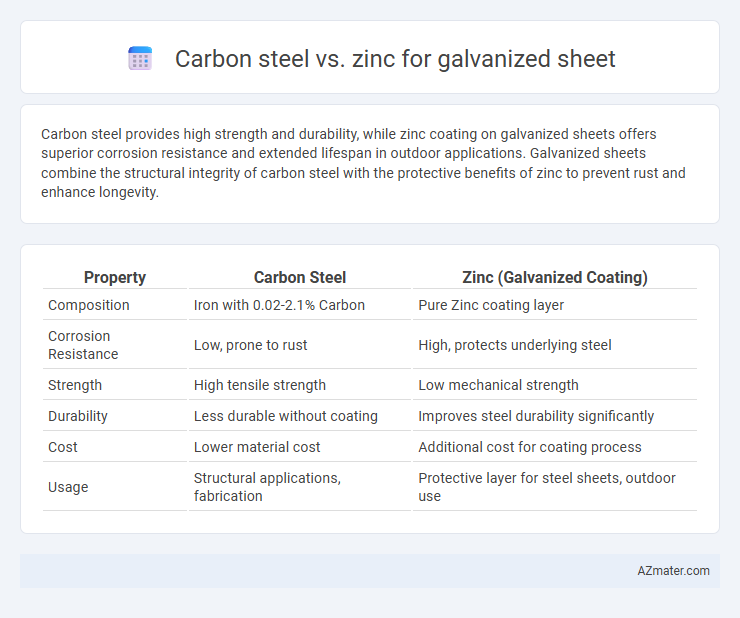
Carbon steel provides high strength and durability, while zinc coating on galvanized sheets offers superior corrosion resistance and extended lifespan in outdoor applications. Galvanized sheets combine the structural integrity of carbon steel with the protective benefits of zinc to prevent rust and enhance longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Zinc (Galvanized Coating) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron with 0.02-2.1% Carbon | Pure Zinc coating layer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, prone to rust | High, protects underlying steel |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Low mechanical strength |
| Durability | Less durable without coating | Improves steel durability significantly |
| Cost | Lower material cost | Additional cost for coating process |
| Usage | Structural applications, fabrication | Protective layer for steel sheets, outdoor use |
Introduction to Galvanized Sheets
Galvanized sheets are primarily composed of carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. The zinc coating acts as a protective barrier, preventing rust formation on the underlying carbon steel by offering sacrificial protection. This combination leverages the strength of carbon steel with the antioxidative properties of zinc, making galvanized sheets ideal for construction, automotive, and industrial applications.
Overview of Carbon Steel
Carbon steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, provides high tensile strength and durability, making it an ideal substrate for galvanized sheets. Its microstructure allows excellent adhesion of zinc coatings, which enhances corrosion resistance and extends the material's lifespan in harsh environments. The affordability and versatile mechanical properties of carbon steel make it a preferred choice in construction, automotive, and industrial applications when combined with zinc galvanization.
Overview of Zinc Coating
The zinc coating on galvanized steel sheets serves as a protective barrier that prevents corrosion by sacrificially oxidizing before the underlying carbon steel can rust. This galvanic protection extends the lifespan of steel in outdoor or humid environments, making zinc an essential element in corrosion resistance. Thickness of the zinc layer, measured in microns or grams per square meter, determines the durability and effectiveness of the protective coating.
Galvanization Process Explained
Galvanization involves coating carbon steel sheets with a layer of zinc to protect against corrosion, enhancing durability and extending lifespan in harsh environments. The process typically uses hot-dip galvanizing, where carbon steel is immersed in molten zinc, forming a metallurgical bond that provides superior adhesion and rust resistance. Zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, preventing oxidation of the underlying steel even if the coating is scratched or damaged.
Corrosion Resistance: Carbon Steel vs Zinc
Carbon steel serves as the base metal in galvanized sheets, providing strength but is prone to corrosion without protective coating. Zinc acts as a sacrificial anode in galvanized steel, effectively preventing rust by forming a protective barrier against moisture and environmental elements. The corrosion resistance of galvanized sheets is primarily attributed to zinc's ability to corrode preferentially, thereby preserving the underlying carbon steel.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Carbon steel galvanized sheets exhibit high tensile strength and excellent hardness, making them suitable for load-bearing and structural applications. Zinc coatings provide corrosion resistance but have lower mechanical strength compared to the steel substrate, which primarily determines the sheet's durability and rigidity. Tensile strength of carbon steel ranges from 400 to 550 MPa, whereas the zinc layer enhances lifespan without compromising the steel's mechanical integrity.
Durability and Longevity
Carbon steel galvanized sheets offer superior durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to mechanical damage, making them ideal for structural applications. Zinc coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance by forming a protective barrier that extends the lifespan of the steel, preventing rust and degradation over time. The combination of carbon steel's robustness and zinc's protective properties ensures galvanized sheets maintain longevity in harsh environments, often lasting 50 years or more with proper maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Steel vs Galvanized Zinc
Carbon steel sheets generally have a lower initial cost compared to galvanized zinc sheets, making them a budget-friendly option for short-term projects. However, the higher durability and corrosion resistance of galvanized zinc sheets can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time, leading to greater long-term cost savings. When evaluating overall value, the choice depends on project lifespan, environmental exposure, and maintenance budgets.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Carbon steel galvanized sheets are widely used in construction, automotive parts, and household appliances due to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Zinc-coated galvanized sheets excel in corrosion resistance, making them ideal for outdoor roofing, fencing, and marine environments where exposure to moisture and harsh weather conditions is prevalent. Both materials provide protective coatings, but carbon steel is favored for structural applications requiring higher tensile strength, while pure zinc coatings offer superior protection against rust in highly corrosive settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel used in galvanized sheets offers high strength and durability but involves significant carbon emissions during production, contributing to environmental concerns. Zinc coating enhances corrosion resistance, extending the steel's lifespan and reducing the need for frequent replacements, which supports sustainability by minimizing resource consumption. Although zinc extraction has its environmental footprint, the overall lifecycle impact of galvanized steel is lower due to improved longevity and recyclability of both materials.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Zinc for Galvanized sheet
 azmater.com
azmater.com