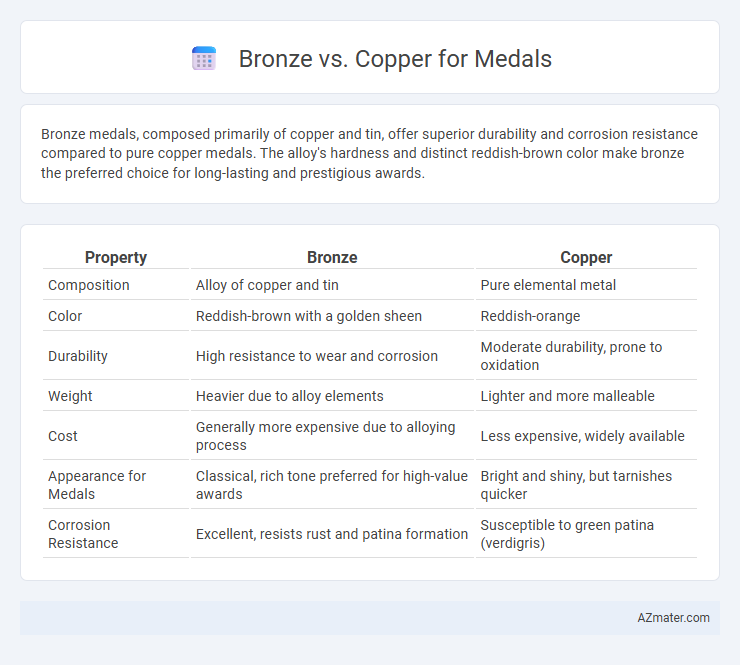
Bronze medals, composed primarily of copper and tin, offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to pure copper medals. The alloy's hardness and distinct reddish-brown color make bronze the preferred choice for long-lasting and prestigious awards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alloy of copper and tin | Pure elemental metal |
| Color | Reddish-brown with a golden sheen | Reddish-orange |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and corrosion | Moderate durability, prone to oxidation |
| Weight | Heavier due to alloy elements | Lighter and more malleable |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to alloying process | Less expensive, widely available |
| Appearance for Medals | Classical, rich tone preferred for high-value awards | Bright and shiny, but tarnishes quicker |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists rust and patina formation | Susceptible to green patina (verdigris) |
Introduction to Medal Materials
Bronze and copper are two primary materials used in medal production, each offering distinct properties and historical significance. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, provides enhanced durability and a rich, warm color that resists corrosion, making it a popular choice for lasting commemorative medals. Copper, prized for its bright reddish hue and malleability, is often used in medals where crafting fine details and a lightweight design are essential.
Historical Use of Bronze and Copper in Medals
Bronze has been historically preferred for medals due to its durability and appealing golden-brown patina, commonly used since ancient civilizations such as Greece and Rome to signify achievement and honor. Copper, while softer and more prone to corrosion, was often alloyed with tin or other metals to create bronze, enhancing strength and longevity in award tokens. The evolution from pure copper to bronze in medals reflects technological advancements and the desire for more resilient commemorative items.
Composition and Properties: Bronze vs Copper
Bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, offers greater hardness and durability compared to pure copper, which is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and malleability. The addition of tin in bronze enhances corrosion resistance and strength, making bronze medals more resistant to wear and environmental factors, while copper medals maintain a distinctive reddish appearance but may tarnish more easily. These compositional differences result in bronze being preferred for medals requiring longevity and toughness, whereas copper medals are valued for their aesthetic coppery luster.
Aesthetic Differences: Color and Finish
Bronze medals display a warm, rich reddish-brown hue due to their copper-tin alloy composition, often featuring a matte or slightly textured finish that enhances depth and character. Copper medals exhibit a brighter, more vibrant orange-red color with a naturally glossy surface that can develop a distinctive greenish patina over time. The contrasting tones and finish treatments between bronze and copper significantly influence their visual appeal and perceived prestige in medal design.
Durability and Longevity of Bronze Medals vs Copper Medals
Bronze medals, composed primarily of copper with tin and other elements, exhibit superior durability and resistance to corrosion compared to pure copper medals. The alloy structure of bronze enhances hardness and longevity, making bronze medals less prone to wear, tarnish, and deformation over time. Copper medals, while aesthetically appealing, tend to oxidize faster and are softer, resulting in reduced lifespan and increased susceptibility to damage.
Cost Comparison: Bronze vs Copper Medals
Bronze medals typically consist of a combination of copper and tin, making them more durable and slightly more expensive than pure copper medals. Copper medals, made from nearly 100% copper, are generally less costly due to lower material and manufacturing expenses but lack the hardness and corrosion resistance found in bronze. Cost comparisons show bronze medals incur higher production costs, yet their enhanced quality and longevity often justify the price difference.
Symbolic Significance in Awarding Medals
Bronze medals symbolize achievement and perseverance, often awarded for third place as a recognition of notable accomplishment despite challenges. Copper, while historically significant as a metal of early currency and ornamental use, lacks the established symbolic tradition in competitive awards that bronze holds. The enduring use of bronze in medals conveys tradition, durability, and honor, reinforcing its symbolic value in recognizing merit and effort in competitions.
Manufacturing Process: Bronze Medals vs Copper Medals
Bronze medals are typically manufactured using an alloy of copper and tin, which involves casting molten metal into molds followed by cooling and polishing to achieve a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish. Copper medals, made from nearly pure copper, undergo processes such as casting or stamping, often requiring additional treatments like annealing and polishing to enhance malleability and surface shine. The alloy composition in bronze offers greater hardness and wear resistance, making bronze medals more suitable for long-term preservation compared to softer, more oxidizable copper medals.
Maintenance and Preservation Tips
Bronze medals, composed mainly of copper with tin, require careful cleaning to prevent tarnish and corrosion, best maintained with mild soap and water followed by drying with a soft cloth. Copper medals tend to oxidize and develop a green patina called verdigris over time, needing gentle polishing with a copper-specific cleaner to preserve their shine without damaging the metal. Storing both bronze and copper medals in low-humidity, airtight containers with anti-tarnish strips helps prolong their appearance and prevent environmental damage.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Medal
Bronze offers superior durability and a rich, warm hue, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting medals that symbolize achievement. Copper provides a more vibrant red tone and excellent malleability, ideal for intricate designs and artistic customization. Selecting the right metal for your medal depends on balancing aesthetic appeal, longevity, and the intended commemorative value.
Infographic: Bronze vs Copper for Medal
 azmater.com
azmater.com