Nanoglass offers superior optical clarity and enhanced durability compared to Ulexite glass in fiber optic applications. Its nanoscale structure reduces signal loss and improves light transmission efficiency.
Table of Comparison
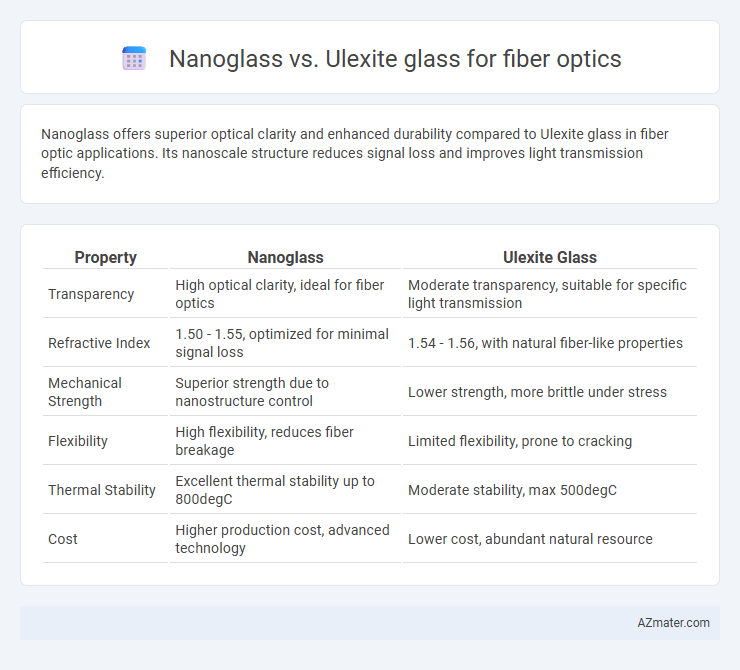
| Property | Nanoglass | Ulexite Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High optical clarity, ideal for fiber optics | Moderate transparency, suitable for specific light transmission |
| Refractive Index | 1.50 - 1.55, optimized for minimal signal loss | 1.54 - 1.56, with natural fiber-like properties |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior strength due to nanostructure control | Lower strength, more brittle under stress |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, reduces fiber breakage | Limited flexibility, prone to cracking |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent thermal stability up to 800degC | Moderate stability, max 500degC |
| Cost | Higher production cost, advanced technology | Lower cost, abundant natural resource |
Introduction to Fiber Optic Materials
Nanoglass and ulexite glass represent two advanced materials used in fiber optic technology, each offering unique optical properties essential for efficient data transmission. Nanoglass provides enhanced transparency and minimized signal attenuation due to its nanoscale structure, improving light propagation and bandwidth capacity. Ulexite glass, known for its natural fiber-like internal structure and excellent light diffusion characteristics, offers cost-effective solutions with reliable performance in fiber optic applications.
Overview of Nanoglass and Ulexite Glass
Nanoglass features nanoscale silica particles that enhance strength and optical clarity, making it ideal for high-performance fiber optic applications. Ulexite glass, composed primarily of hydrated borate minerals, offers excellent light transmission and natural fiber-optic-like properties due to its unique needle-like crystal structure. While nanoglass provides superior durability and customizable refractive indices, ulexite glass is valued for its intrinsic fiber optic characteristics and cost-effectiveness in specific communication technologies.
Key Properties of Nanoglass for Fiber Optics
Nanoglass for fiber optics offers superior transparency and minimal light scattering due to its ultra-fine grain structure, enhancing signal clarity over long distances. Its high thermal stability and mechanical strength ensure durability under varying environmental conditions, surpassing traditional Ulexite glass. Nanoglass's low refractive index and exceptional corrosion resistance make it ideal for efficient light transmission and long-term performance in fiber optic applications.
Unique Characteristics of Ulexite Glass
Ulexite glass exhibits a unique natural fiber-optic property due to its internal parallel tubular structures that channel light along its fibers, enabling efficient light transmission without external power. Unlike typical nanoglass materials, ulexite's crystalline borate composition allows it to act as a natural fiber optic conduit, making it valuable in specialized optical applications that demand natural light guiding. Its inherent ability to transmit light through internal reflections sets ulexite apart from synthetic nanoglass, which relies on engineered nanostructures for optical performance.
Transmission Efficiency: Nanoglass vs Ulexite Glass
Nanoglass exhibits superior transmission efficiency compared to Ulexite glass in fiber optic applications due to its lower scattering and higher transparency across a broader wavelength range. The nanoscale structure of Nanoglass minimizes light attenuation, enhancing signal clarity and throughput. Ulexite glass, while effective in certain light-guiding scenarios, typically suffers from higher transmission losses and less uniform refractive properties.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Nanoglass exhibits superior durability compared to Ulexite glass due to its enhanced resistance to micro-cracking and environmental degradation, benefiting fiber optic applications that demand long-term stability. Ulexite glass, while effective in light transmission, tends to degrade faster under thermal and mechanical stress, reducing its operational lifespan in fiber optic systems. The inherent nanostructure of Nanoglass provides a more robust framework, significantly extending the longevity of fiber optic components relative to conventional Ulexite glass.
Cost Analysis: Production and Implementation
Nanoglass offers higher initial production costs due to advanced manufacturing techniques but provides long-term savings from enhanced durability and improved light transmission efficiency in fiber optics. Ulexite glass, typically lower in upfront expenses, may incur higher maintenance and replacement costs over time because of its comparatively lower strength and optical clarity. Evaluating total cost of ownership, Nanoglass delivers better value for large-scale, high-performance fiber optic applications despite the steeper production investment.
Applications in Fiber Optic Technologies
Nanoglass and Ulexite glass serve distinct roles in fiber optic technologies, with Nanoglass offering superior optical clarity and enhanced light transmission efficiency, making it ideal for high-precision data transmission and advanced telecommunication networks. Ulexite glass, known for its natural fiber-optic properties and ability to channel light along its fibers, is often utilized in specialized sensors and low-cost fiber optic displays. The integration of Nanoglass improves signal fidelity and bandwidth, while Ulexite provides cost-effective solutions for niche fiber optic applications requiring natural light diffusion and directional light guiding.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanoglass fiber optics exhibit a lower environmental impact compared to Ulexite glass due to their enhanced durability and reduced material consumption during manufacturing. The production of Nanoglass fibers requires less energy and generates fewer carbon emissions, supporting sustainable practices in the fiber optic industry. Conversely, Ulexite glass involves mining and processing of borate minerals, which can lead to ecological disturbances and higher environmental costs.
Future Trends and Material Innovations
Nanoglass exhibits significant advancements in fiber optic technology due to its superior optical clarity and enhanced durability compared to Ulexite glass, enabling higher data transmission rates and resistance to environmental degradation. Emerging material innovations in Nanoglass focus on nanostructured coatings and hybrid composites that improve light dispersion and reduce signal attenuation, positioning it as a key component in next-generation fiber optic networks. Future trends indicate increasing adoption of Nanoglass in high-performance communications infrastructure, driven by its scalability and compatibility with advanced photonic devices.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Ulexite glass for Fiber optic
 azmater.com
azmater.com