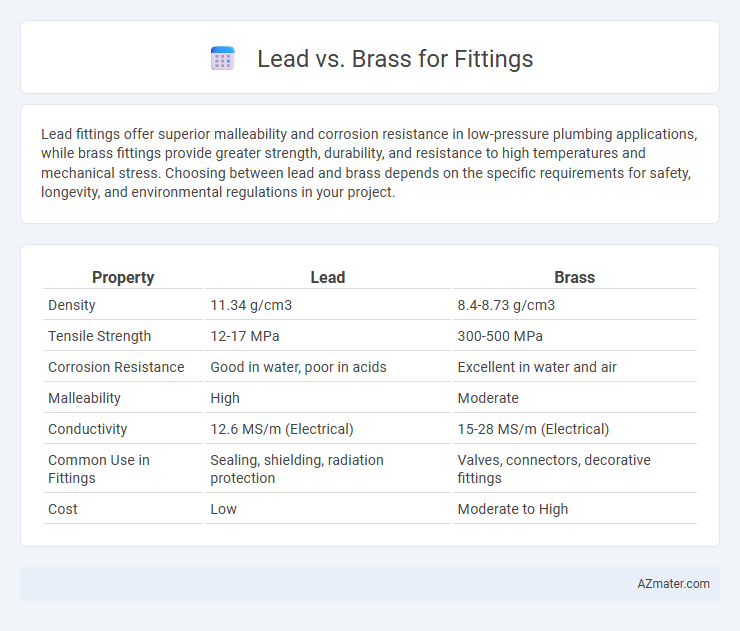
Lead fittings offer superior malleability and corrosion resistance in low-pressure plumbing applications, while brass fittings provide greater strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures and mechanical stress. Choosing between lead and brass depends on the specific requirements for safety, longevity, and environmental regulations in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 11.34 g/cm3 | 8.4-8.73 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 12-17 MPa | 300-500 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good in water, poor in acids | Excellent in water and air |
| Malleability | High | Moderate |
| Conductivity | 12.6 MS/m (Electrical) | 15-28 MS/m (Electrical) |
| Common Use in Fittings | Sealing, shielding, radiation protection | Valves, connectors, decorative fittings |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
Introduction: Lead vs Brass in Fittings
Lead and brass are two common materials used in fittings, each with distinct properties affecting their suitability for plumbing applications. Brass fittings offer superior corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for water systems, while lead fittings, once prevalent for their malleability, are now largely avoided due to health risks linked to lead contamination. Choosing between lead and brass fittings depends on factors like safety standards, longevity, and regulatory compliance in plumbing installations.
Material Composition of Lead and Brass
Lead fittings consist primarily of lead, a dense, malleable metal known for its corrosion resistance and ease of casting, but it poses health risks due to toxicity. Brass fittings are composed mainly of copper and zinc, offering superior strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and dezincification in plumbing systems. The inherent material properties of brass make it a safer and more reliable choice for most water supply applications compared to lead.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Brass fittings exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to lead fittings due to their resistance to corrosion, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Lead fittings, while softer and easier to shape, are prone to corrosion and degradation over time, leading to potential leaks and contamination risks. Brass's robust properties make it the preferred choice for long-lasting, reliable plumbing and industrial applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Lead vs Brass
Brass fittings exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to lead, as brass is an alloy of copper and zinc known for its durability and resistance to tarnishing and rust in various environments. Lead fittings, while historically used, are more prone to corrosion and leaching, posing health risks in potable water systems. Due to brass's enhanced stability and compliance with safety standards, it is the preferred material for fittings in plumbing and industrial applications requiring long-term corrosion resistance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Brass fittings are widely preferred over lead for plumbing due to their lower toxicity and reduced risk of lead contamination in drinking water. Exposure to lead fittings can cause serious health issues, including neurological damage and developmental delays, especially in children. Regulatory agencies like the EPA strictly limit lead content in plumbing materials, making brass a safer, compliant choice for health-conscious installations.
Environmental Impact of Lead and Brass
Lead fittings pose significant environmental risks due to lead's toxic nature, which can contaminate soil and water, harming ecosystems and human health. Brass fittings, composed primarily of copper and zinc, are more environmentally friendly as they are less toxic and highly recyclable, reducing landfill waste and resource extraction impact. Choosing brass over lead fittings supports sustainable practices by minimizing pollution and promoting safer materials in plumbing and industrial applications.
Cost Comparison: Lead vs Brass Fittings
Lead fittings are generally less expensive due to the lower cost of raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making them a budget-friendly option for some applications. Brass fittings, although more costly upfront, offer superior durability, corrosion resistance, and longevity, often resulting in lower replacement and maintenance expenses over time. The initial price difference between lead and brass fittings can be significant, but the total cost of ownership often favors brass in long-term plumbing and industrial installations.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Brass fittings are widely favored for plumbing due to compliance with NSF/ANSI 61 and 372 standards, ensuring low lead content and safe potable water use. Lead-based fittings, once common, have been largely phased out or banned under regulations such as the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) in the U.S. because of health risks associated with lead contamination. Compliance with these regulatory standards mandates the use of lead-free brass alloys to meet modern safety and environmental requirements in water system installations.
Common Applications in Plumbing and Industry
Lead fittings are historically used in plumbing for their malleability and corrosion resistance but are largely replaced due to health risks associated with lead exposure. Brass fittings dominate in plumbing and industrial applications because of their durability, excellent corrosion resistance, and compatibility with water and gas systems. Industries rely on brass for valves, connectors, and instrumentation fittings where reliability and safety standards are critical.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Fittings
Choosing the right material for your fittings is crucial for durability and safety, with brass offering excellent corrosion resistance and longevity in plumbing applications. Lead fittings, while historically common, pose health risks due to toxicity and are generally unsuitable for potable water systems. Brass fittings provide a safer, more reliable option, especially in environments requiring robust performance and compliance with modern building codes.
Infographic: Lead vs Brass for Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com