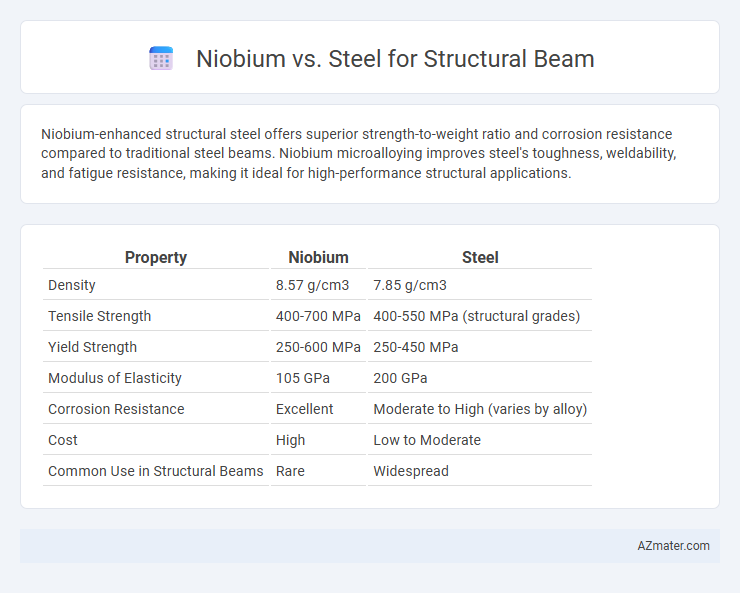
Niobium-enhanced structural steel offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance compared to traditional steel beams. Niobium microalloying improves steel's toughness, weldability, and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for high-performance structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.57 g/cm3 | 7.85 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 400-700 MPa | 400-550 MPa (structural grades) |
| Yield Strength | 250-600 MPa | 250-450 MPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 105 GPa | 200 GPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate to High (varies by alloy) |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
| Common Use in Structural Beams | Rare | Widespread |
Introduction to Structural Beams: Niobium vs Steel
Structural beams rely heavily on material properties such as strength, durability, and weight. Niobium-enhanced steel alloys offer superior tensile strength and improved corrosion resistance compared to conventional carbon steel, making them ideal for high-stress applications. While pure steel remains widely used due to cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing processes, niobium's ability to increase load-bearing capacity without significant weight increase drives its growing adoption in advanced structural beam construction.
Material Properties: Niobium and Steel Compared
Niobium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to conventional structural steel, enhancing load-bearing capacity while reducing overall beam weight. Its excellent corrosion resistance and higher ductility contribute to improved durability and resilience in harsh environments. Steel, though widely used for its cost-effectiveness and high tensile strength, can suffer from corrosion and fatigue, making niobium alloys a compelling alternative for critical structural applications.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Niobium-alloyed steel exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced fatigue resistance compared to conventional steel, making it an optimal choice for structural beams exposed to high stress. The addition of niobium refines the grain structure, significantly improving toughness and elongation without compromising weldability. These properties result in greater load-bearing capacity and longer service life, especially in demanding construction environments.
Weight and Density Considerations
Niobium-alloyed steel offers significant advantages in structural beams due to its lower density and higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to conventional steel, reducing overall structural weight without compromising durability. Niobium's addition refines grain structure, enhancing toughness and fatigue resistance, which allows for thinner, lighter beam designs in construction. This weight efficiency contributes to easier transportation and installation, lowering costs and environmental impact in large-scale engineering projects.
Corrosion Resistance: Niobium vs Steel
Niobium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to conventional steel, making it highly suitable for structural beams exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Unlike standard carbon steel, niobium forms a stable oxide layer that effectively prevents rust and degradation over time. This enhanced corrosion resistance reduces maintenance costs and extends the longevity of structural frameworks in marine, industrial, and chemical environments.
Cost and Availability Factors
Niobium-enhanced steel offers superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional carbon steel, allowing for thinner, lighter structural beams that reduce material costs and transportation expenses. Despite higher initial niobium alloy costs, the overall economic benefit arises from decreased fabrication time and increased durability, lowering long-term maintenance fees. Availability of niobium depends on limited global mining sources, predominantly Brazil and Canada, which can influence price volatility and supply chain reliability relative to the more widely accessible and produced steel varieties.
Fabrication and Workability Differences
Niobium-enhanced steel offers superior fabrication benefits compared to regular steel, including improved weldability and increased resistance to cracking during forming processes. The addition of niobium refines the grain structure, resulting in higher strength and better ductility, which simplifies bending, cutting, and shaping of structural beams. Steel without niobium requires more heat treatment and is prone to reduced workability, making niobium steel a preferred choice for complex structural applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Niobium-enhanced steel offers significant environmental benefits by requiring less material for equivalent strength, reducing overall resource consumption and energy use in production compared to traditional steel beams. The incorporation of niobium results in lighter, stronger structural beams that lower carbon emissions during transportation and construction phases. Sustainable construction practices increasingly favor niobium-infused steel for its ability to extend building lifespan and improve recyclability, minimizing environmental footprint over the lifecycle.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Niobium-enhanced steel alloys significantly improve structural beam performance in the construction and automotive industries due to their superior strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance compared to conventional carbon steel. Case studies from bridge construction demonstrate that niobium microalloyed beams reduce steel thickness and weight while maintaining load-bearing capacity, leading to cost savings and enhanced durability. Industrial applications in high-rise buildings and offshore platforms leverage niobium steel's enhanced weldability and resistance to brittle fracture under extreme environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Structural Beams
Niobium-enhanced steel offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and improved corrosion resistance compared to conventional steel, making it an excellent choice for structural beams in demanding applications. Steel remains cost-effective and widely available, suitable for standard construction projects with moderate load requirements. Selecting the appropriate material depends on balancing performance needs, budget constraints, and environmental conditions to ensure long-term durability and structural integrity.
Infographic: Niobium vs Steel for Structural Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com