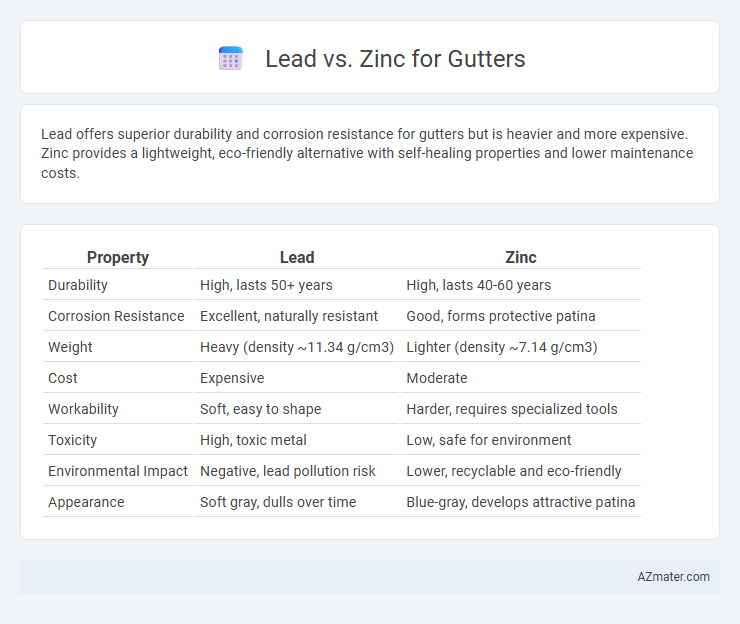
Lead offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for gutters but is heavier and more expensive. Zinc provides a lightweight, eco-friendly alternative with self-healing properties and lower maintenance costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, lasts 50+ years | High, lasts 40-60 years |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, naturally resistant | Good, forms protective patina |
| Weight | Heavy (density ~11.34 g/cm3) | Lighter (density ~7.14 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Expensive | Moderate |
| Workability | Soft, easy to shape | Harder, requires specialized tools |
| Toxicity | High, toxic metal | Low, safe for environment |
| Environmental Impact | Negative, lead pollution risk | Lower, recyclable and eco-friendly |
| Appearance | Soft gray, dulls over time | Blue-gray, develops attractive patina |
Introduction to Lead and Zinc Gutters
Lead gutters are renowned for their durability, malleability, and natural resistance to corrosion, making them a long-lasting choice for historic and traditional roofing systems. Zinc gutters offer a modern alternative, valued for their lightweight properties, self-healing patina, and low maintenance requirements. Both materials provide excellent water management solutions, but zinc gutters tend to be more cost-effective and environmentally friendly compared to lead.
Material Properties: Lead vs Zinc Gutters
Lead gutters offer exceptional malleability and corrosion resistance, allowing for easy shaping and long-lasting performance in various weather conditions. Zinc gutters provide superior durability and natural patina formation, which enhances resistance to rust while requiring minimal maintenance over time. Both materials exhibit excellent longevity, but zinc's strength and self-healing properties make it a preferred choice for modern gutter systems.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Lead gutters offer exceptional durability due to their high corrosion resistance and flexibility, often lasting over 100 years with minimal maintenance. Zinc gutters, while slightly less durable, provide impressive longevity of 80 to 100 years and develop a protective patina that enhances weather resistance. Both materials resist rust and harsh environmental conditions, but lead's superior malleability makes it more adaptable to complex gutter designs, extending its functional lifespan.
Environmental Impact of Lead and Zinc Gutters
Lead gutters release toxic metals into the environment, posing significant risks to soil and water quality due to lead's persistence and bioaccumulation. Zinc gutters, while also impacting ecosystems through metal runoff, tend to have lower toxicity and are more readily recoverable and recyclable. Choosing zinc over lead reduces long-term environmental contamination and aligns better with sustainable building practices.
Cost Analysis: Lead vs Zinc Gutters
Lead gutters typically incur higher upfront costs due to the material's weight and complex installation process, averaging $50 to $100 per linear foot. Zinc gutters offer a more cost-effective alternative, with prices ranging from $25 to $45 per linear foot, making them budget-friendly for large-scale projects. Long-term expenses should also consider zinc's lower maintenance needs and corrosion resistance compared to lead, which can add to overall savings despite the initial investment.
Installation Process & Techniques
Lead gutters require precise folding and soldering techniques to create watertight seams, demanding skilled craftsmanship and careful handling due to lead's malleability and weight. Zinc gutters are installed using mechanical seaming methods such as standing seams and crimping, offering easier handling and faster installation with reduced risk of damage from bending. Proper installation of both metals ensures durability and effective water drainage, but zinc's lighter weight and corrosion resistance often result in lower labor costs compared to lead.
Maintenance Requirements and Upkeep
Lead gutters demand minimal maintenance due to their self-healing properties and natural resistance to corrosion, reducing long-term upkeep costs. Zinc gutters require regular inspections to check for patina development and potential corrosion, which protects the metal but may necessitate periodic cleaning to maintain aesthetics. Both materials benefit from debris removal and gutter guard installation to prevent blockages and extend functional lifespan.
Aesthetic and Design Differences
Lead gutters offer a timeless, traditional aesthetic with a soft gray patina that evolves to a matte finish, complementing historic and classic architectural styles. Zinc gutters provide a modern, sleek appearance featuring a bluish-gray metallic sheen that gradually develops a protective layer of natural patina, suitable for contemporary and minimalist designs. The design flexibility of lead allows for intricate custom shaping, whereas zinc's durability supports streamlined profiles and longer seamless runs.
Safety Considerations for Lead and Zinc Gutters
Lead gutters pose significant safety risks due to the metal's toxicity, necessitating careful handling and protective measures during installation and maintenance to prevent lead exposure. Zinc gutters offer a safer alternative, as zinc is less toxic and environmentally friendly, reducing health hazards for homeowners and workers. Both materials require proper installation practices, but zinc's lower toxicity makes it preferable for residential applications where safety is a primary concern.
Choosing the Best Gutter Material for Your Home
Lead gutters offer exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making them a premium choice for long-term performance in various climates. Zinc gutters provide a balance of cost-effectiveness and natural patina development that enhances aesthetic appeal while resisting rust and requiring minimal maintenance. Selecting between lead and zinc depends on budget considerations, desired gutter lifespan, and the architectural style of your home.
Infographic: Lead vs Zinc for Gutter
 azmater.com
azmater.com