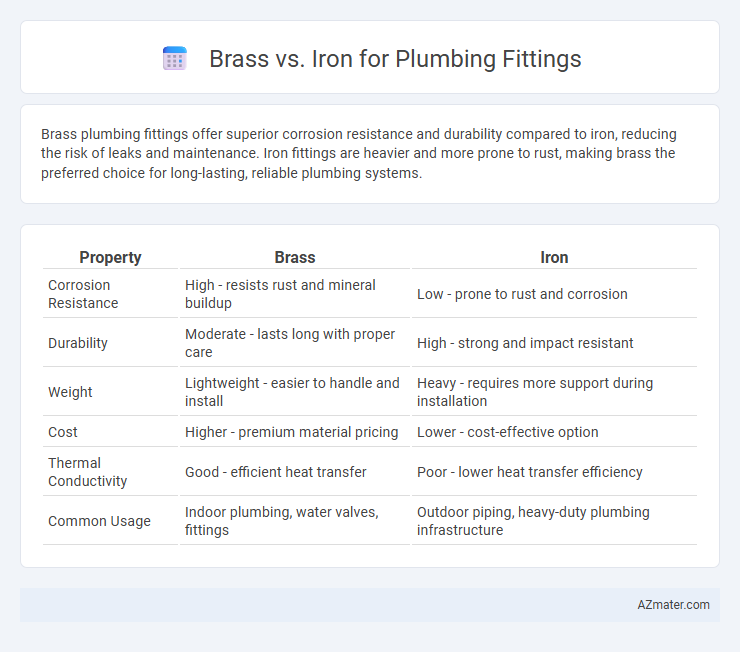
Brass plumbing fittings offer superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to iron, reducing the risk of leaks and maintenance. Iron fittings are heavier and more prone to rust, making brass the preferred choice for long-lasting, reliable plumbing systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brass | Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High - resists rust and mineral buildup | Low - prone to rust and corrosion |
| Durability | Moderate - lasts long with proper care | High - strong and impact resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight - easier to handle and install | Heavy - requires more support during installation |
| Cost | Higher - premium material pricing | Lower - cost-effective option |
| Thermal Conductivity | Good - efficient heat transfer | Poor - lower heat transfer efficiency |
| Common Usage | Indoor plumbing, water valves, fittings | Outdoor piping, heavy-duty plumbing infrastructure |
Introduction to Plumbing Fittings
Brass plumbing fittings offer excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and machinability, making them ideal for water supply lines and HVAC systems. Iron fittings, particularly cast iron, provide high strength and are commonly used in drainage and sewer systems due to their robustness and longevity. Both materials serve distinct purposes in plumbing, with brass preferred for residential water fittings and iron favored for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Material Composition: Brass vs Iron
Brass plumbing fittings consist primarily of copper and zinc, offering excellent corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties ideal for potable water systems. Iron fittings, typically made from cast iron or ductile iron, contain iron with small amounts of carbon and other elements, providing high strength but increased susceptibility to rust without protective coatings. The material composition of brass makes it more durable and resistant to water-induced degradation compared to iron, impacting longevity and maintenance requirements in plumbing applications.
Durability and Longevity Compared
Brass plumbing fittings offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to iron, making them less prone to rust and degradation over time. Iron fittings tend to corrode faster, especially in moist environments, leading to potential leaks and reduced lifespan. The longevity of brass fittings often exceeds 40 years, while iron fittings typically last around 15 to 20 years before requiring replacement.
Corrosion Resistance in Plumbing
Brass plumbing fittings exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to iron, making them ideal for water supply systems where longevity and durability are critical. Brass resists rust and mineral buildup, which helps maintain water quality and reduces maintenance frequency. Iron fittings tend to corrode more quickly, especially in moist environments, leading to leaks and possible contamination over time.
Cost Analysis: Brass versus Iron Fittings
Brass plumbing fittings generally cost more upfront than iron fittings due to their superior corrosion resistance and durability, which reduces long-term maintenance expenses. Iron fittings are cheaper initially but often require more frequent replacements and repairs, increasing overall lifecycle costs. Considering total cost of ownership, brass fittings provide better value for applications exposed to moisture and corrosive environments.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Brass plumbing fittings offer easier installation due to their corrosion resistance and excellent machinability, allowing for tighter seals without cracking or deforming. Iron fittings, while durable, often require additional surface preparation and rust prevention treatments during installation to avoid corrosion over time. Maintenance demands for brass fittings are generally lower since they resist mineral buildup and corrosion, whereas iron fittings need regular inspections and anti-corrosion coatings to prolong their lifespan.
Compatibility with Plumbing Systems
Brass plumbing fittings offer superior compatibility with a wide range of plumbing systems due to their corrosion resistance and ability to handle high temperatures. Iron fittings, while strong and durable, often face challenges with rust and scaling, which can lead to reduced lifespan in water supply lines. Choosing brass endures well in systems with potable water and various pipe materials, ensuring longevity and leak resistance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Brass plumbing fittings offer superior corrosion resistance and contain copper and zinc, which are less likely to leach harmful substances compared to iron fittings that can rust and release iron particles into water supply. Brass's antimicrobial properties help reduce bacterial growth, making it a safer choice for potable water systems, while iron fittings pose risks of rust contamination and potential pipe degradation over time. Considering lead content in some brass alloys is essential, thus opting for lead-free brass fittings ensures compliance with health and safety standards in plumbing applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Brass plumbing fittings offer superior environmental benefits due to their high recyclability and lower energy consumption during recycling compared to iron. Iron fittings, while durable, require more energy to recycle and often contribute to higher carbon emissions throughout their lifecycle. Choosing brass supports sustainable plumbing solutions by reducing waste and promoting efficient material reuse.
Final Recommendations for Plumbing Applications
Brass fittings offer superior corrosion resistance, durability, and machinability, making them ideal for water supply lines and indoor plumbing that requires a long-lasting, leak-resistant solution. Iron fittings, particularly galvanized iron, are better suited for outdoor or heavy-duty applications due to their strength but are prone to rust and corrosion over time, limiting their indoor use. For most residential and commercial plumbing systems, brass is recommended because it ensures reliability, safety, and ease of installation in potable water environments.
Infographic: Brass vs Iron for Plumbing Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com