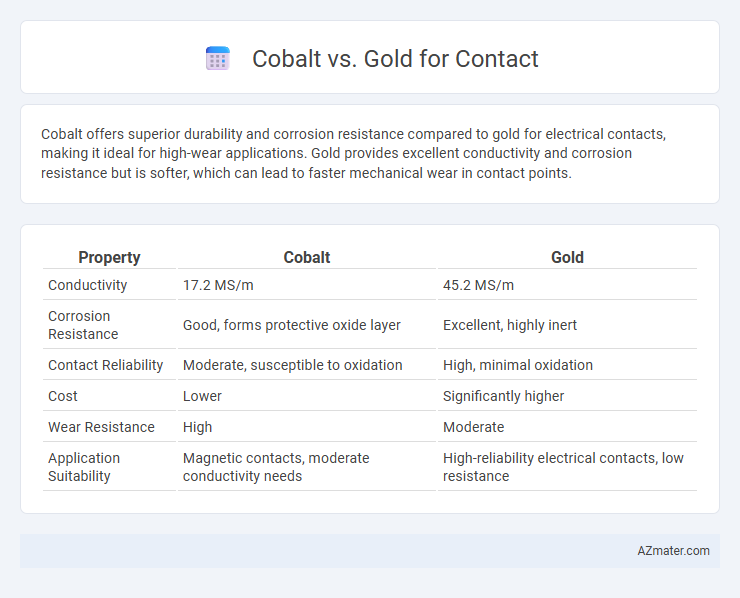
Cobalt offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to gold for electrical contacts, making it ideal for high-wear applications. Gold provides excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance but is softer, which can lead to faster mechanical wear in contact points.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cobalt | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | 17.2 MS/m | 45.2 MS/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, forms protective oxide layer | Excellent, highly inert |
| Contact Reliability | Moderate, susceptible to oxidation | High, minimal oxidation |
| Cost | Lower | Significantly higher |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Application Suitability | Magnetic contacts, moderate conductivity needs | High-reliability electrical contacts, low resistance |
Introduction to Cobalt vs Gold for Contacts
Cobalt and gold are widely used materials for electrical contacts due to their distinct properties impacting conductivity and durability. Gold offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for low-voltage, low-current applications requiring long-term reliability. Cobalt, known for its hardness and wear resistance, is favored in high-stress environments where mechanical robustness and cost efficiency are critical.
Material Properties: Cobalt vs Gold
Cobalt exhibits excellent hardness and high wear resistance, making it ideal for durable electrical contacts subject to mechanical stress, while gold offers superior corrosion resistance and exceptional electrical conductivity, ensuring reliable signal transmission in low-current applications. Gold's non-oxidizing surface prevents contact degradation over time, whereas cobalt's robust mechanical properties provide better structural integrity under high load conditions. Balancing conductivity and durability, cobalt is favored in heavy-duty environments, whereas gold is preferred in precision electronics requiring stable, low-resistance connections.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Cobalt contacts exhibit lower electrical conductivity compared to gold contacts, with gold's conductivity around 45.2 MS/m versus cobalt's approximately 17.0 MS/m. Gold's superior conductivity reduces contact resistance, enhancing performance in high-frequency and sensitive electronic applications. Despite cobalt's durability and corrosion resistance, gold remains the preferred material for contacts requiring minimal signal loss and optimal electrical efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Cobalt contacts exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to gold, making them highly durable in harsh environments. Cobalt's oxide layer protects the contact surface from wear and chemical degradation, enhancing longevity in electrically demanding applications. Gold contacts resist corrosion exceptionally well but are softer, leading to potential wear under mechanical stress, whereas cobalt offers a robust balance of conductivity and mechanical strength.
Cost Analysis: Cobalt and Gold Contacts
Cobalt contacts generally offer a cost-effective alternative to gold due to their lower raw material and processing expenses, making them suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Gold contacts, while pricier, provide superior corrosion resistance and conductivity, justifying their premium cost in high-reliability environments. The total cost of cobalt versus gold contacts depends on factors like application requirements, environmental conditions, and longevity, with gold favored for performance-critical uses despite higher initial investment.
Applications in Electronics
Cobalt is frequently used in electronic contacts due to its excellent wear resistance and high-temperature stability, making it suitable for high-performance connectors and switches. Gold offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, which ensures reliable signal transmission and longevity in low-current and sensitive electronic applications. The choice between cobalt and gold depends on the specific electronic context, balancing durability and conductivity requirements.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Cobalt contacts exhibit superior performance in high-temperature environments due to their excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, maintaining conductivity under prolonged heat exposure. Gold contacts, while highly conductive and corrosion-resistant, tend to soften and degrade at elevated temperatures, reducing reliability in harsh thermal conditions. Cobalt's enhanced durability makes it the preferred choice for applications requiring sustained electrical performance under extreme heat.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Cobalt and gold differ significantly in environmental and health impacts for contact applications; cobalt mining often involves toxic chemicals and poses risks of respiratory issues due to particulate exposure, whereas gold extraction primarily uses cyanide, raising concerns about water contamination. Recycling gold reduces environmental harm and health risks, while cobalt's extraction and processing frequently contribute to ecological degradation and human toxicity. Selecting gold for contact materials typically offers a safer profile for both the environment and workers compared to cobalt.
Industry Trends and Innovations
Cobalt is gaining traction over gold in contact applications due to its superior conductivity and durability, especially in high-wear environments like electronics and automotive industries. Innovations in cobalt-based alloys and plating technologies enhance corrosion resistance and electrical performance, driving adoption in next-generation devices such as 5G infrastructure and electric vehicle components. Industry trends highlight a shift toward cost-effective, sustainable materials with cobalt providing a balance of performance and supply chain stability compared to the traditionally expensive and limited gold resources.
Choosing the Right Contact Material
Cobalt offers excellent hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-wear electrical contacts in harsh environments, whereas gold provides superior electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance, ensuring consistent low contact resistance in sensitive electronic applications. Choosing the right contact material depends on balancing durability needs with electrical performance requirements, where cobalt fits rugged, high-current scenarios and gold suits precision, low-current connections. Understanding the operational environment and application-specific stressors is crucial for optimizing contact reliability and longevity.
Infographic: Cobalt vs Gold for Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com