Carbon steel offers superior strength and impact resistance for automotive body panels, enhancing vehicle safety and durability. Aluminum provides lightweight benefits, improving fuel efficiency and corrosion resistance while potentially increasing manufacturing costs.
Table of Comparison
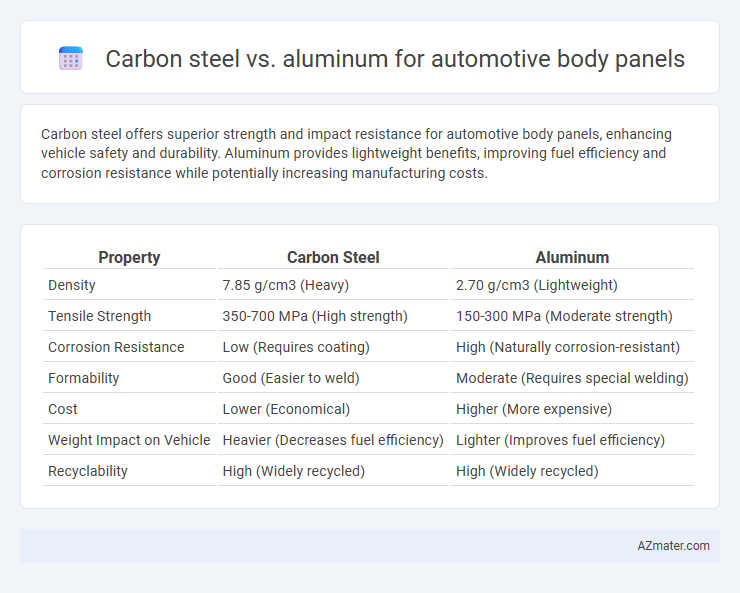
| Property | Carbon Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.85 g/cm3 (Heavy) | 2.70 g/cm3 (Lightweight) |
| Tensile Strength | 350-700 MPa (High strength) | 150-300 MPa (Moderate strength) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low (Requires coating) | High (Naturally corrosion-resistant) |
| Formability | Good (Easier to weld) | Moderate (Requires special welding) |
| Cost | Lower (Economical) | Higher (More expensive) |
| Weight Impact on Vehicle | Heavier (Decreases fuel efficiency) | Lighter (Improves fuel efficiency) |
| Recyclability | High (Widely recycled) | High (Widely recycled) |
Introduction to Carbon Steel and Aluminum in Automotive Body Panels
Carbon steel is widely used in automotive body panels for its high strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, offering excellent impact resistance and formability during manufacturing. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties, which significantly improve fuel efficiency and reduce vehicle emissions, while maintaining good corrosion resistance and sufficient structural integrity. The choice between carbon steel and aluminum hinges on balancing performance, cost, and weight considerations in automotive design.
Material Properties: Carbon Steel vs Aluminum
Carbon steel offers higher tensile strength and excellent durability, making it ideal for impact resistance in automotive body panels. Aluminum provides a better strength-to-weight ratio and superior corrosion resistance, resulting in lighter vehicles with improved fuel efficiency. The thermal conductivity of aluminum also enhances heat dissipation compared to carbon steel, influencing overall vehicle performance.
Weight Differences and Impact on Fuel Efficiency
Carbon steel automotive body panels typically weigh significantly more than aluminum counterparts, with aluminum offering up to 40% weight reduction. The lower weight of aluminum panels directly contributes to improved fuel efficiency by reducing overall vehicle mass, allowing engines to expend less energy during acceleration and cruising. This weight advantage not only enhances fuel economy but also supports stricter emissions regulations by lowering CO2 output.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon steel offers superior strength and durability compared to aluminum, making it more resistant to dents and impacts in automotive body panels. While aluminum provides lighter weight for improved fuel efficiency, its lower tensile strength often necessitates thicker gauge sheets to match carbon steel's robustness. The enhanced fatigue resistance of carbon steel contributes to longer-lasting body panels under repeated stress and environmental exposure.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel due to its natural oxide layer that prevents rust formation, making it more durable in harsh weather conditions. Carbon steel, while strong and cost-effective, requires protective coatings like paint or galvanization to combat oxidation and prolong its lifespan. In automotive body panels, aluminum's inherent resistance contributes to longer-lasting durability and reduced maintenance costs over time.
Manufacturing and Formability Considerations
Carbon steel offers superior strength and cost-effectiveness in automotive body panel manufacturing, enabling robust structural integrity and ease of welding during mass production. Aluminum, with its lower density, provides excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight advantages, but requires specialized forming techniques such as hydroforming or high-pressure stamping due to its lower ductility and higher springback. Manufacturers must balance the trade-offs between carbon steel's ease of formability and aluminum's weight reduction benefits to optimize production efficiency and vehicle performance.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Steel vs Aluminum Panels
Carbon steel panels generally offer a lower initial material cost compared to aluminum, making them more economically viable for mass production in automotive body panels. Aluminum panels incur higher raw material and manufacturing expenses due to complex alloy compositions and specialized forming techniques, which increase overall production costs. Despite the higher price, aluminum's weight reduction benefits contribute to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions, potentially offsetting initial costs over the vehicle's lifecycle.
Repairability and Maintenance Issues
Carbon steel offers superior repairability for automotive body panels due to its excellent weldability and compatibility with traditional auto body repair techniques, making it easier to restore after damage. Aluminum panels, while lightweight and corrosion-resistant, present challenges in maintenance because of their specialized repair requirements, such as the need for specific welding equipment and techniques to prevent warping or weakening. Repair shops often face higher labor costs and longer repair times with aluminum, impacting overall maintenance efficiency compared to carbon steel.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon steel automotive body panels have a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive mining and smelting processes, but their durability and recyclability contribute to long-term sustainability. Aluminum panels offer significant weight reduction, improving fuel efficiency and lowering emissions over the vehicle's lifetime, yet aluminum production involves considerable energy consumption and environmental impact. Both materials demonstrate recyclability; however, advances in recycling technologies for aluminum enhance its circular economy potential over carbon steel.
Choosing the Right Material for Automotive Body Panels
Carbon steel offers superior strength and durability for automotive body panels, providing enhanced crash resistance and structural integrity. Aluminum panels are significantly lighter, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle weight, but may require additional corrosion protection. Selecting the right material depends on balancing weight reduction goals with performance requirements and cost considerations in automotive design.
Infographic: Carbon steel vs Aluminum for Automotive body panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com