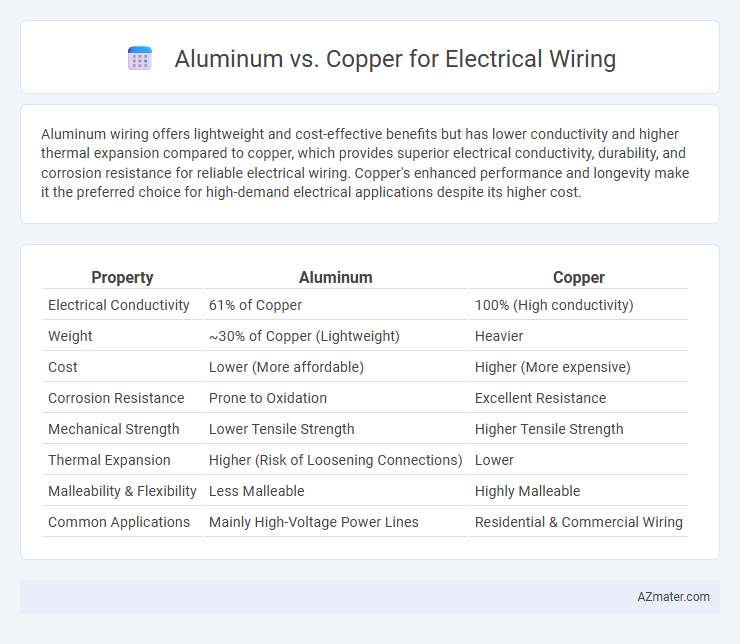
Aluminum wiring offers lightweight and cost-effective benefits but has lower conductivity and higher thermal expansion compared to copper, which provides superior electrical conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance for reliable electrical wiring. Copper's enhanced performance and longevity make it the preferred choice for high-demand electrical applications despite its higher cost.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 61% of Copper | 100% (High conductivity) |
| Weight | ~30% of Copper (Lightweight) | Heavier |
| Cost | Lower (More affordable) | Higher (More expensive) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prone to Oxidation | Excellent Resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower Tensile Strength | Higher Tensile Strength |
| Thermal Expansion | Higher (Risk of Loosening Connections) | Lower |
| Malleability & Flexibility | Less Malleable | Highly Malleable |
| Common Applications | Mainly High-Voltage Power Lines | Residential & Commercial Wiring |
Introduction to Aluminum and Copper Wiring
Aluminum wiring, known for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness, has been widely used in electrical systems since the 1960s, particularly in residential and commercial applications. Copper wiring offers superior electrical conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it a preferred choice for most critical and high-performance electrical installations. Understanding the distinct properties of aluminum and copper wiring helps optimize safety, efficiency, and longevity in electrical networks.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity at approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it a preferred choice for electrical wiring due to lower resistance and improved efficiency. Aluminum's conductivity is about 3.5 x 10^7 S/m, roughly 61% that of copper, necessitating larger gauge wires to carry the same current safely. While aluminum offers weight and cost advantages, copper's higher conductivity ensures better performance and reliability in electrical systems.
Cost Differences: Aluminum vs Copper
Aluminum wiring typically costs 30-50% less per foot compared to copper, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale electrical projects. Despite its lower initial price, aluminum requires larger gauge wires to carry the same current due to its higher electrical resistivity, potentially increasing installation costs. Copper's superior conductivity and durability often result in lower maintenance expenses, which may offset its higher upfront cost over the lifespan of the wiring system.
Weight and Flexibility in Installation
Aluminum wiring weighs approximately 50% less than copper, making it significantly easier to handle and transport during electrical installations. Its lower density contributes to enhanced flexibility, especially in longer cable runs where reducing overall weight is crucial. Copper, though heavier, offers superior malleability and durability, but aluminum's lightweight nature often results in faster and more cost-effective installation processes.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Copper offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, maintaining reliable conductivity over time without significant degradation. Aluminum tends to oxidize, forming an insulating oxide layer that can increase connection resistance and risk electrical faults. Proper installation and use of anti-oxidant compounds are critical to enhance aluminum wiring longevity but copper remains the preferred choice for durability and safety in electrical wiring applications.
Safety Concerns and Fire Hazards
Copper wiring offers superior conductivity and durability, significantly reducing the risk of overheating and fire hazards compared to aluminum. Aluminum wiring, prone to oxidation and thermal expansion, can lead to loose connections and increased fire risks if not properly installed or maintained. Enhanced safety measures such as using CO/ALR-rated connectors and regular inspections are crucial when aluminum wiring is present to mitigate potential fire hazards.
Applications and Usage Scenarios
Aluminum wiring is commonly used in large-scale electrical systems, such as power distribution networks and utility service connections, due to its lightweight and cost-effectiveness. Copper wiring is preferred for residential and commercial applications where high conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion are critical for safety and long-term reliability. In scenarios requiring extended cable runs or compact installations, copper provides superior electrical performance, while aluminum is favored in industrial or utility settings where budget constraints and weight reduction are priorities.
Code Compliance and Industry Standards
Copper wiring is preferred in electrical installations due to its superior conductivity and compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) requiring copper or aluminum cables rated for specific applications. Aluminum wiring must meet strict industry standards such as ASTM B800 for aluminum alloy electrical conductors to ensure safety and prevent issues like oxidation and thermal expansion. Code compliance often mandates using connectors and devices listed for aluminum wiring to avoid potential fire hazards and ensure long-term reliability.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Aluminum wiring requires more frequent inspection due to its higher susceptibility to oxidation and thermal expansion, which can loosen connections and increase fire risk. Copper wiring offers superior durability with less maintenance, as it resists corrosion and maintains stable conductivity over time. Repair procedures on aluminum wiring often demand specialized connectors and anti-oxidant compounds to ensure safe, long-lasting joints, unlike the simpler, more reliable repairs typical with copper wiring.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aluminum wiring offers a lighter weight and lower environmental footprint due to its abundance and lower energy requirements during extraction and processing compared to copper. Copper, while more durable and efficient in conductivity, involves higher energy consumption and environmental degradation from mining activities. Choosing aluminum supports reduced carbon emissions and resource conservation, aligning with sustainable building practices in electrical wiring applications.
Infographic: Aluminum vs Copper for Electrical Wiring
 azmater.com
azmater.com