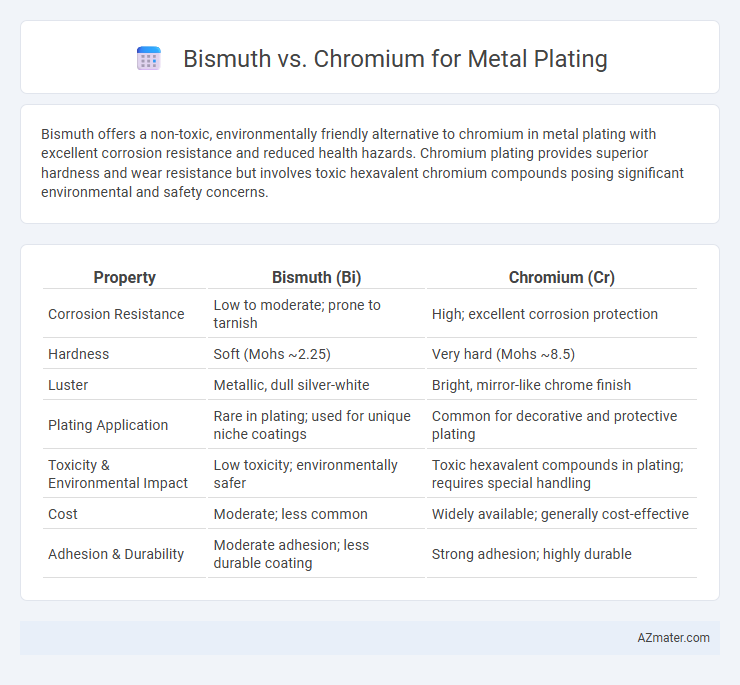
Bismuth offers a non-toxic, environmentally friendly alternative to chromium in metal plating with excellent corrosion resistance and reduced health hazards. Chromium plating provides superior hardness and wear resistance but involves toxic hexavalent chromium compounds posing significant environmental and safety concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth (Bi) | Chromium (Cr) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to moderate; prone to tarnish | High; excellent corrosion protection |
| Hardness | Soft (Mohs ~2.25) | Very hard (Mohs ~8.5) |
| Luster | Metallic, dull silver-white | Bright, mirror-like chrome finish |
| Plating Application | Rare in plating; used for unique niche coatings | Common for decorative and protective plating |
| Toxicity & Environmental Impact | Low toxicity; environmentally safer | Toxic hexavalent compounds in plating; requires special handling |
| Cost | Moderate; less common | Widely available; generally cost-effective |
| Adhesion & Durability | Moderate adhesion; less durable coating | Strong adhesion; highly durable |
Overview of Metal Plating Processes
Bismuth and chromium are both used in metal plating, but chromium plating is more common due to its exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Bismuth plating, though less conventional, offers a non-toxic, environmentally friendly alternative with good lubricity and anti-friction properties, often used in electronics and specialized coatings. The plating process for chromium typically involves hexavalent or trivalent chromium baths requiring strict environmental controls, whereas bismuth plating uses safer, low-toxicity solutions with simpler waste management requirements.
Introduction to Bismuth Plating
Bismuth plating offers a non-toxic, eco-friendly alternative to traditional chromium plating, commonly used for corrosion resistance and decorative finishes. Its unique properties include excellent electrical conductivity, low toxicity, and a bright, smooth surface that enhances wear resistance without the hazardous effects associated with hexavalent chromium. Bismuth plating is gaining popularity in industries seeking sustainable metal finishing solutions while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal.
Introduction to Chromium Plating
Chromium plating is a popular metal finishing process known for its exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, commonly used in automotive, industrial, and decorative applications. Compared to bismuth plating, chromium offers superior wear resistance and a more durable, reflective surface ideal for high-stress environments. While bismuth plating provides a non-toxic alternative with good lubricity, chromium plating remains the industry standard for protective and ornamental coatings due to its longevity and mechanical strength.
Chemical Properties: Bismuth vs Chromium
Bismuth exhibits low toxicity and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a safer and environmentally friendly option for metal plating compared to chromium, which is known for its high hardness and wear resistance but poses significant health and environmental hazards due to hexavalent chromium compounds. Chemically, bismuth has a relatively low melting point of 271degC and forms stable oxide layers that protect against corrosion, whereas chromium has a higher melting point of 1907degC and readily forms a thin, passivating chromium oxide film that enhances durability and resistance to oxidation. The unique chemical inertness of bismuth provides a non-toxic plating alternative, whereas chromium plating remains favored in applications requiring superior hardness and abrasion resistance despite its environmental concerns.
Plating Performance and Durability Comparison
Bismuth plating offers superior corrosion resistance and non-toxicity compared to chromium, making it ideal for environmentally sensitive applications and electronics. Chromium plating excels in hardness and wear resistance, providing longer-lasting protection in high-friction environments and decorative finishes. While bismuth coatings excel in non-conductive and anti-microbial properties, chromium remains the preferred choice for industrial durability and aesthetic luster in metal plating.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Bismuth offers significantly lower toxicity and environmental impact compared to hexavalent chromium, which is highly carcinogenic and poses severe risks to workers and ecosystems. Chromium plating processes generate hazardous waste requiring strict regulation and costly disposal, while bismuth plating produces less harmful byproducts and presents safer alternatives for industrial applications. Selecting bismuth over chromium enhances workplace safety and promotes sustainable manufacturing practices by minimizing exposure to toxic substances and reducing environmental pollution.
Cost Analysis: Bismuth vs Chromium
Bismuth plating offers a cost-effective alternative to chromium plating due to lower material costs and reduced environmental compliance expenses, as bismuth is less toxic and easier to handle. Chromium plating involves higher operational costs stemming from stringent regulatory requirements and hazardous waste disposal associated with hexavalent chromium. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, bismuth plating provides significant savings in processing, handling, and ecological impact compared to the traditional chromium method.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Bismuth plating is favored in the electronics and pharmaceutical industries due to its non-toxic nature, excellent corrosion resistance, and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for biomedical devices and environmentally sensitive applications. Chromium plating is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors for its superior hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal, providing durable, mirror-like finishes on engine components, tools, and decorative surfaces. Both metals serve critical roles in metal plating, with bismuth chosen for eco-friendly and specialized coatings, while chromium dominates where high durability and surface toughness are paramount.
Recent Advances in Plating Technologies
Recent advances in metal plating technologies highlight bismuth as an eco-friendly alternative to chromium, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and reduced toxicity. Innovations in bismuth plating processes have improved electrodeposition techniques, achieving uniform coatings with superior hardness and wear resistance compared to traditional hexavalent chromium plating. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing bath chemistry and pulse plating methods to increase the efficiency and environmental safety of bismuth-based coatings in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Metal for Plating Needs
Bismuth offers superior environmental benefits and non-toxic properties compared to chromium, making it an excellent choice for eco-friendly metal plating applications. Chromium plating provides exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, widely used in automotive and industrial components requiring durability. Selecting between bismuth and chromium depends on the plating's functional requirements, regulatory compliance, and desired appearance, with bismuth favored for sustainable solutions and chromium for high-performance finishes.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Chromium for Metal plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com