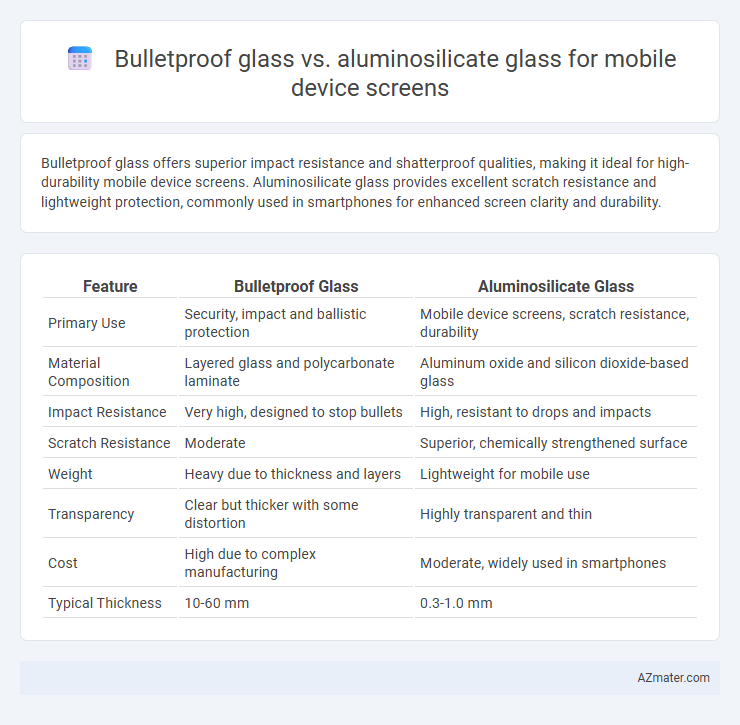
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance and shatterproof qualities, making it ideal for high-durability mobile device screens. Aluminosilicate glass provides excellent scratch resistance and lightweight protection, commonly used in smartphones for enhanced screen clarity and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bulletproof Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Security, impact and ballistic protection | Mobile device screens, scratch resistance, durability |
| Material Composition | Layered glass and polycarbonate laminate | Aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide-based glass |
| Impact Resistance | Very high, designed to stop bullets | High, resistant to drops and impacts |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Superior, chemically strengthened surface |
| Weight | Heavy due to thickness and layers | Lightweight for mobile use |
| Transparency | Clear but thicker with some distortion | Highly transparent and thin |
| Cost | High due to complex manufacturing | Moderate, widely used in smartphones |
| Typical Thickness | 10-60 mm | 0.3-1.0 mm |
Introduction to Mobile Device Screen Protection
Mobile device screen protection relies heavily on materials such as bulletproof glass and aluminosilicate glass, each offering distinct advantages in durability and impact resistance. Bulletproof glass, typically composed of laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, provides superior shatter resistance for extreme impact scenarios. Aluminosilicate glass, engineered through ion-exchange processes, delivers enhanced scratch resistance and structural strength while maintaining lightweight transparency essential for mobile screens.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass is a laminated or layered material made from multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate, designed to resist high-impact forces and prevent penetration. This type of glass provides enhanced protection against physical damage such as drops and blunt attacks, making it highly suitable for mobile device screens in extreme conditions. Compared to aluminosilicate glass, which is chemically strengthened for scratch resistance and durability, bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance and shatter-proof properties.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a category of durable glass made primarily from aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, known for its high resistance to scratches and impacts, making it ideal for mobile device screens. Unlike traditional bulletproof glass, which is designed to stop high-velocity projectiles through multiple layered laminates, aluminosilicate glass offers a lightweight and thin profile with exceptional toughness and thermal stability. Its widespread use in smartphones, such as Corning Gorilla Glass, results from its ability to withstand daily wear and drop impacts while maintaining clarity and touch sensitivity.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Bulletproof glass, typically made from layered laminated glass with polycarbonate or resin interlayers, offers exceptional impact resistance through multiple bonded layers, while aluminosilicate glass, composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, undergoes ion-exchange strengthening to enhance scratch resistance and durability. Manufacturing bulletproof glass involves a complex lamination process combining glass and plastic layers for shatterproof protection; aluminosilicate glass is produced via melting and controlled cooling, followed by chemical tempering techniques. The chemical structure of aluminosilicate glass allows for thinner, lighter mobile screens with high strength, contrasting with the bulkier, heavier composite makeup of bulletproof glass designed primarily for ballistic protection.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Bulletproof glass offers superior impact resistance due to its multi-layered construction, designed to absorb and dissipate high-energy shocks, making it highly durable against severe impacts. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in mobile device screens, provides excellent hardness and scratch resistance but is more prone to shattering under extreme force compared to bulletproof glass. For mobile devices, aluminosilicate glass balances durability and weight, while bulletproof glass excels in environments requiring maximum impact protection.
Scratch Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Bulletproof glass is primarily designed for impact resistance and typically incorporates multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, which may make it more prone to surface scratches compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in mobile device screens like Gorilla Glass, features a chemically strengthened surface through ion-exchange processes, resulting in superior scratch resistance and durability against everyday abrasions. Consequently, aluminosilicate glass generally performs better in scratch resistance for mobile devices while still maintaining adequate toughness.
Optical Clarity and Touch Sensitivity
Bulletproof glass offers strong impact resistance but can suffer from slight haze or reduced optical clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass, which delivers superior transparency and vibrant color accuracy essential for mobile displays. Aluminosilicate glass, often chemically strengthened, provides enhanced touch sensitivity and smoothness due to its lower surface roughness, improving the responsiveness and precision of capacitive touchscreens. Choosing aluminosilicate glass optimizes user experience in bright environments and touch interaction, whereas bulletproof glass prioritizes durability at a slight cost to optical performance.
Thickness and Weight Considerations
Bulletproof glass used in mobile device screens typically measures between 3 to 5 mm in thickness, contributing to significant weight increase compared to standard materials. Aluminosilicate glass, such as Gorilla Glass, offers superior thinness often under 1 mm, maintaining lightweight design while delivering high scratch and impact resistance. The reduced thickness and weight of aluminosilicate glass enhance device portability and ergonomics without compromising durable protection.
Cost and Availability for Mobile Devices
Aluminosilicate glass is more cost-effective and widely available for mobile device screens due to its mass production and extensive use in consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets. Bulletproof glass, typically made from laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate, incurs higher manufacturing costs and is less common in mobile devices primarily reserved for specialized high-security applications. The affordability and accessibility of aluminosilicate glass drive its dominance in the mobile device market, balancing durability with cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Smartphone
Bulletproof glass offers exceptional impact resistance and thickness, making it ideal for rugged environments but often adds weight and reduces touch sensitivity. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphones as Gorilla Glass, provides superior scratch resistance, high transparency, and enhanced durability while maintaining a lightweight and responsive touch experience. Choosing the right glass depends on prioritizing either maximum protection or everyday usability and screen clarity for your smartphone.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Mobile device screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com