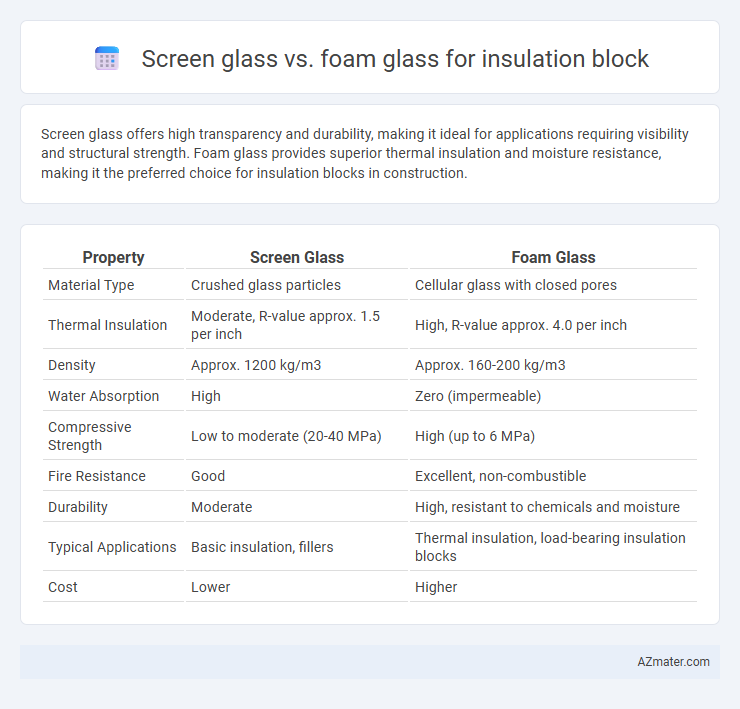
Screen glass offers high transparency and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility and structural strength. Foam glass provides superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making it the preferred choice for insulation blocks in construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Screen Glass | Foam Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Crushed glass particles | Cellular glass with closed pores |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, R-value approx. 1.5 per inch | High, R-value approx. 4.0 per inch |
| Density | Approx. 1200 kg/m3 | Approx. 160-200 kg/m3 |
| Water Absorption | High | Zero (impermeable) |
| Compressive Strength | Low to moderate (20-40 MPa) | High (up to 6 MPa) |
| Fire Resistance | Good | Excellent, non-combustible |
| Durability | Moderate | High, resistant to chemicals and moisture |
| Typical Applications | Basic insulation, fillers | Thermal insulation, load-bearing insulation blocks |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Screen Glass and Foam Glass Insulation Blocks
Screen glass insulation blocks are manufactured from recycled glass processed into lightweight, rigid panels that offer excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance for energy-efficient building applications. Foam glass insulation blocks consist of crushed glass melted and foamed into a cellular structure, providing superior compressive strength, fire resistance, and durability in both residential and industrial insulation. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction by utilizing recycled glass, but foam glass delivers enhanced mechanical properties ideal for heavy-load environments.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Screen glass insulation blocks consist primarily of recycled glass particles melted and formed into a rigid, porous structure through a controlled heating and cooling process, emphasizing a high silica content for durability and thermal resistance. Foam glass insulation blocks are produced by mixing finely ground glass powder with a foaming agent, then heating the mixture to create a closed-cell, lightweight structure with superior insulating properties and moisture resistance. Both materials leverage recycled glass but differ significantly in manufacturing techniques, with screen glass relying on particle aggregation and foam glass utilizing gas expansion to achieve distinct insulation characteristics.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Screen glass insulation blocks exhibit superior thermal insulation properties due to their low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.04 W/m*K, which effectively reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency. Foam glass blocks also provide excellent thermal insulation, with thermal conductivity values ranging from 0.05 to 0.07 W/m*K, offering additional benefits such as moisture resistance and durability in harsh environments. Both materials significantly improve building thermal performance, but screen glass insulation is preferred where maximum heat resistance and lightweight solutions are essential.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Screen glass insulation blocks offer higher mechanical strength compared to foam glass due to their dense structure, making them suitable for load-bearing applications. Foam glass blocks provide superior durability with excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and fire, promoting long-term stability in harsh environments. Both materials excel in insulation, but selecting screen glass enhances structural integrity, whereas foam glass prioritizes longevity under corrosive conditions.
Moisture and Fire Resistance
Screen glass insulation blocks exhibit superior moisture resistance due to their dense, non-porous structure that prevents water absorption and mold growth. Foam glass insulation blocks offer exceptional fire resistance with a high melting point and non-combustible composition, providing reliable protection against flames and heat. Both materials are effective for insulation, but foam glass is preferred in high fire risk environments, while screen glass excels in moisture-prone applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Screen glass insulation blocks offer enhanced sustainability through the use of recycled glass materials, reducing landfill waste and lowering energy consumption during production compared to foam glass. Foam glass provides excellent insulating properties and resistance to moisture but typically involves higher energy inputs and the use of synthetic binders, impacting its overall environmental footprint. Choosing screen glass insulation contributes to circular economy goals and minimizes resource depletion, making it a more environmentally friendly option in sustainable building practices.
Installation and Handling
Screen glass insulation blocks offer straightforward installation due to their rigid structure, allowing for precise cutting and secure fitting with minimal tools. Foam glass insulation blocks are lightweight and resistant to moisture, simplifying handling and reducing labor costs, but they require careful protection from impact to prevent chipping. Both materials provide effective thermal insulation, but screen glass may need additional support during installation, while foam glass excels in ease of transport and installation speed.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Screen glass insulation blocks generally offer lower initial costs due to the abundance of raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes compared to foam glass blocks, which require more energy-intensive production. Foam glass provides superior thermal insulation and durability, potentially reducing long-term energy expenses despite higher upfront prices. When evaluating economic considerations, the slightly higher investment in foam glass can result in better lifecycle cost savings, especially in applications demanding enhanced insulation and moisture resistance.
Applications in Construction
Screen glass insulation blocks offer superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making them ideal for exterior wall cladding and roofing applications in residential and commercial buildings. Foam glass insulation blocks provide excellent compressive strength and fire resistance, suited for foundation insulation, underground structures, and industrial facilities. Both materials enhance energy efficiency but serve different structural requirements based on load-bearing capacity and environmental exposure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulation Block
Screen glass insulation blocks offer superior thermal resistance and durability, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Foam glass blocks provide excellent moisture resistance and lightweight properties, suitable for environments prone to water exposure or where structural load is a concern. Selecting the right insulation block depends on balancing thermal insulation needs, environmental factors, and mechanical requirements to optimize energy efficiency and longevity.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Foam glass for Insulation block
 azmater.com
azmater.com