Carbon steel offers higher tensile strength and durability but lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, making copper the preferred choice for electrical wiring due to its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. Copper's excellent electrical properties ensure efficient power transmission and reduced energy loss in electrical systems.
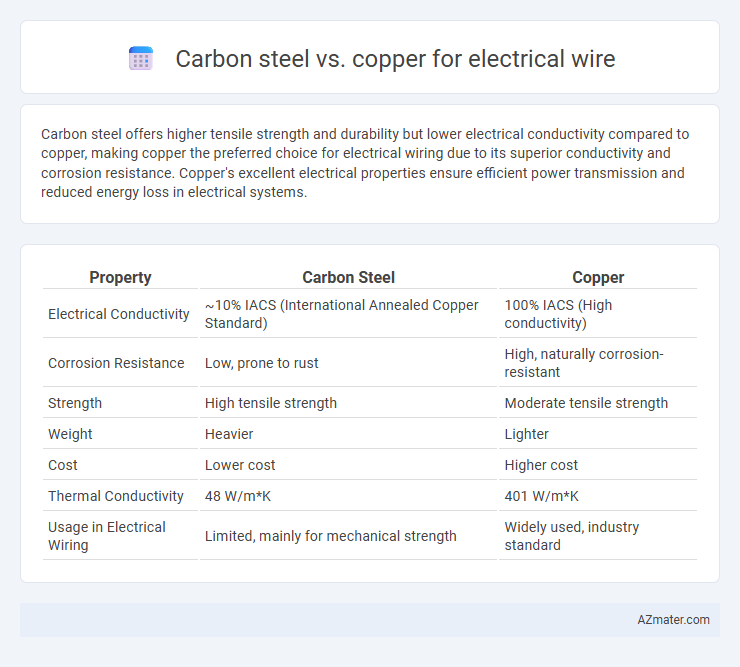
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~10% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) | 100% IACS (High conductivity) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, prone to rust | High, naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Thermal Conductivity | 48 W/m*K | 401 W/m*K |
| Usage in Electrical Wiring | Limited, mainly for mechanical strength | Widely used, industry standard |
Introduction to Electrical Wire Materials
Carbon steel and copper are two prevalent materials used in electrical wiring, each offering distinct electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and flexibility, making it the preferred choice for residential and commercial wiring. Carbon steel, while less conductive, provides enhanced tensile strength and durability, suitable for specific applications where mechanical robustness is prioritized over electrical performance.
Key Properties of Carbon Steel Wires
Carbon steel wires exhibit high tensile strength and durability, making them suitable for applications requiring mechanical endurance and resistance to wear. They have lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, with conductivity approximately 20% that of copper, which limits their efficiency in electrical transmission but allows for greater structural support in overhead power lines. Carbon steel's magnetic properties and cost-effectiveness contribute to its extensive use in reinforced electrical cabling and grounding systems where mechanical robustness is prioritized over conductivity.
Key Properties of Copper Wires
Copper wires exhibit excellent electrical conductivity, typically around 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making them highly efficient for electrical transmission compared to carbon steel, which has significantly lower conductivity. Copper's superior ductility and corrosion resistance enhance durability and ease of installation in electrical systems. Its thermal conductivity also aids in heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating in wiring applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity, approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, compared to carbon steel, which has conductivity around 1.45 x 10^7 S/m, making copper the preferred choice for efficient electrical wiring. The superior conductivity of copper reduces energy loss and heat generation in electrical systems, enhancing overall performance and longevity. Carbon steel, with its lower conductivity, is less efficient but may be selected for applications requiring greater mechanical strength or cost considerations.
Mechanical Strength: Carbon Steel vs Copper
Carbon steel exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to copper, making it more resistant to physical damage and deformation under stress, which is critical in applications requiring durability and structural support. Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity but has lower tensile strength and is more prone to stretching or breaking under mechanical load. Therefore, carbon steel is often preferred for reinforcing and protective applications in electrical wiring systems where mechanical robustness is essential.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Copper offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel, maintaining conductivity and structural integrity over extended periods, especially in humid or corrosive environments. Carbon steel, while typically more affordable, is prone to rust and degradation unless coated or galvanized, which can increase maintenance requirements and reduce overall durability. For electrical wiring applications that demand long-term reliability and minimal signal loss, copper is generally preferred due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical durability.
Cost and Availability
Carbon steel electrical wires are generally more affordable and widely available compared to copper, making them a cost-effective choice for large-scale or budget-conscious projects. Copper wires offer superior conductivity but come at a significantly higher price due to limited supply and increased demand in electrical and industrial applications. Availability of carbon steel is more consistent globally, while copper prices fluctuate with market trends, impacting overall project costs.
Application Suitability and Industry Use
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance electrical wiring in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Carbon steel, with lower conductivity and higher tensile strength, is primarily used for structural support in cable armoring or grounding systems rather than main electrical conductors. The electrical industry predominantly favors copper wiring for efficient energy transmission, while carbon steel's role remains limited to protective and mechanical functions.
Safety Considerations and Standards
Copper electrical wire is preferred over carbon steel due to its superior conductivity and resistance to corrosion, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical fires. Safety standards such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) emphasize copper wire for residential and commercial wiring because it maintains stable performance under high loads and adverse conditions. Carbon steel wire, while stronger mechanically, is prone to oxidation and increased resistance, which can lead to unsafe heat buildup and potential code violations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it the preferred choice for most electrical wiring applications. Carbon steel offers greater mechanical strength and lower cost but falls short in conductivity and is prone to rust, limiting its use to specific structural or protective roles in wiring systems. Selecting the right material depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, and environmental factors for optimal electrical efficiency and durability.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Copper for Electrical wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com