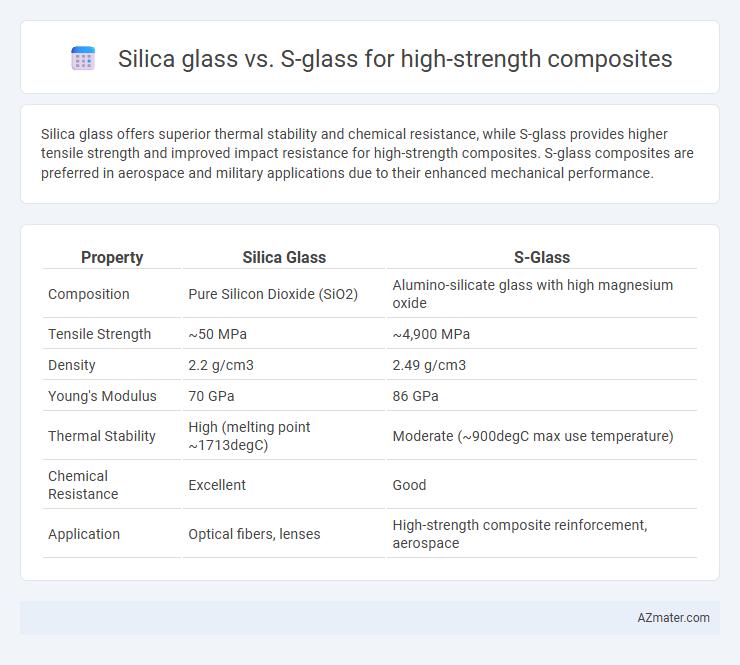
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, while S-glass provides higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance for high-strength composites. S-glass composites are preferred in aerospace and military applications due to their enhanced mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) | Alumino-silicate glass with high magnesium oxide |
| Tensile Strength | ~50 MPa | ~4,900 MPa |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | 2.49 g/cm3 |
| Young's Modulus | 70 GPa | 86 GPa |
| Thermal Stability | High (melting point ~1713degC) | Moderate (~900degC max use temperature) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Application | Optical fibers, lenses | High-strength composite reinforcement, aerospace |
Introduction to High-Strength Composites
High-strength composites utilize reinforcing fibers embedded in a matrix to achieve superior mechanical properties such as increased tensile strength and durability. Silica glass fibers offer excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance but have moderate tensile strength compared to S-glass fibers, which are specifically engineered for high tensile strength and impact resistance in demanding structural applications. Selecting between silica glass and S-glass fibers involves balancing factors like stiffness, strength, cost, and environmental durability to optimize composite performance.
Overview of Silica Glass and S-Glass
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), offers exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications requiring durability and heat resistance. S-glass, a high-strength aluminosilicate fiber, outperforms standard E-glass fibers with superior tensile strength and impact resistance, enhancing composite performance in aerospace and defense industries. Both materials provide critical benefits for composite reinforcement, with silica glass excelling in insulation and chemical stability, while S-glass delivers enhanced mechanical strength and dynamic load resistance.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Silica glass primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with minor amounts of metal oxides, offering high purity and thermal stability essential for high-strength composites. S-glass contains a complex silicate composition rich in alumina (Al2O3), magnesia (MgO), and calcium oxide (CaO), providing superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to silica glass. The enriched alumina and magnesia content in S-glass enhances its mechanical properties, making it more suitable for aerospace and defense applications requiring exceptional durability.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Stiffness
S-glass exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to silica glass, offering higher tensile strength typically around 4.8 GPa versus silica's 3.5 GPa, and enhanced stiffness with a modulus of elasticity approximately 87 GPa compared to silica glass's 70 GPa. The increased strength and stiffness of S-glass arise from its optimized alumina-silica composition that improves fiber-matrix bonding and resistance to mechanical deformation. These properties make S-glass a preferred reinforcement material in high-strength composite applications requiring enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability with a high melting point of around 1713degC, making it ideal for high-strength composites exposed to extreme heat. S-glass provides enhanced mechanical performance and higher tensile strength but has a lower thermal resistance compared to silica glass. For applications requiring both durability and prolonged thermal exposure, silica glass composites outperform S-glass in maintaining structural integrity and minimizing thermal degradation.
Weight Considerations in Composite Design
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but has a higher density (approximately 2.2 g/cm3) compared to S-glass fibers, which have a density around 2.5 g/cm3. S-glass provides greater tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for weight-sensitive composite designs where strength-to-weight ratio is critical. Optimizing composite weight requires balancing the lower density of silica glass against the enhanced mechanical properties of S-glass to achieve desired performance in aerospace and automotive applications.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
S-glass offers superior durability and environmental resistance compared to silica glass, making it ideal for high-strength composite applications exposed to harsh conditions. S-glass fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and better resistance to moisture, chemicals, and thermal degradation, enhancing the longevity and performance of composites. In contrast, silica glass provides good thermal stability but lacks the toughness and chemical resistance required for demanding structural environments.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Silica glass, known for its excellent thermal stability and optical clarity, tends to be more expensive but offers superior corrosion resistance compared to S-glass, which is engineered for high tensile strength and impact resistance at a lower cost. S-glass is widely available and favored in high-strength composite applications where cost-effectiveness and mechanical performance are critical, making it a preferred choice in aerospace and automotive industries. The balance between silica glass's higher material cost and S-glass's broader availability influences selection based on specific performance requirements and budget constraints.
Common Applications in Industry
Silica glass is widely used in high-strength composite applications such as aerospace windows, optical fibers, and semiconductor manufacturing due to its excellent thermal stability and optical clarity. S-glass, known for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance, is commonly applied in aerospace structural components, sports equipment, and military armor. Both materials serve critical roles in industries demanding lightweight, durable composites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
Choosing the Right Glass Fiber for Your Composite
S-glass fibers provide superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to silica glass, making them ideal for high-strength composite applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance. Silica glass fibers offer excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, suitable for composites exposed to high temperatures or corrosive environments. Selecting the right glass fiber depends on the specific requirements of your composite, balancing strength, durability, and environmental factors to optimize material performance.
Infographic: Silica glass vs S-glass for High-strength composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com