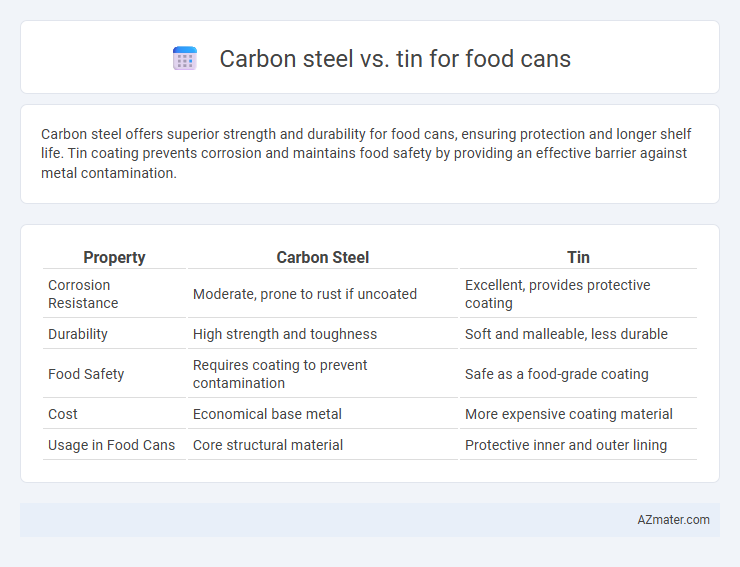
Carbon steel offers superior strength and durability for food cans, ensuring protection and longer shelf life. Tin coating prevents corrosion and maintains food safety by providing an effective barrier against metal contamination.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, prone to rust if uncoated | Excellent, provides protective coating |
| Durability | High strength and toughness | Soft and malleable, less durable |
| Food Safety | Requires coating to prevent contamination | Safe as a food-grade coating |
| Cost | Economical base metal | More expensive coating material |
| Usage in Food Cans | Core structural material | Protective inner and outer lining |
Introduction to Food Can Materials
Carbon steel and tin are primary materials used in food can manufacturing, each offering distinct advantages for food preservation. Carbon steel provides strength and durability, making cans resistant to deformation during transport and storage. Tin coatings prevent corrosion and extend shelf life by creating a protective barrier against acidic or moisture-rich foods.
Overview of Carbon Steel and Tin
Carbon steel is a strong and durable alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, widely used for food cans due to its excellent rigidity and resistance to mechanical damage. Tin, a soft and malleable metal, is commonly applied as a protective coating on carbon steel cans to prevent corrosion and maintain food safety by providing a non-toxic barrier. The combination of carbon steel's structural integrity and tin's corrosion resistance ensures optimal preservation and packaging in the food industry.
Manufacturing Process of Carbon Steel Cans
The manufacturing process of carbon steel cans for food involves cold rolling steel sheets into thin plates, followed by forming, welding, and trimming to shape the can body and ends. These cans often undergo coating with a protective lacquer or enamel inside to prevent corrosion and contamination from the acidic food contents. Carbon steel's strength and formability make it ideal for high-speed fabrication, ensuring durability and airtight sealing essential for food preservation.
Properties and Benefits of Tin Cans
Tin cans offer excellent corrosion resistance due to their protective tin coating, preventing food contamination and extending shelf life compared to carbon steel cans, which are more prone to rust. The tin coating provides a non-reactive barrier, preserving the flavor and nutritional quality of canned food. Tin cans are also highly durable, lightweight, and easy to seal, making them ideal for long-term food storage and transportation.
Corrosion Resistance: Carbon Steel vs Tin
Carbon steel offers limited corrosion resistance in food cans due to its susceptibility to rust when exposed to moisture and acidic foods. Tin, used as a coating on carbon steel cans, significantly enhances corrosion resistance by providing a protective barrier that prevents direct contact with the metal. The tin coating maintains food safety and shelf life by minimizing metal contamination and preserving the can's structural integrity against acidic or salty contents.
Food Safety and Chemical Reactivity
Carbon steel cans offer strong structural integrity but require protective coatings to prevent corrosion and chemical reactions with acidic foods, which can compromise food safety. Tin, used primarily as a coating for steel cans, provides excellent corrosion resistance and is non-reactive with most food types, ensuring preservation of food quality and safety. The combination of tin coating over carbon steel creates an effective barrier that minimizes metal leaching and helps maintain the food's original flavor and nutritional value.
Durability and Shelf Life Comparison
Carbon steel cans offer superior durability due to their robust metal structure, providing enhanced resistance to dents and deformation during transportation and storage. Tin cans, often used as a coating on carbon steel, prevent corrosion and extend the shelf life of food products by creating an effective barrier against moisture and oxygen. The combined use of carbon steel with a tin layer results in food cans that maintain product freshness over extended periods, outperforming alternatives lacking this protective coating.
Cost Efficiency: Steel Cans vs Tin Cans
Carbon steel cans offer superior cost efficiency compared to tin cans due to their lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making them a popular choice for large-scale food packaging. The reduced production costs of carbon steel enable manufacturers to achieve economies of scale, resulting in more affordable pricing without compromising durability or shelf life. Tin cans, while providing excellent corrosion resistance, come with higher material costs that often limit their use to specialized or premium food products.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Carbon steel food cans have a higher environmental impact due to their energy-intensive production and potential for rust, while tin-plated steel cans offer enhanced corrosion resistance, extending shelf life and reducing food waste. Both materials are recyclable, but carbon steel's magnetic properties facilitate efficient recycling processes, contributing to a circular economy. Tin plating adds a minimal environmental footprint and does not hinder recyclability, making tin-coated cans a sustainable choice for food packaging.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Material for Food Cans
Carbon steel offers superior strength and durability for food cans, making it ideal for preserving a wide variety of foods under high pressure and extended shelf life conditions. Tin provides excellent corrosion resistance and a non-toxic coating, ensuring food safety and preventing metallic taste contamination. Choosing the best material depends on the specific food type, storage requirements, and cost considerations, with carbon steel preferred for heavy-duty applications and tin favored for enhanced food safety and flavor preservation.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Tin for Food can
 azmater.com
azmater.com