Copper offers excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it a durable choice for coins. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, provides greater hardness and wear resistance, resulting in longer-lasting coins with enhanced detail retention.
Table of Comparison
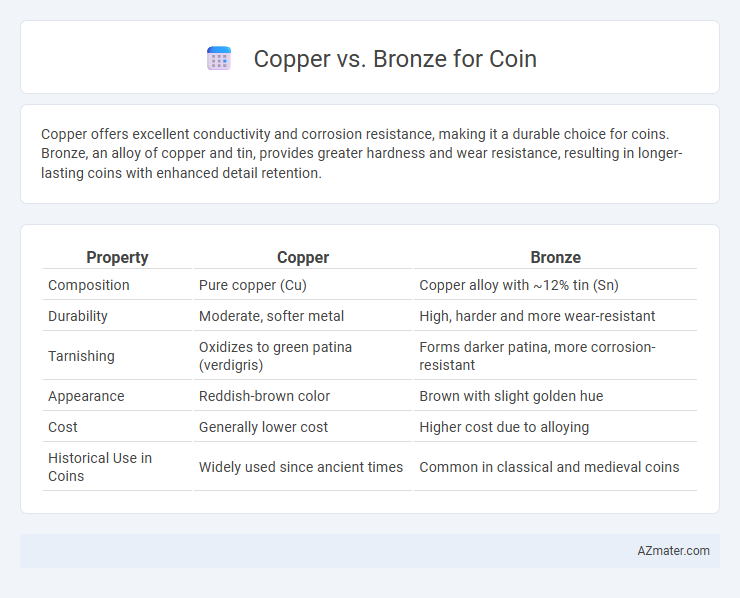
| Property | Copper | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure copper (Cu) | Copper alloy with ~12% tin (Sn) |
| Durability | Moderate, softer metal | High, harder and more wear-resistant |
| Tarnishing | Oxidizes to green patina (verdigris) | Forms darker patina, more corrosion-resistant |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown color | Brown with slight golden hue |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to alloying |
| Historical Use in Coins | Widely used since ancient times | Common in classical and medieval coins |
Introduction to Copper and Bronze Coins
Copper coins, widely used in ancient and modern times, are valued for their durability and antimicrobial properties, making them a popular choice for low-denomination currency. Bronze coins, composed primarily of copper alloyed with tin, offer enhanced hardness and corrosion resistance compared to pure copper, resulting in longer-lasting circulation coins. The transition from copper to bronze in coinage marked a significant advancement in metallurgy, improving the physical qualities and aesthetic appeal of currency throughout history.
Historical Significance of Copper and Bronze in Coinage
Copper and bronze have played pivotal roles in coinage since ancient times, with copper being one of the earliest metals used due to its natural abundance and malleability. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, gained prominence for its enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for longer-lasting coins in classical civilizations like Rome and Greece. The transition from pure copper to bronze in coinage reflects technological advancements and the evolving economic complexities of historical societies.
Composition Differences Between Copper and Bronze
Copper is a pure elemental metal with a chemical symbol Cu, characterized by its reddish color and high malleability, whereas bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, often with additional elements like phosphorus or aluminum to enhance strength and corrosion resistance. The typical copper content in bronze ranges from 80% to 90%, while the remaining percentage consists mostly of tin, which significantly improves hardness and durability compared to pure copper coins. These compositional differences impact coinage properties, with bronze coins offering greater wear resistance and longevity than coins made of pure copper.
Durability and Wear Resistance of Copper vs Bronze Coins
Bronze coins exhibit superior durability and wear resistance compared to copper coins due to their alloy composition, typically consisting of copper and tin. The addition of tin in bronze increases hardness and reduces oxidation, resulting in coins that maintain detail and structural integrity longer under circulation conditions. Consequently, bronze coins are generally preferred for minting currency when longevity and resistance to abrasion are critical factors.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color and Luster Comparisons
Copper coins boast a warm, reddish-brown hue that develops a distinctive patina over time, enhancing their vintage appeal and rich character. Bronze coins, composed primarily of copper and tin, exhibit a deeper, richer brown color with a subtle golden undertone and maintain a brighter luster longer due to their alloy composition. The contrast between the warmer, more vibrant shine of copper and the muted, elegant glow of bronze allows collectors to appreciate differing aesthetic qualities in numismatic design.
Cost and Availability of Copper and Bronze
Copper is generally more expensive than bronze due to its higher purity and demand in electrical and industrial applications. Bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, tends to be more cost-effective because tin is relatively cheaper and copper content is reduced. The availability of copper is more limited compared to bronze, as tin in bronze alloys can be sourced more readily, making bronze a more accessible option for coin production.
Corrosion Resistance in Everyday Use
Copper exhibits moderate corrosion resistance but tends to develop a greenish patina called verdigris when exposed to moisture and air over time, which can alter the coin's appearance and surface integrity. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, offers superior corrosion resistance due to the protective oxide layer it forms, making it more durable in everyday handling and exposure to environmental elements. This enhanced resistance to tarnishing and corrosion ensures bronze coins maintain their aesthetic and structural qualities longer than pure copper coins.
Minting Process: Copper vs Bronze Performance
Copper coins offer excellent malleability, allowing for precise detailing during the minting process, which results in sharp, well-defined designs. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, provides increased hardness and durability, reducing wear and extending the coin's lifespan without sacrificing fine detail. However, the higher hardness of bronze can require more pressure and advanced minting equipment compared to pure copper, impacting production efficiency.
Collectible Value and Market Trends
Copper coins, often prized for their historical authenticity and lower market price, appeal to collectors seeking early coinage and affordable additions. Bronze coins, typically alloyed with tin or zinc, demonstrate increased durability and patina development, enhancing their collectible value in numismatic markets. Recent market trends indicate rising demand for well-preserved bronze coins due to rarity and aesthetic appeal, while copper coins maintain steady interest for their significance in ancient and early modern coin collections.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Copper coins require extensive mining with significant environmental disruption and high energy consumption, leading to increased carbon emissions. Bronze coins, composed primarily of copper and tin, involve mining two metals but often use recycled materials, reducing raw extraction and lowering overall environmental impact. Sustainable coin production prioritizes recycled copper and bronze alloys to minimize resource depletion and promote circular economy practices in numismatics.
Infographic: Copper vs Bronze for Coin
 azmater.com
azmater.com