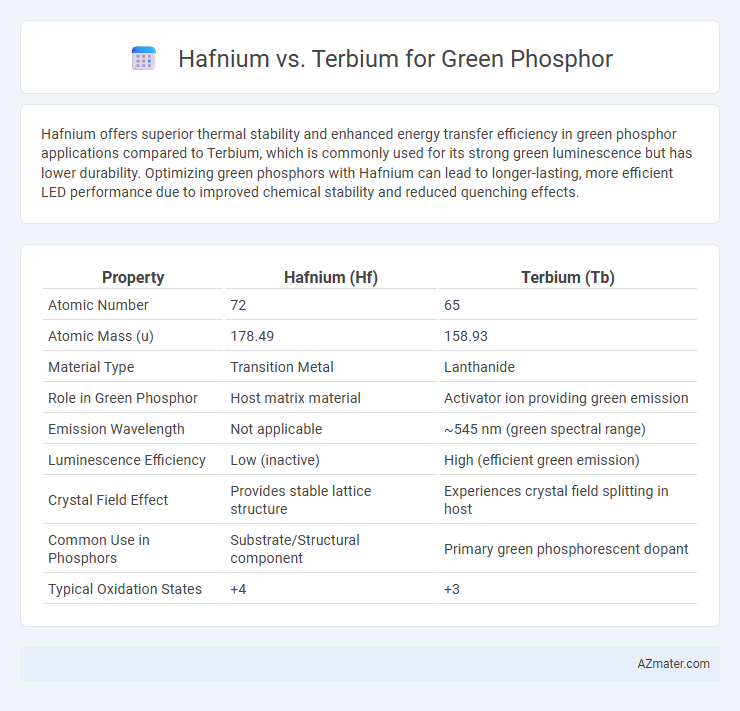
Hafnium offers superior thermal stability and enhanced energy transfer efficiency in green phosphor applications compared to Terbium, which is commonly used for its strong green luminescence but has lower durability. Optimizing green phosphors with Hafnium can lead to longer-lasting, more efficient LED performance due to improved chemical stability and reduced quenching effects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) | Terbium (Tb) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 72 | 65 |
| Atomic Mass (u) | 178.49 | 158.93 |
| Material Type | Transition Metal | Lanthanide |
| Role in Green Phosphor | Host matrix material | Activator ion providing green emission |
| Emission Wavelength | Not applicable | ~545 nm (green spectral range) |
| Luminescence Efficiency | Low (inactive) | High (efficient green emission) |
| Crystal Field Effect | Provides stable lattice structure | Experiences crystal field splitting in host |
| Common Use in Phosphors | Substrate/Structural component | Primary green phosphorescent dopant |
| Typical Oxidation States | +4 | +3 |
Introduction to Hafnium and Terbium
Hafnium and Terbium are critical elements used in green phosphors for advanced display and lighting technologies. Hafnium, a transition metal with atomic number 72, contributes to stability and enhanced luminescence efficiency in phosphor compounds. Terbium, a rare-earth element with atomic number 65, is renowned for its strong green emission and high color purity, making it indispensable in vibrant phosphor applications.
Importance of Green Phosphors in Modern Technology
Green phosphors incorporating hafnium and terbium play a critical role in enhancing the efficiency and color purity of modern display technologies such as OLEDs and LED screens. Terbium's strong green emission and excellent luminescent properties make it ideal for achieving vivid green hues, while hafnium contributes to structural stability and improved phosphor performance under high excitation conditions. Optimizing the balance between hafnium's durability and terbium's brightness is essential for advancing vibrant, energy-efficient green phosphors in cutting-edge electronic devices.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Hafnium (Hf) and Terbium (Tb) exhibit distinct chemical and physical properties influencing their efficacy in green phosphor applications. Hafnium, with its high atomic number (72) and stable oxidation state (+4), provides robust thermal stability and strong resistance to corrosion, crucial for durable phosphor materials. Terbium, a rare earth element with atomic number 65 and common +3 oxidation state, excels in luminescent efficiency due to its unique 4f electron transitions, making it highly effective for bright green phosphor emission.
Luminescence Efficiency: Hafnium vs Terbium
Terbium exhibits significantly higher luminescence efficiency than Hafnium when used in green phosphors due to its strong 4f-4f electron transitions that emit bright green light. Hafnium, although chemically stable, lacks efficient electronic transitions needed for intense green emission, resulting in lower brightness and overall phosphor performance. Therefore, terbium-based phosphors dominate applications requiring high luminance and color purity in green displays and lighting.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Hafnium-based green phosphors exhibit lower energy consumption due to their efficient electron transition mechanisms, leading to reduced power requirements in LED applications compared to Terbium-based phosphors. Terbium phosphors, while offering high luminous efficiency, tend to require higher excitation energy, increasing overall energy use and environmental footprint. Environmentally, Hafnium's relative abundance and lower toxicity contribute to more sustainable manufacturing processes and end-of-life recycling options than Terbium, which involves rare earth mining with significant ecological impact.
Cost-Effectiveness and Material Availability
Hafnium and Terbium are critical elements in green phosphor applications, with Terbium offering superior luminescent efficiency at higher costs due to its rarity. Hafnium, while less efficient in green phosphor emission, benefits from greater material availability and lower cost, improving overall cost-effectiveness for large-scale production. Evaluating phosphor materials for commercial use requires balancing performance characteristics of Terbium against the affordability and supply stability of Hafnium.
Performance in LED and Display Applications
Hafnium and terbium exhibit distinct performance characteristics in green phosphor applications for LEDs and displays, with terbium offering superior luminescence efficiency and color purity due to its strong green emission lines in the visible spectrum. Hafnium, while less efficient in green light emission, provides enhanced thermal stability and durability, which can improve device longevity under high operating temperatures. Terbium's higher quantum yield and brightness make it the preferred choice for vibrant green displays, whereas hafnium's robustness suits applications requiring long-term reliability.
Stability and Longevity of Green Phosphors
Hafnium-based green phosphors exhibit exceptional chemical stability and thermal endurance, making them highly suitable for long-term applications in display and lighting technologies. Terbium-doped green phosphors are well-known for their bright luminescence but often suffer from reduced stability under prolonged exposure to heat and moisture. Comparing both, hafnium phosphors provide superior longevity by maintaining consistent green emission intensity and structural integrity in demanding environments.
Safety, Handling, and Regulatory Considerations
Hafnium and terbium differ significantly in safety, handling, and regulatory concerns when used in green phosphors. Hafnium poses lower toxicity risks but requires careful dust control due to its reactive dust and potential inhalation hazards, while terbium compounds can be more hazardous, necessitating stringent protective measures against lung accumulation and sensitization. Regulatory guidelines for terbium are generally stricter, reflecting its higher biological risk and environmental impact compared to the relatively inert nature of hafnium.
Future Prospects: Hafnium or Terbium for Green Phosphor Development
Terbium remains a critical element for green phosphor development due to its efficient green emission and established use in display technologies, driving ongoing research into enhancing brightness and stability. Hafnium, despite less traditional use in phosphors, shows potential through doped hafnium oxide materials offering improved thermal stability and novel luminescent properties that could revolutionize next-generation displays. Future prospects favor terbium's proven performance for immediate applications while hafnium's emerging properties promise innovative opportunities in advanced green phosphor development.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Terbium for Green Phosphor
 azmater.com
azmater.com