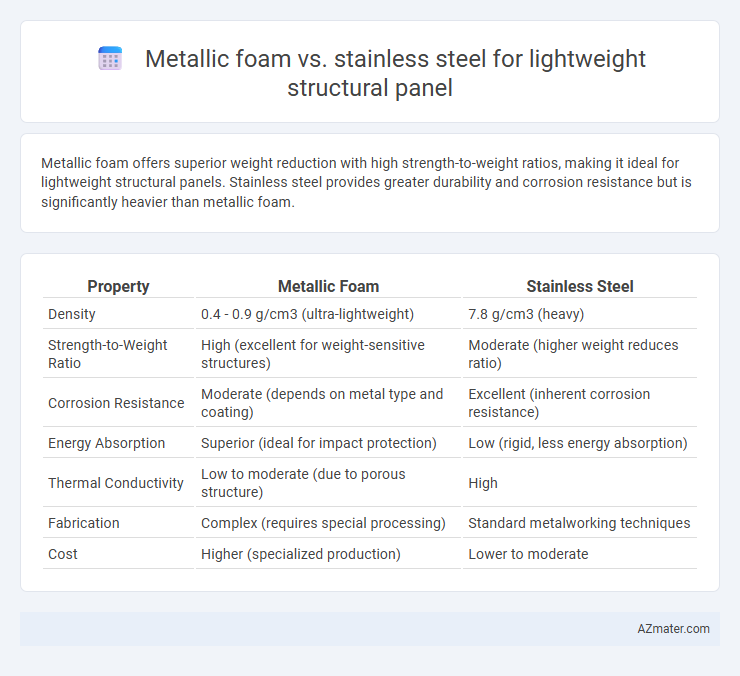
Metallic foam offers superior weight reduction with high strength-to-weight ratios, making it ideal for lightweight structural panels. Stainless steel provides greater durability and corrosion resistance but is significantly heavier than metallic foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Metallic Foam | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.4 - 0.9 g/cm3 (ultra-lightweight) | 7.8 g/cm3 (heavy) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High (excellent for weight-sensitive structures) | Moderate (higher weight reduces ratio) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (depends on metal type and coating) | Excellent (inherent corrosion resistance) |
| Energy Absorption | Superior (ideal for impact protection) | Low (rigid, less energy absorption) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate (due to porous structure) | High |
| Fabrication | Complex (requires special processing) | Standard metalworking techniques |
| Cost | Higher (specialized production) | Lower to moderate |
Introduction to Lightweight Structural Panels
Lightweight structural panels play a critical role in modern construction and automotive industries by offering high strength-to-weight ratios. Metallic foam provides exceptional energy absorption and thermal insulation due to its porous structure, making it ideal for impact-resistant applications. Stainless steel, known for its durability and corrosion resistance, offers superior mechanical strength but with higher weight compared to metallic foam.
Overview of Metallic Foam: Composition and Properties
Metallic foam, composed primarily of metals such as aluminum or titanium with a cellular structure containing numerous gas-filled pores, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratios ideal for lightweight structural panels. Its unique properties include high energy absorption, excellent thermal insulation, and superior damping capacity compared to solid stainless steel. This combination of lightweight design and mechanical performance positions metallic foam as a highly effective alternative to traditional stainless steel in applications requiring both structural integrity and weight reduction.
Stainless Steel: Characteristics and Applications
Stainless steel offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it ideal for lightweight structural panels requiring long-term performance in harsh environments. Its high tensile strength and excellent weldability allow for robust fabrication and structural integrity in architectural, automotive, and aerospace applications. The material's recyclability and heat resistance further enhance its suitability for demanding structural designs compared to metallic foam alternatives.
Comparative Density and Weight Reduction
Metallic foam exhibits a significantly lower density, ranging from 0.4 to 1.0 g/cm3, compared to stainless steel's density of approximately 8.0 g/cm3, enabling remarkable weight reduction in lightweight structural panels. This density difference translates into metallic foam panels achieving up to 80-90% weight savings while maintaining sufficient structural integrity for load-bearing applications. The reduced weight of metallic foam not only enhances fuel efficiency in transportation but also simplifies handling and installation in construction projects.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Metallic foam offers excellent energy absorption and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for lightweight structural panels requiring impact resistance and vibration damping. Stainless steel provides superior mechanical strength and exceptional durability with corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments. Comparing both, metallic foam excels in weight reduction and shock absorption, while stainless steel delivers unmatched toughness and structural integrity under sustained loads.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Metallic foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to dense stainless steel panels. The open-cell design in metallic foam enhances acoustic absorption, effectively dampening sound vibrations and reducing noise transmission. Stainless steel panels provide structural strength but have lower thermal and acoustic insulation performance due to their solid, non-porous nature.
Corrosion Resistance in Structural Environments
Metallic foam offers enhanced corrosion resistance in structural environments due to its porous nature, which facilitates protective oxide layer formation, reducing degradation compared to conventional stainless steel. Stainless steel provides strong corrosion resistance in various industrial and marine settings but may suffer from localized pitting and crevice corrosion under aggressive conditions. Selecting metallic foam for lightweight structural panels improves long-term durability by minimizing corrosion-induced failures, especially in environments with fluctuating moisture and chemical exposure.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Metallic foam manufacturing techniques such as powder metallurgy, casting with gas injection, and additive manufacturing enable the creation of lightweight panels with high energy absorption and complex geometries, albeit with challenges in uniform porosity control and lower production speeds. Stainless steel panels are typically produced through conventional processes like rolling, stamping, and welding that benefit from mature industrial scalability and consistent material properties but result in higher weight compared to metallic foam. Scalability for metallic foam is currently limited by process complexity and cost, whereas stainless steel offers established, cost-effective mass production suited for large-scale structural applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Metallic foam offers significant weight reduction compared to stainless steel, which can lower transportation and installation costs in lightweight structural panels. Although metallic foam typically has a higher initial material cost, its improved energy absorption and thermal insulation properties can reduce long-term maintenance and operational expenses. Stainless steel, while more affordable upfront and providing superior corrosion resistance, may lead to higher overall costs due to increased weight and potential need for reinforcement in structural applications.
Optimal Applications: Choosing Between Metallic Foam and Stainless Steel
Metallic foam offers superior energy absorption and thermal insulation, making it ideal for lightweight structural panels in automotive and aerospace industries where weight reduction and impact resistance are critical. Stainless steel provides high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, better suited for harsh environments in marine, construction, and industrial applications requiring long-term structural integrity. Selecting between metallic foam and stainless steel depends on balancing factors like load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency for optimal application performance.
Infographic: Metallic foam vs Stainless steel for Lightweight structural panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com