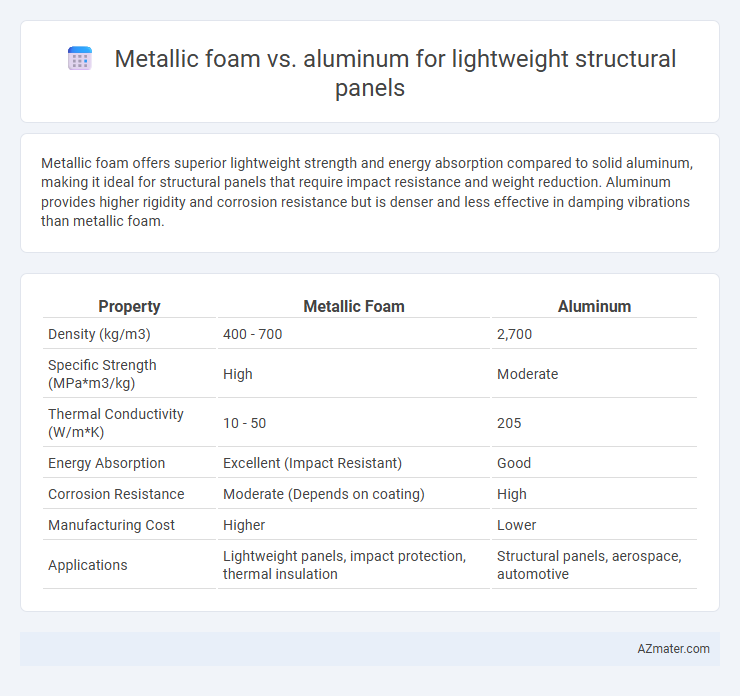
Metallic foam offers superior lightweight strength and energy absorption compared to solid aluminum, making it ideal for structural panels that require impact resistance and weight reduction. Aluminum provides higher rigidity and corrosion resistance but is denser and less effective in damping vibrations than metallic foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Metallic Foam | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 400 - 700 | 2,700 |
| Specific Strength (MPa*m3/kg) | High | Moderate |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 10 - 50 | 205 |
| Energy Absorption | Excellent (Impact Resistant) | Good |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (Depends on coating) | High |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Lightweight panels, impact protection, thermal insulation | Structural panels, aerospace, automotive |
Introduction to Lightweight Structural Panels
Lightweight structural panels leverage materials like metallic foam and aluminum to achieve high strength-to-weight ratios essential in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. Metallic foam offers superior energy absorption and thermal insulation due to its porous microstructure, whereas aluminum provides excellent corrosion resistance and ease of fabrication. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing mechanical performance, weight savings, and application-specific durability requirements.
Overview of Metallic Foam Technology
Metallic foam technology utilizes metal alloys, primarily aluminum, to create lightweight structures with a cellular architecture that significantly reduces density while maintaining mechanical strength. This porous material offers superior energy absorption, thermal insulation, and sound dampening compared to solid aluminum panels, making it highly advantageous in aerospace, automotive, and construction applications. Advanced manufacturing techniques like powder metallurgy and casting processes enable precise control over pore size and distribution, optimizing the balance between weight and structural integrity for lightweight panel designs.
Properties and Types of Aluminum Panels
Metallic foam offers exceptional energy absorption and vibration damping, making it ideal for impact-resistant lightweight structural panels. Aluminum panels, including honeycomb, corrugated, and solid sheet types, provide high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal conductivity. While metallic foam excels in shock absorption, aluminum panels are preferred for applications requiring stiffness and durability combined with lightweight properties.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Metallic foam offers significantly lower density compared to solid aluminum, resulting in superior weight reduction for lightweight structural panels. Despite its reduced mass, metallic foam exhibits impressive compressive strength and energy absorption, often surpassing aluminum alloys under impact and stress conditions. However, aluminum panels generally provide higher tensile strength and better fatigue resistance, making them suitable for applications requiring sustained load-bearing capacity.
Weight Reduction Capabilities
Metallic foam offers superior weight reduction capabilities compared to traditional aluminum due to its porous structure, which drastically decreases density while maintaining structural integrity. Aluminum solid panels typically weigh around 2.7 g/cm3, whereas metallic foam can reduce weight by up to 70-90% without significant loss of mechanical strength. This exceptional strength-to-weight ratio makes metallic foam an ideal choice for lightweight structural panels in automotive and aerospace applications aiming for fuel efficiency and performance enhancement.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Metallic foam outperforms aluminum in lightweight structural panels by providing superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure that traps air, reducing heat transfer significantly. Acoustic insulation is enhanced in metallic foam panels through sound absorption and dampening of vibrations, making them ideal for noise reduction applications. Aluminum, while strong and lightweight, lacks the inherent porous characteristics necessary for effective thermal and acoustic insulation compared to metallic foam.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Metallic foam offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum due to its inherent porous structure combined with protective oxide layers, which reduce the likelihood of surface degradation in harsh environments. Aluminum panels possess excellent durability with high strength-to-weight ratios but are more susceptible to pitting and galvanic corrosion, especially in marine or chemically aggressive settings. Therefore, metallic foam panels provide enhanced long-term performance and reduced maintenance costs for lightweight structural applications exposed to corrosive conditions.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Considerations
Metallic foam offers significant weight reduction and enhanced energy absorption compared to aluminum but comes with higher production costs due to complex manufacturing processes such as powder metallurgy or investment casting. Aluminum panels provide a cost-effective solution with established fabrication methods like extrusion and rolling, ensuring lower material and processing expenses. Manufacturing considerations for metallic foam include limited scalability and longer cycle times, whereas aluminum benefits from widespread industrial infrastructure and recyclability, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of lightweight structural panels.
Applications in Aerospace, Automotive, and Construction
Metallic foam offers superior energy absorption and thermal insulation compared to aluminum, making it ideal for lightweight structural panels in aerospace where impact resistance and weight reduction are critical. In automotive applications, metallic foam enhances crashworthiness and noise reduction while maintaining structural strength, outperforming traditional aluminum panels. Construction benefits from metallic foam's fire resistance and durability, providing safer, lighter, and more efficient building materials than conventional aluminum.
Future Trends in Lightweight Structural Materials
Metallic foam exhibits superior energy absorption and thermal insulation properties compared to traditional aluminum, positioning it as a key material in the evolution of lightweight structural panels. Advances in additive manufacturing and material engineering are enabling the production of metallic foam with tailored pore structures, enhancing strength-to-weight ratios and multifunctional performance. Emerging trends highlight the integration of metallic foam composites with aluminum alloys to optimize durability and weight reduction in aerospace and automotive industries.
Infographic: Metallic foam vs Aluminum for Lightweight structural panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com