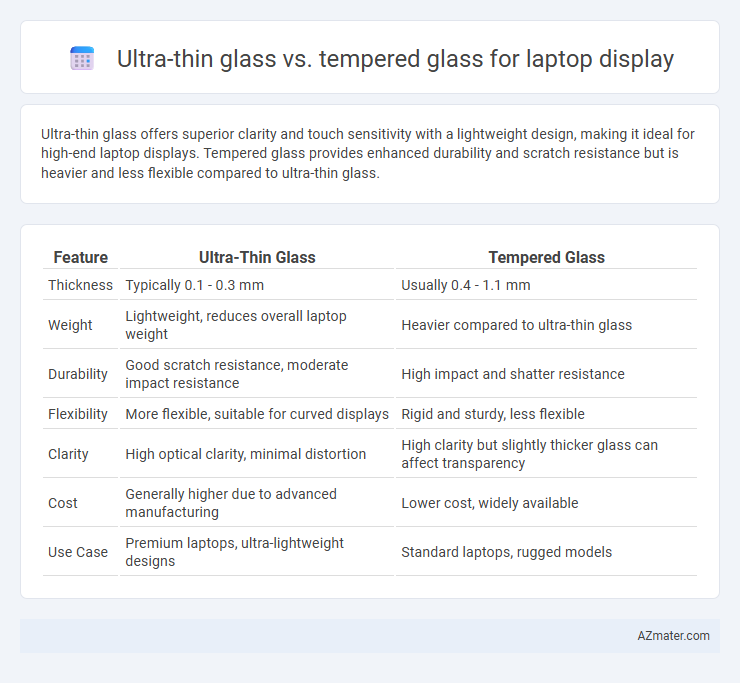
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and touch sensitivity with a lightweight design, making it ideal for high-end laptop displays. Tempered glass provides enhanced durability and scratch resistance but is heavier and less flexible compared to ultra-thin glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Thin Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 0.1 - 0.3 mm | Usually 0.4 - 1.1 mm |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces overall laptop weight | Heavier compared to ultra-thin glass |
| Durability | Good scratch resistance, moderate impact resistance | High impact and shatter resistance |
| Flexibility | More flexible, suitable for curved displays | Rigid and sturdy, less flexible |
| Clarity | High optical clarity, minimal distortion | High clarity but slightly thicker glass can affect transparency |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Use Case | Premium laptops, ultra-lightweight designs | Standard laptops, rugged models |
Introduction: Ultra-thin Glass vs Tempered Glass for Laptop Displays
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties compared to traditional tempered glass, enhancing portability and touch sensitivity in laptop displays. Tempered glass provides exceptional durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for protecting screens against scratches and drops. Choosing between ultra-thin and tempered glass depends on balancing the need for lightweight design with robust protection in laptop manufacturing.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Ultra-thin glass for laptop displays is composed primarily of aluminosilicate glass, engineered through a specialized fusion draw or float process that yields ultra-slim, highly flexible panels with superior clarity and scratch resistance. Tempered glass, made by heating standard soda-lime silica glass to around 620degC and rapidly cooling it, achieves enhanced strength through induced compressive stress, but remains thicker and less flexible compared to ultra-thin glass. The manufacturing process of ultra-thin glass demands precise control over thickness and uniformity to maintain durability at minimal thickness, whereas tempered glass emphasizes thermal treatment for robust impact resistance.
Thickness and Weight Comparison
Ultra-thin glass for laptop displays typically measures between 0.1 to 0.3 millimeters in thickness, significantly thinner than tempered glass, which usually ranges from 0.5 to 2 millimeters. This reduced thickness in ultra-thin glass leads to a lighter overall display weight, enhancing device portability and contributing to slimmer laptop designs. In contrast, tempered glass increases display durability and scratch resistance but adds more bulk and weight, impacting the laptop's sleek profile.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Ultra-thin glass offers exceptional scratch resistance and durability while maintaining a lightweight and slim profile, making it ideal for modern laptop displays. Tempered glass, known for its superior impact resistance due to heat-treatment processes, provides robust protection against drops and shocks but tends to be thicker and heavier. When prioritizing durability and impact resistance, tempered glass excels in shock absorption, whereas ultra-thin glass balances durability with a sleek, lightweight design for enhanced portability.
Optical Clarity and Display Quality
Ultra-thin glass offers superior optical clarity for laptop displays, minimizing light refraction and enhancing color accuracy compared to tempered glass. Its reduced thickness contributes to a more vibrant, high-resolution viewing experience with less distortion and glare. Tempered glass, while more impact-resistant, tends to slightly compromise display brightness and sharpness due to its thicker, multi-layered structure.
Touch Sensitivity and Responsiveness
Ultra-thin glass enhances laptop display touch sensitivity by offering a thinner substrate that allows for more precise capacitive touch detection compared to thicker tempered glass. Its reduced thickness minimizes signal attenuation, resulting in faster and more accurate touch responsiveness, crucial for activities requiring high precision such as drawing or handwriting. Tempered glass, while providing superior durability and impact resistance, often compromises touch responsiveness due to its thicker profile and slightly reduced signal conductivity.
Flexibility and Design Versatility
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility compared to tempered glass, allowing for more innovative and curved laptop display designs without compromising durability. Its reduced thickness contributes to lighter, slimmer laptop profiles, enhancing portability and aesthetic appeal. Tempered glass, while highly resistant to scratches and impact, is more rigid and limits design adaptability, making ultra-thin glass the preferred choice for cutting-edge, flexible laptop screens.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Management
Ultra-thin glass offers superior heat dissipation and enhanced thermal conductivity compared to tempered glass, making it more effective for managing the high temperatures generated by laptop displays. The reduced thickness of ultra-thin glass minimizes thermal resistance, allowing quicker heat transfer away from critical components, which helps maintain optimal device performance and longevity. Tempered glass, while strong and impact-resistant, typically has lower thermal conductivity, making it less efficient in heat resistance and thermal management for high-performance laptops.
Cost Implications and Market Availability
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and scratch resistance for laptop displays but typically incurs higher production costs compared to tempered glass, making it less prevalent in budget-friendly models. Tempered glass remains widely available and cost-effective, favored by manufacturers aiming to balance durability with affordability in mass-market laptops. Market trends indicate a gradual increase in ultra-thin glass adoption driven by premium segment demand, though tempered glass dominates overall due to its established supply chains and lower price points.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Laptop Display
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and lightweight protection for laptop displays, ideal for enhancing touch sensitivity and maintaining sleek device profiles. Tempered glass provides robust impact resistance and scratch protection, ensuring durability against accidental drops and daily wear. Selecting the best glass depends on balancing the need for advanced screen responsiveness and minimalist design against the requirement for maximum toughness and longevity.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Tempered glass for Laptop display
 azmater.com
azmater.com