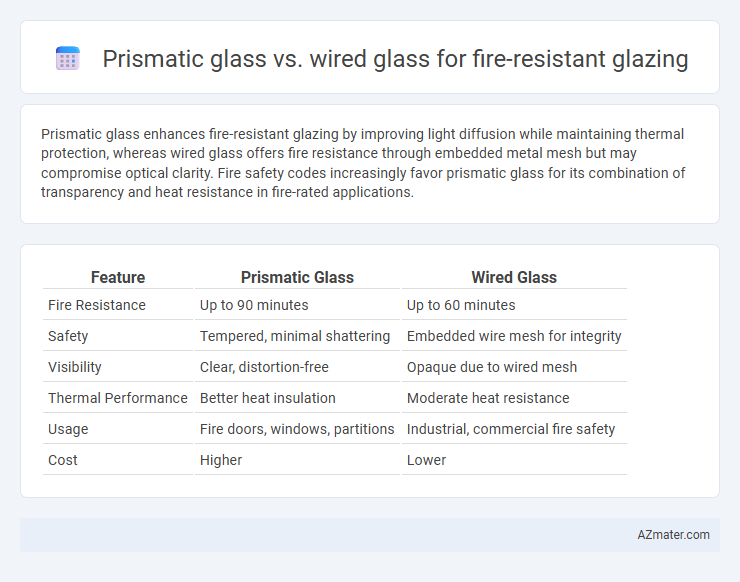
Prismatic glass enhances fire-resistant glazing by improving light diffusion while maintaining thermal protection, whereas wired glass offers fire resistance through embedded metal mesh but may compromise optical clarity. Fire safety codes increasingly favor prismatic glass for its combination of transparency and heat resistance in fire-rated applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Prismatic Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Up to 90 minutes | Up to 60 minutes |
| Safety | Tempered, minimal shattering | Embedded wire mesh for integrity |
| Visibility | Clear, distortion-free | Opaque due to wired mesh |
| Thermal Performance | Better heat insulation | Moderate heat resistance |
| Usage | Fire doors, windows, partitions | Industrial, commercial fire safety |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Glazing
Fire-resistant glazing is engineered to prevent the spread of fire and smoke, maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat conditions. Prismatic glass offers enhanced light diffusion with fire-resistant properties, optimizing visibility and safety during emergencies. Wired glass incorporates embedded metal mesh, providing stability during fire exposure but with reduced clarity compared to prismatic alternatives.
Understanding Prismatic Glass
Prismatic glass enhances fire-resistant glazing by redirecting and diffusing light, improving visibility while maintaining fire protection. Its unique structure refracts light through geometric patterns, optimizing natural illumination without compromising safety standards. Compared to wired glass, prismatic glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal alongside reliable fire resistance ratings.
Key Features of Wired Glass
Wired glass offers superior fire resistance and impact protection due to its embedded steel wire mesh, which helps maintain structural integrity during high temperatures. It provides excellent visibility while preventing the spread of flames and smoke in fire-rated glazing applications. Wired glass is commonly used in fire doors, windows, and partitions requiring both safety and durability.
Fire-Resistance Performance Comparison
Prismatic glass offers enhanced fire-resistance performance by diffusing heat and reducing radiant heat transmission compared to wired glass, which primarily relies on embedded wire mesh to hold glass integrity during fire exposure. Wired glass provides effective containment of fire and smoke but tends to have lower thermal insulation, leading to faster heat transfer and potential failure under prolonged fire conditions. Prismatic glass, by combining optical properties with fire resistance, meets stricter fire rating requirements, making it suitable for applications demanding superior heat and flame control.
Safety and Impact Resistance
Prismatic glass and wired glass differ significantly in fire-resistant glazing applications, particularly in safety and impact resistance. Wired glass contains embedded metal mesh that provides additional fire resistance but is prone to shattering under impact, posing safety hazards from falling glass shards. Prismatic glass offers enhanced impact resistance with a smooth surface that reduces the risk of injury, while maintaining effective fire performance through advanced heat reflection and diffusion technologies.
Aesthetic and Light Transmission Qualities
Prismatic glass offers superior light diffusion and decorative aesthetics with its unique textured patterns that enhance interior ambiance while maintaining fire resistance. Wired glass provides a traditional, industrial look with embedded metal mesh that ensures structural integrity during fire but reduces visible clarity and light transmission. The choice between prismatic and wired glass balances the desire for architectural elegance and optimal natural light against robust fire safety standards.
Compliance with Building Codes and Standards
Prismatic glass for fire-resistant glazing complies with key building codes like NFPA 80 and ASTM E119 by providing controlled fire resistance and light diffusion properties, while wired glass meets standards such as UL 9 and NFPA 257 through its embedded metal mesh, which maintains integrity under fire exposure. Both types must adhere to local and national regulations, including the International Building Code (IBC), ensuring they provide adequate fire protection and safety performance. Selecting between prismatic and wired glass depends on the specific code requirements for fire rating, impact resistance, and smoke control in the installation area.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Prismatic glass for fire-resistant glazing requires precise alignment during installation to maximize its light-directing properties, often necessitating specialized mounting techniques. Wired glass offers simpler installation with standard framing but demands frequent inspections for wire corrosion and glass integrity to maintain fire resistance. Maintenance for prismatic glass centers on cleaning without abrasives to prevent surface damage, while wired glass benefits from routine checks to detect any cracks or wire mesh degradation impacting its protective performance.
Cost and Long-Term Value
Prismatic glass typically offers higher upfront costs than wired glass but provides superior optical clarity and enhanced fire-resistant performance, contributing to better long-term value in commercial and institutional settings. Wired glass is generally more affordable initially, yet it may require more frequent replacement or maintenance due to reduced durability and clarity after exposure to heat, which can increase life-cycle costs. Investing in prismatic glass results in improved safety and lower total cost of ownership, making it a cost-effective choice for fire-resistant glazing over time.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Prismatic glass offers enhanced light diffusion and architectural aesthetics, making it ideal for projects prioritizing both fire resistance and design appeal. Wired glass provides superior fire protection with embedded wire mesh that maintains integrity under high temperatures, suitable for safety-critical applications. Selecting the right fire-resistant glazing depends on balancing visual requirements, fire code compliance, and mechanical strength for your specific project needs.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant glazing
 azmater.com
azmater.com