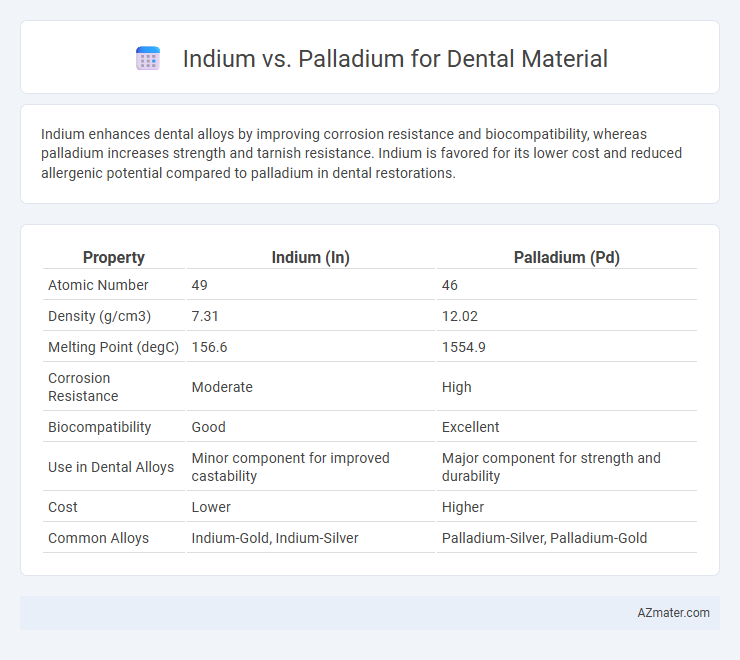
Indium enhances dental alloys by improving corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, whereas palladium increases strength and tarnish resistance. Indium is favored for its lower cost and reduced allergenic potential compared to palladium in dental restorations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Indium (In) | Palladium (Pd) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 49 | 46 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 7.31 | 12.02 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 156.6 | 1554.9 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Biocompatibility | Good | Excellent |
| Use in Dental Alloys | Minor component for improved castability | Major component for strength and durability |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Alloys | Indium-Gold, Indium-Silver | Palladium-Silver, Palladium-Gold |
Introduction to Dental Materials: Indium vs Palladium
Indium and palladium are key metals used in dental alloys for crowns, bridges, and other restorations due to their corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Indium enhances alloy wettability and oxidation resistance, improving casting quality and marginal fit, while palladium contributes high strength and durability with excellent tarnish resistance. Selecting between indium and palladium depends on balancing mechanical properties, cost considerations, and specific clinical requirements for long-lasting dental restorations.
Chemical Properties of Indium and Palladium
Indium exhibits a low melting point of 156.6degC and excellent corrosion resistance, making it valuable for dental alloys where biocompatibility and durability are essential. Palladium offers superior hardness, high melting point of 1554.9degC, and exceptional resistance to oxidation and tarnishing, enhancing the longevity and mechanical strength of dental restorations. Both metals contribute to improved alloy properties, but palladium's chemical stability supports better performance under oral environmental stresses.
Biocompatibility in the Oral Environment
Indium and palladium are both used in dental alloys, but palladium exhibits superior biocompatibility in the oral environment due to its corrosion resistance and low cytotoxicity. Indium can improve alloy castability but may release ions that cause local tissue irritation or allergic reactions over time. Palladium-based alloys are preferred for long-term dental restorations as they maintain structural integrity and minimize adverse biological responses in oral tissues.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Indium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and flexibility, enhancing the mechanical strength of dental alloys, while palladium offers excellent hardness and wear resistance, contributing to long-lasting restorations. Palladium-based dental materials typically provide higher durability due to their increased resistance to deformation under masticatory forces compared to indium-containing alloys. The choice between indium and palladium influences the balance between flexibility and rigidity in dental prosthetics, impacting longevity and patient comfort.
Corrosion Resistance: Indium vs Palladium
Indium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance in dental applications due to its ability to form a stable oxide layer that protects against oral fluids. Palladium also offers strong corrosion resistance but tends to be more resistant to oxidation and tarnishing over time, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting dental restorations. Comparative studies highlight that while both metals resist corrosion effectively, palladium's superior chemical stability often results in enhanced durability in the oral environment.
Applications in Dental Restorations
Indium enhances dental amalgams by improving corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for long-lasting dental restorations. Palladium is essential in dental alloys for crowns and bridges due to its excellent biocompatibility, durability, and resistance to tarnishing. Both metals contribute to the stability and longevity of restorative materials, with indium primarily improving amalgam performance and palladium widely used in noble metal-based dental prosthetics.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Indium dental materials generally offer a lower-cost alternative to palladium, significantly reducing expenses in dental alloy formulations. Palladium, while more expensive, provides superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, justifying its higher price in premium dental restorations. Cost analysis reveals that using indium alloys can enhance affordability in large-scale dental applications without severely compromising performance, making it a strategic choice for budget-conscious practices.
Aesthetic Outcomes in Dental Prosthetics
Indium offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, contributing to better long-term aesthetic outcomes in dental prosthetics compared to palladium. Palladium enhances alloy strength and wear resistance but tends to cause slight discoloration over time due to oxidation. Dental prosthetics incorporating indium maintain a more stable color and luster, improving patient satisfaction with the restoration's appearance.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Indium enhances dental alloys by improving corrosion resistance and ductility, contributing to better clinical performance in restorations exposed to oral environments. Palladium offers high strength and excellent tarnish resistance, often extending the longevity of crowns and bridges through its stable noble metal properties. Studies indicate palladium-containing alloys generally demonstrate superior durability, while indium's role is critical in refining mechanical and chemical stability within dental materials.
Future Trends and Research in Dental Alloys
Emerging research highlights palladium's superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility compared to indium, making it increasingly favored in dental alloys for long-term restorations. Advances in nanotechnology and alloy engineering aim to enhance palladium-based materials' mechanical strength and aesthetic integration, driving future innovation in dental prosthetics. Ongoing studies focus on optimizing palladium-indium ratios to balance cost-effectiveness with performance, addressing sustainability and patient-specific customization in dental materials.
Infographic: Indium vs Palladium for Dental Material
 azmater.com
azmater.com