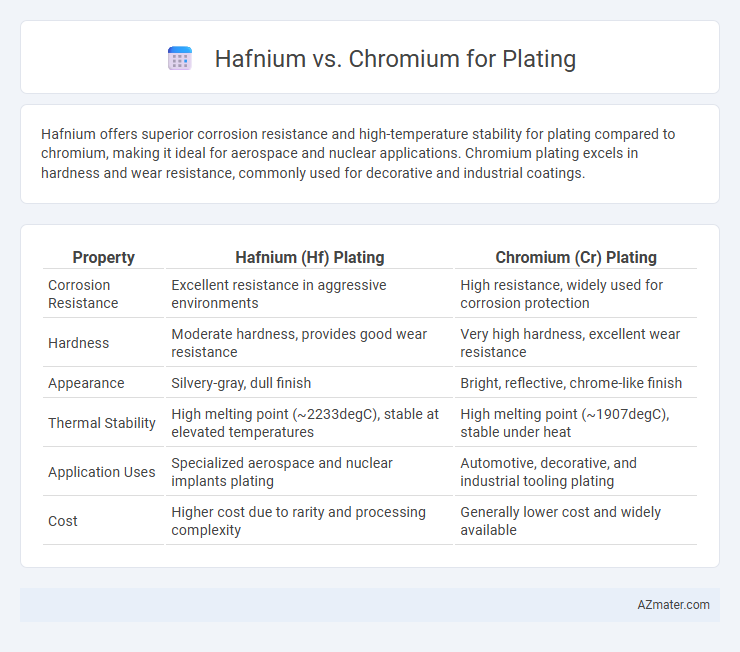
Hafnium offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability for plating compared to chromium, making it ideal for aerospace and nuclear applications. Chromium plating excels in hardness and wear resistance, commonly used for decorative and industrial coatings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hafnium (Hf) Plating | Chromium (Cr) Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance in aggressive environments | High resistance, widely used for corrosion protection |
| Hardness | Moderate hardness, provides good wear resistance | Very high hardness, excellent wear resistance |
| Appearance | Silvery-gray, dull finish | Bright, reflective, chrome-like finish |
| Thermal Stability | High melting point (~2233degC), stable at elevated temperatures | High melting point (~1907degC), stable under heat |
| Application Uses | Specialized aerospace and nuclear implants plating | Automotive, decorative, and industrial tooling plating |
| Cost | Higher cost due to rarity and processing complexity | Generally lower cost and widely available |
Introduction to Hafnium and Chromium Plating
Hafnium and chromium plating are both valued for their corrosion resistance and hardness, with hafnium offering superior high-temperature oxidation resistance and excellent neutron absorption properties essential in aerospace and nuclear industries. Chromium plating is widely used for decorative and industrial purposes due to its hardness, wear resistance, and ability to provide a bright, corrosion-resistant finish on automotive, machinery, and plumbing components. The choice between hafnium and chromium plating depends heavily on application-specific requirements such as thermal stability, radiation shielding, and aesthetic appeal.
Chemical Properties: Hafnium vs Chromium
Hafnium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point of 2233degC, making it ideal for extreme environments, whereas chromium offers superior hardness and excellent oxidation resistance with a melting point of 1907degC. Chemically, hafnium forms stable oxides that protect against chemical attack, while chromium's passivation layer of chromium oxide prevents surface corrosion. The differing electron configurations--hafnium with [Xe] 4f14 5d2 6s2 and chromium with [Ar] 3d5 4s1--contribute to their unique plating characteristics and chemical stability.
Plating Process Overview
Hafnium and chromium plating processes differ significantly in deposition methods and applications, with chromium typically applied via electroplating for corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, while hafnium coatings are often deposited using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD) to enhance high-temperature performance and wear resistance. Chromium plating involves the reduction of chromium ions from a chromic acid bath onto the substrate, creating a hard, corrosion-resistant layer widely used in automotive and industrial parts. Hafnium plating, although less common, requires complex vacuum-based processes that produce dense, adherent films suited for aerospace and nuclear industries due to hafnium's high melting point and neutron absorption capabilities.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Hafnium plating exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to chromium due to its exceptional ability to form a stable, dense oxide layer that protects the underlying substrate from oxidation and chemical attack. Chromium plating, while offering good corrosion resistance in many environments, is more prone to pitting and oxidation under harsh or acidic conditions. The choice between hafnium and chromium plating depends on specific application requirements, with hafnium favored in highly corrosive or high-temperature environments for enhanced durability.
Durability and Wear Performance
Hafnium plating offers exceptional durability and wear resistance due to its high melting point and strong corrosion resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and nuclear industries. Chromium plating provides excellent hardness and good wear performance, commonly used for automotive and industrial components to enhance surface hardness and reduce friction. While chromium is more cost-effective for general wear applications, hafnium's superior resistance to extreme conditions ensures longer service life under severe mechanical and thermal stress.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Hafnium plating offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility compared to chromium, reducing the risk of environmental contamination from toxic hexavalent chromium compounds. Chromium plating involves hazardous chemicals that pose significant health risks, including respiratory issues and carcinogenic exposure, requiring stringent safety protocols. Selecting hafnium over chromium plating supports greener manufacturing processes with lower ecological impact and enhanced worker safety.
Applications in Various Industries
Hafnium plating offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for aerospace and nuclear industries where durability under extreme conditions is crucial. Chromium plating is widely used in automotive, electronics, and decorative applications due to its hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Both metals serve specialized roles, with hafnium preferred for critical, high-stress environments and chromium excelling in mass-produced, cost-sensitive applications.
Cost Analysis: Hafnium vs Chromium
Hafnium plating typically incurs higher costs compared to chromium due to the metal's rarity and complex extraction processes, with hafnium prices averaging around $300-$400 per kilogram versus chromium's $10-$15 per kilogram. Chromium plating remains more cost-effective for large-scale industrial applications, benefiting from abundant supply and streamlined electroplating methods. However, hafnium's superior corrosion resistance and high melting point justify its premium pricing in specialized aerospace and nuclear industries.
Maintenance and Longevity
Hafnium plating offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to chromium, making it ideal for high-wear environments requiring minimal maintenance. Chromium plating provides excellent hardness and aesthetic appeal but often requires frequent upkeep due to its susceptibility to oxidation and wear over time. Choosing hafnium over chromium for plating significantly enhances longevity and reduces maintenance intervals in industrial applications.
Future Trends in Plating Technologies
Hafnium plating is emerging as a promising alternative to chromium due to its superior corrosion resistance and thermal stability, critical for aerospace and nuclear applications. Chromium plating, long valued for hardness and wear resistance, faces regulatory pressure over hexavalent chromium toxicity, driving innovation toward eco-friendly hafnium-based coatings. Future plating technologies prioritize sustainable, high-performance materials like hafnium to meet stringent environmental standards and enhance durability in advanced industrial sectors.
Infographic: Hafnium vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com