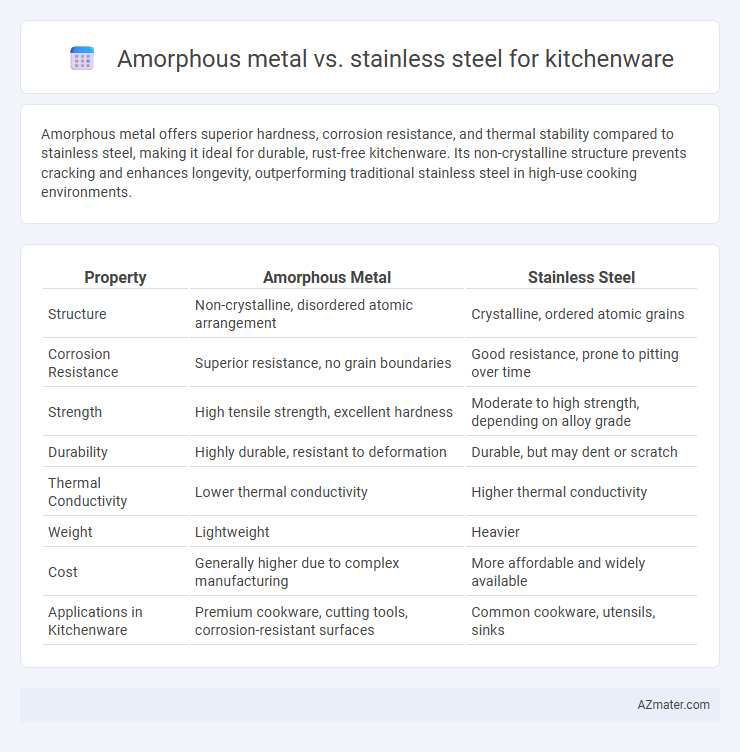
Amorphous metal offers superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability compared to stainless steel, making it ideal for durable, rust-free kitchenware. Its non-crystalline structure prevents cracking and enhances longevity, outperforming traditional stainless steel in high-use cooking environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Amorphous Metal | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Non-crystalline, disordered atomic arrangement | Crystalline, ordered atomic grains |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior resistance, no grain boundaries | Good resistance, prone to pitting over time |
| Strength | High tensile strength, excellent hardness | Moderate to high strength, depending on alloy grade |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to deformation | Durable, but may dent or scratch |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity | Higher thermal conductivity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complex manufacturing | More affordable and widely available |
| Applications in Kitchenware | Premium cookware, cutting tools, corrosion-resistant surfaces | Common cookware, utensils, sinks |
Introduction to Kitchenware Materials
Amorphous metals, also known as metallic glasses, offer superior corrosion resistance and exceptional strength compared to traditional stainless steel, making them a promising material for kitchenware. Stainless steel, widely used due to its durability, heat resistance, and ease of maintenance, remains the industry standard for cookware and utensils. Advances in amorphous metal technology highlight their potential to improve kitchenware longevity and performance by minimizing wear and reducing contamination risk.
What is Amorphous Metal?
Amorphous metal, also known as metallic glass, is a non-crystalline alloy characterized by a disordered atomic structure that enhances its strength and corrosion resistance. Unlike stainless steel, which has a crystalline structure, amorphous metals exhibit superior hardness and resistance to wear, making them ideal for durable kitchenware. The unique properties of amorphous metal result from rapid cooling during manufacturing, preventing the formation of grain boundaries typical in stainless steel.
Stainless Steel: Properties and Uses
Stainless steel is an alloy known for its high corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of maintenance, making it ideal for kitchenware such as pots, pans, and cutlery. Its composition typically includes chromium, which forms a passive layer to prevent rust, and nickel to enhance strength and resistance to acidic foods. Versatile and hygienic, stainless steel withstands high temperatures and frequent washing without degrading, ensuring long-lasting performance in both home and professional kitchens.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Amorphous metal exhibits superior strength due to its non-crystalline atomic structure, making it more resistant to deformation compared to stainless steel. Its enhanced durability arises from higher wear and corrosion resistance, ensuring longer-lasting kitchenware under frequent use. Stainless steel, while strong and corrosion-resistant, typically demonstrates lower hardness and is more prone to surface scratches and dents over time.
Corrosion Resistance: Amorphous Metal vs Stainless Steel
Amorphous metal exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel due to its non-crystalline atomic structure, which eliminates grain boundaries susceptible to corrosion. Unlike stainless steel, which may corrode under prolonged exposure to acidic or salty environments, amorphous metal maintains its integrity and resists pitting and rust effectively. This enhanced durability makes amorphous metal an ideal material for kitchenware exposed to moisture and harsh cleaning agents.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Amorphous metals offer superior design flexibility compared to stainless steel due to their non-crystalline atomic structure, enabling complex shapes and thinner profiles without compromising strength. The smooth, glossy finish of amorphous metals enhances aesthetic appeal with a modern, sleek look that resists fingerprints and scratches better than traditional stainless steel. Stainless steel remains popular for its classic appearance and durability, but it lacks the same level of customization and contemporary design potential offered by amorphous metal.
Maintenance and Longevity
Amorphous metal kitchenware offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains its sleek finish longer than stainless steel, reducing the need for frequent polishing or replacement. Its non-crystalline structure resists wear and pitting more effectively, leading to enhanced durability under rigorous kitchen conditions. Stainless steel, while resilient and easier to repair, often requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and maintain its appearance over time.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Amorphous metals, also known as metallic glasses, exhibit superior corrosion resistance and non-reactivity compared to traditional stainless steel, making them highly safe and compatible for kitchenware applications. Their unique atomic structure prevents leaching of harmful metals into food, ensuring purity and safety during cooking and storage. Stainless steel, while durable, can sometimes release trace amounts of nickel or chromium, which may pose allergic risks or contaminate food under acidic conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Amorphous metal kitchenware offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to stainless steel, reducing waste and resource consumption over time. The production of amorphous metals typically involves fewer energy-intensive processes and lower greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Stainless steel, while recyclable, often requires more intensive mining and smelting activities that contribute to higher environmental degradation and carbon footprint.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Kitchenware
Amorphous metal kitchenware offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability compared to traditional stainless steel, making it ideal for long-lasting cookware. Its non-crystalline structure reduces susceptibility to scratches and staining, ensuring a sleek appearance over time. While stainless steel remains a popular choice for affordability and ease of maintenance, selecting amorphous metal can elevate kitchen performance through improved strength and resistance to wear.
Infographic: Amorphous metal vs Stainless steel for Kitchenware
 azmater.com
azmater.com