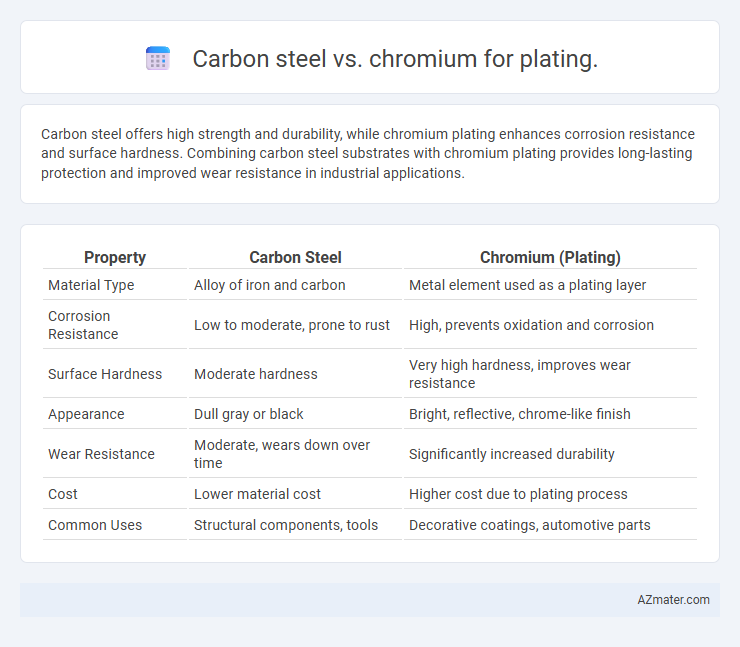
Carbon steel offers high strength and durability, while chromium plating enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness. Combining carbon steel substrates with chromium plating provides long-lasting protection and improved wear resistance in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Steel | Chromium (Plating) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alloy of iron and carbon | Metal element used as a plating layer |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to moderate, prone to rust | High, prevents oxidation and corrosion |
| Surface Hardness | Moderate hardness | Very high hardness, improves wear resistance |
| Appearance | Dull gray or black | Bright, reflective, chrome-like finish |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate, wears down over time | Significantly increased durability |
| Cost | Lower material cost | Higher cost due to plating process |
| Common Uses | Structural components, tools | Decorative coatings, automotive parts |
Introduction to Plating Materials
Carbon steel offers strength and durability but requires protective plating to enhance corrosion resistance and surface hardness. Chromium plating is widely used for its excellent wear resistance, corrosion protection, and distinctive bright finish on various substrates, including carbon steel. The choice between carbon steel and chromium plating depends on the application demands, balancing mechanical properties with surface protection requirements.
What Is Carbon Steel Plating?
Carbon steel plating involves applying a protective or decorative layer over carbon steel, enhancing its corrosion resistance and surface hardness. This process typically uses chromium or other metals to create a durable coating that improves wear resistance and longevity. Compared to chromium plating on other substrates, carbon steel plating requires precise surface preparation to ensure optimal adhesion and performance.
What Is Chromium Plating?
Chromium plating is a process that deposits a thin layer of chromium onto a metal, such as carbon steel, to enhance surface properties like corrosion resistance, hardness, and aesthetic appeal. Unlike carbon steel, which is prone to oxidation and wear, chromium-plated surfaces exhibit superior durability and a reflective finish. This plating technique is widely used in automotive, industrial, and decorative applications to extend the lifespan and improve the performance of steel components.
Key Differences: Carbon Steel vs Chromium
Carbon steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, known for its strength and affordability but prone to rust and corrosion without protective coatings. Chromium plating provides a durable, corrosion-resistant surface with enhanced hardness and a reflective finish, significantly extending the lifespan of the underlying carbon steel. The key differences lie in carbon steel's structural role versus chromium's function as a protective and aesthetic coating to improve performance and longevity.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Carbon steel plated with chromium exhibits enhanced corrosion resistance due to the protective chromium layer that prevents rust and oxidation. Chromium plating significantly improves the surface hardness and durability of carbon steel, extending the lifespan of mechanical parts and tools. However, the overall corrosion resistance depends on the thickness and quality of the chromium coating, as damage to the plating can expose the underlying carbon steel to corrosive elements.
Aesthetic and Finish Comparison
Carbon steel plating offers a rugged, matte finish with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for industrial and utilitarian aesthetics. Chromium plating provides a high-gloss, mirror-like surface that enhances visual appeal and reflects light for a sleek, polished look. The superior hardness and anti-tarnish properties of chromium plating contribute to a durable, long-lasting decorative finish compared to the more functional appearance of carbon steel.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Steel vs Chromium Plating
Carbon steel offers a lower initial material cost compared to chromium plating, making it an economical choice for applications with budget constraints. Chromium plating significantly increases upfront expenses due to the specialized coating process, but it provides enhanced corrosion resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses reveals that while carbon steel may save money initially, chromium plating can deliver better value in environments requiring extended wear protection.
Common Applications and Industries
Carbon steel plating is widely used in automotive parts, construction tools, and heavy machinery due to its strength and cost-effectiveness, while chromium plating is favored in aerospace, electronics, and decorative hardware for its superior corrosion resistance and hardness. Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and oil and gas rely on carbon steel plating for durability under heavy loads, whereas chromium plating is preferred in precision instruments and consumer goods where wear resistance and aesthetic appeal are critical. Both materials serve critical roles across diverse sectors, optimizing performance based on environmental conditions and mechanical demands.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Carbon steel plating often involves fewer toxic chemicals and presents lower environmental risks compared to chromium plating, which uses hexavalent chromium--a known carcinogen harmful to both ecosystems and human health. Chromium plating requires stringent safety measures and waste management protocols to mitigate its significant hazardous waste byproducts and air emissions. Choosing carbon steel with eco-friendly coatings can reduce toxic waste and occupational hazards, promoting safer manufacturing and environmental sustainability.
Choosing the Right Plating for Your Needs
Choosing the right plating depends on the performance requirements and environmental conditions; carbon steel offers strength and affordability but lacks corrosion resistance, making chromium plating ideal for adding hardness and a protective, corrosion-resistant layer. Chromium plating enhances wear resistance and provides a bright, attractive finish suitable for automotive, industrial, and decorative applications. Evaluate factors like exposure to moisture, abrasion, and desired aesthetics to determine whether carbon steel with chromium plating or an alternative corrosion-resistant coating best fits your needs.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Chromium for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com