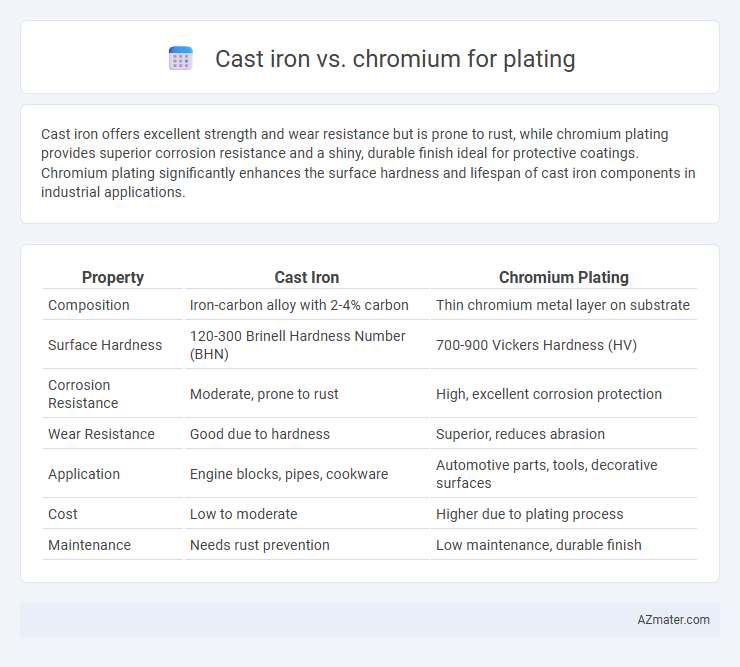
Cast iron offers excellent strength and wear resistance but is prone to rust, while chromium plating provides superior corrosion resistance and a shiny, durable finish ideal for protective coatings. Chromium plating significantly enhances the surface hardness and lifespan of cast iron components in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cast Iron | Chromium Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron-carbon alloy with 2-4% carbon | Thin chromium metal layer on substrate |
| Surface Hardness | 120-300 Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) | 700-900 Vickers Hardness (HV) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, prone to rust | High, excellent corrosion protection |
| Wear Resistance | Good due to hardness | Superior, reduces abrasion |
| Application | Engine blocks, pipes, cookware | Automotive parts, tools, decorative surfaces |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher due to plating process |
| Maintenance | Needs rust prevention | Low maintenance, durable finish |
Introduction to Plating Materials
Cast iron is a popular substrate for plating due to its durability and excellent machinability, making it ideal for wear-resistant coatings. Chromium plating on cast iron enhances corrosion resistance, reduces friction, and provides a hard, aesthetically appealing surface. The compatibility of chromium with cast iron ensures strong adhesion and long-lasting performance in industrial applications.
Overview of Cast Iron in Plating
Cast iron, known for its high carbon content and excellent wear resistance, serves as a durable base material in plating applications. Its porous surface often requires thorough surface preparation, such as sandblasting or acid cleaning, to ensure strong adhesion of chromium plating. Chromium plating on cast iron significantly enhances corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for automotive and industrial components.
Overview of Chromium as a Plating Material
Chromium plating offers exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for enhancing the durability of cast iron components. The plating process creates a smooth, reflective surface that reduces friction and improves wear resistance in industrial applications. Chromium's ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments extends the lifespan of cast iron parts, ensuring sustained performance in automotive and machinery industries.
Key Properties of Cast Iron for Plating
Cast iron offers excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it an ideal substrate for chromium plating applications that require durability and corrosion resistance. Its high carbon content and microstructure provide a firm base that enhances the adhesion and longevity of chromium plating layers. Furthermore, cast iron's thermal conductivity allows for uniform heat dissipation during the plating process, ensuring consistent coating quality and performance.
Key Properties of Chromium Plating
Chromium plating offers exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance, making it ideal for protecting cast iron surfaces from rust and mechanical damage. Its low friction coefficient enhances durability and reduces wear in high-contact applications, while its bright, reflective finish improves aesthetic appeal and facilitates easy cleaning. The thermal stability of chromium plating also maintains coating integrity under high temperatures, ensuring long-lasting performance on cast iron components.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Chromium plating on cast iron significantly enhances durability by creating a hard, wear-resistant surface that withstands mechanical abrasion and extends component lifespan. Cast iron alone is prone to rust and surface degradation, but the chromium layer acts as a robust barrier against corrosion, preventing oxidation even in harsh environments. This combination results in superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity compared to untreated cast iron, making it ideal for industrial and automotive applications.
Cost Analysis: Cast Iron vs Chromium Plating
Chromium plating on cast iron offers superior corrosion resistance and durability but comes at a higher initial cost compared to cast iron alone. The cost analysis reveals that while cast iron is inexpensive and widely available, chromium plating adds 20-30% to material and processing expenses due to specialized surface preparation and plating equipment. Over the long term, chrome-plated cast iron reduces maintenance and replacement costs, making it more cost-effective for industrial applications despite the upfront price difference.
Common Applications for Each Material
Cast iron plating is commonly used in heavy machinery and automotive parts due to its excellent wear resistance and durability under high stress conditions. Chromium plating is favored in decorative and industrial applications such as automotive trim, tools, and hydraulic cylinders for its corrosion resistance and shiny, smooth finish. Both materials enhance surface properties but cater to distinct functional and aesthetic requirements across manufacturing sectors.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Chromium plating on cast iron enhances corrosion resistance but poses significant environmental hazards due to hexavalent chromium compounds, which are toxic and carcinogenic, requiring strict handling and waste disposal protocols. Cast iron itself is durable and recyclable, presenting lower environmental risks compared to chromium plating processes that release hazardous byproducts affecting air and water quality. Safer alternatives and advancements in trivalent chromium plating or other eco-friendly coatings are increasingly favored to reduce occupational health risks and comply with environmental regulations.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Cast Iron and Chromium Plating
Choosing between cast iron and chromium plating depends on the desired durability and corrosion resistance; cast iron offers exceptional strength and heat retention, while chromium plating provides superior surface hardness and a sleek, rust-resistant finish. Cast iron is ideal for heavy-duty applications with high thermal requirements, whereas chromium plating enhances aesthetics and wear resistance on lighter steel substrates. For long-lasting protection combined with visual appeal, chromium plating is often the preferred choice in automotive and industrial components.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com