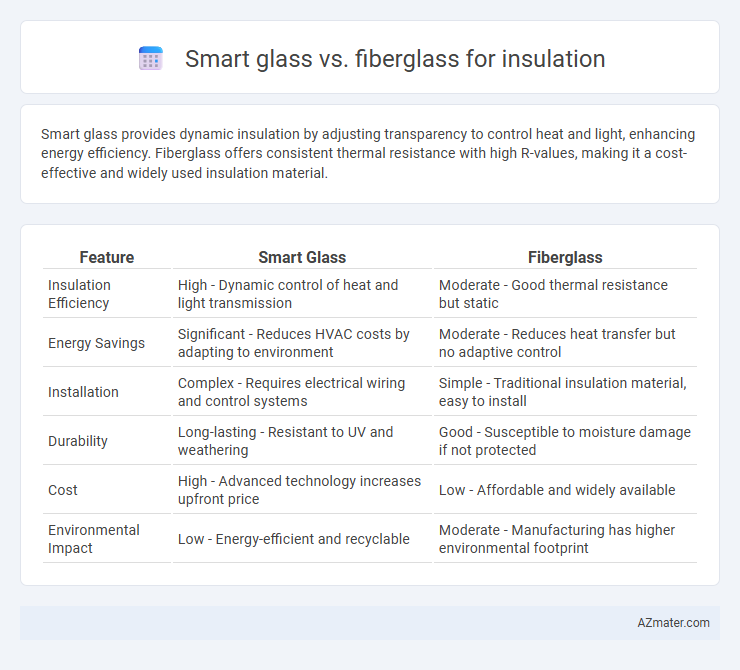
Smart glass provides dynamic insulation by adjusting transparency to control heat and light, enhancing energy efficiency. Fiberglass offers consistent thermal resistance with high R-values, making it a cost-effective and widely used insulation material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Glass | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Efficiency | High - Dynamic control of heat and light transmission | Moderate - Good thermal resistance but static |
| Energy Savings | Significant - Reduces HVAC costs by adapting to environment | Moderate - Reduces heat transfer but no adaptive control |
| Installation | Complex - Requires electrical wiring and control systems | Simple - Traditional insulation material, easy to install |
| Durability | Long-lasting - Resistant to UV and weathering | Good - Susceptible to moisture damage if not protected |
| Cost | High - Advanced technology increases upfront price | Low - Affordable and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Low - Energy-efficient and recyclable | Moderate - Manufacturing has higher environmental footprint |
Introduction to Smart Glass and Fiberglass Insulation
Smart glass insulation utilizes electrochromic or thermochromic technology to regulate heat transfer and natural light, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Fiberglass insulation, composed of fine glass fibers, provides thermal resistance by trapping air within its matrix, reducing heat flow and improving indoor comfort. Both materials offer distinct advantages in insulation performance, with smart glass integrating dynamic control and fiberglass serving as a traditional, cost-effective solution.
Key Properties of Smart Glass for Insulation
Smart glass for insulation offers dynamic control over solar heat gain, reducing energy costs by adjusting opacity based on sunlight intensity. It provides superior thermal regulation with low U-values and high solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) compared to fiberglass, enhancing indoor comfort. Unlike fiberglass, smart glass combines insulation with glare reduction and UV protection, making it a multifunctional solution for modern building envelopes.
Core Features of Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation provides superior thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 2.2 to 2.7 per inch, effectively reducing heat transfer in walls and ceilings. Its core features include sound absorption, fire resistance, and moisture resistance, making it a durable and energy-efficient option for residential and commercial buildings. Unlike smart glass, which adjusts light transmission, fiberglass focuses primarily on enhancing thermal insulation and reducing energy costs.
Thermal Performance: Smart Glass vs Fiberglass
Smart glass offers superior thermal performance compared to traditional fiberglass insulation by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and minimizing heat loss through its adjustable tinting technology. While fiberglass provides consistent thermal resistance with an R-value typically between R-2.2 and R-3.8 per inch, smart glass can improve energy efficiency by reducing reliance on HVAC systems through active modulation of light and heat transmission. The integration of low-emissivity coatings and electrochromic capabilities in smart glass makes it a more adaptable solution for thermal management in modern buildings.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Smart glass offers superior energy efficiency compared to fiberglass insulation by dynamically controlling solar heat gain and natural light transmission, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling. Fiberglass insulation primarily slows heat transfer but cannot adapt to changing environmental conditions or optimize daylight usage. Integrating smart glass with existing insulation systems can enhance overall building energy performance, lowering HVAC energy consumption and utility costs significantly.
Installation Process and Practical Considerations
Smart glass installation involves precise electrical wiring and integration with control systems, requiring skilled technicians, whereas fiberglass insulation offers a straightforward, cost-effective installation process suitable for DIY projects. Smart glass demands careful handling to avoid damage to its conductive layers, while fiberglass requires protective gear to prevent irritation from glass fibers. Maintenance of smart glass includes electrical system checks, contrasting with fiberglass's need for occasional inspection for moisture or compression affecting its insulating properties.
Cost Analysis: Smart Glass vs Fiberglass
Smart glass typically has a higher upfront cost ranging from $50 to $120 per square foot compared to fiberglass insulation, which costs between $0.40 to $1.50 per square foot. Despite the expensive initial investment, smart glass can reduce long-term energy costs through improved thermal regulation and UV filtering, offering potential payback within 7-10 years. Fiberglass insulation remains the most budget-friendly option for basic thermal resistance but lacks smart glass's advanced energy-saving features and dynamic control.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Smart glass offers high durability with resistance to scratches and weathering, reducing the need for frequent maintenance compared to traditional materials. Fiberglass insulation is durable but can degrade over time due to moisture exposure and physical damage, requiring periodic inspection and potential replacement. Both options demand specific maintenance routines, but smart glass typically provides longer-lasting performance with less upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart glass offers superior energy efficiency by dynamically controlling light and heat transmission, significantly reducing HVAC energy consumption and lowering carbon emissions. Fiberglass insulation, while effective in thermal resistance, has environmental drawbacks due to energy-intensive manufacturing processes and challenges in recyclability. Smart glass technology supports sustainability goals by enhancing building energy performance and minimizing environmental footprint over its lifecycle.
Choosing the Best Insulation: Smart Glass or Fiberglass?
Smart glass offers dynamic insulation by adjusting transparency to control heat and light, reducing energy costs in climates with fluctuating temperatures. Fiberglass insulation provides consistent thermal resistance with an R-value typically between R-2.9 and R-3.8 per inch, excelling in static insulation applications. Choosing between smart glass and fiberglass depends on factors like desired energy efficiency, installation area, and budget, with smart glass ideal for adaptive environments and fiberglass best for traditional insulation needs.
Infographic: Smart glass vs Fiberglass for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com