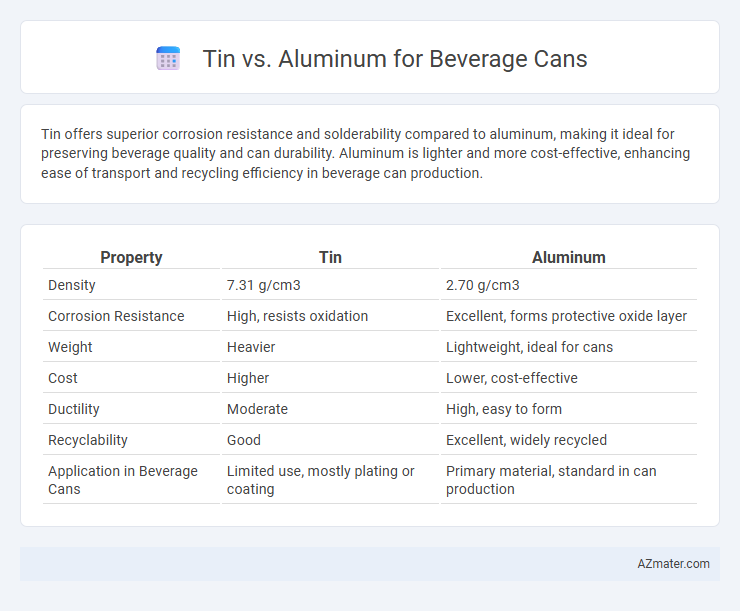
Tin offers superior corrosion resistance and solderability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for preserving beverage quality and can durability. Aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective, enhancing ease of transport and recycling efficiency in beverage can production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.31 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, resists oxidation | Excellent, forms protective oxide layer |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight, ideal for cans |
| Cost | Higher | Lower, cost-effective |
| Ductility | Moderate | High, easy to form |
| Recyclability | Good | Excellent, widely recycled |
| Application in Beverage Cans | Limited use, mostly plating or coating | Primary material, standard in can production |
Introduction: Tin vs Aluminum Beverage Cans
Tin and aluminum are the primary materials used for beverage cans, each offering distinct benefits. Aluminum cans dominate the market due to their lightweight nature, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior recyclability, reducing environmental impact. Tin, once widely used, remains valued for its corrosion-resistant properties but is heavier and less cost-effective compared to aluminum in modern beverage packaging.
Historical Overview: Evolution of Can Materials
The evolution of beverage can materials began with tin-coated steel cans in the early 20th century, valued for their corrosion resistance and ease of manufacturing. Aluminum emerged in the 1950s as a lightweight, rust-proof alternative, revolutionizing the industry by enhancing portability and reducing shipping costs. Today, aluminum dominates the market due to its superior recyclability and lower environmental impact compared to traditional tin-plated steel cans.
Material Properties: Tin and Aluminum Compared
Tin offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent solderability, making it ideal for protective coatings in beverage cans, but it is heavier and more expensive than aluminum. Aluminum boasts a lightweight structure, high strength-to-weight ratio, and exceptional recyclability, which enhances transportation efficiency and reduces environmental impact in beverage can production. The choice between tin and aluminum hinges on balancing durability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability within the beverage packaging industry.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Tin and aluminum differ significantly in their beverage can manufacturing processes due to material properties. Tinplate involves coating steel sheets with a thin layer of tin, requiring additional tinning and coating steps to prevent corrosion before shaping, while aluminum cans are manufactured from aluminum alloy sheets that are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and directly formed without the need for extra coating. Aluminum's manufacturing process includes extrusion and impact extrusion techniques that enable thinner walls and more efficient recycling, leading to streamlined production and reduced energy consumption compared to tinplate cans.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tin and aluminum differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for beverage cans, with aluminum offering a more eco-friendly profile due to its high recyclability and lower energy consumption during recycling. Aluminum cans recycle at rates exceeding 70%, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to primary production, while tin's limited recycling infrastructure results in higher resource depletion and waste. The lightweight nature of aluminum also lowers transportation emissions, enhancing its overall sustainability advantage in the beverage packaging industry.
Cost Analysis: Production and Recycling
Aluminum dominates beverage can production due to lower manufacturing costs driven by abundant bauxite reserves and efficient smelting processes, resulting in cost-effective large-scale output compared to tin. Recycling aluminum consumes only 5% of the energy required for primary production, enabling significant cost savings and reducing environmental impact, whereas tin recycling is less developed and more expensive due to limited supply and higher processing complexity. The economic advantage of aluminum is further enhanced by established global recycling infrastructures that drive down costs and ensure material availability for manufacturers.
Beverage Preservation and Taste
Tin offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent sealing properties, which help preserve beverage freshness and maintain original taste profiles in cans. Aluminum, while lightweight and widely used, can be more reactive with acidic beverages, potentially impacting flavor and shelf life without specialized coatings. Advanced organic and inorganic linings on aluminum cans mitigate taste alteration, but tin's natural protective qualities make it a preferred choice for optimal beverage preservation and flavor integrity.
Health and Safety Considerations
Tin coatings on beverage cans provide robust corrosion resistance, minimizing metal leaching and reducing potential health risks associated with aluminum exposure. Aluminum cans often have an internal polymer lining to prevent direct contact between the metal and beverage, addressing concerns about aluminum migration and its debated neurotoxicity. Choosing tin-coated cans can enhance safety by limiting chemical interactions, but modern aluminum cans with effective linings remain a widely accepted and regulated option in the beverage industry.
Market Trends in Beverage Can Materials
The beverage can market increasingly favors aluminum over tin due to aluminum's lightweight, recyclability, and lower production costs, driving a dominant share in global packaging. Growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions further boosts aluminum can adoption, with industry reports projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% for aluminum cans through 2030. Tin remains limited to specific uses like lining or decoration but lacks the scalability and environmental benefits that aluminum offers in beverage can manufacturing.
Future Innovations in Beverage Can Packaging
Future innovations in beverage can packaging increasingly focus on improving sustainability and performance through advanced materials like tin and aluminum alloys that enhance durability and recyclability. Research is exploring tin coatings to reduce corrosion and improve the taste integrity of aluminum cans, while lightweight aluminum formulations aim to decrease material use and carbon footprint. Emerging technologies such as nano-coatings and smart packaging integration promise to elevate product freshness and consumer engagement in the beverage industry.
Infographic: Tin vs Aluminum for Beverage Can
 azmater.com
azmater.com