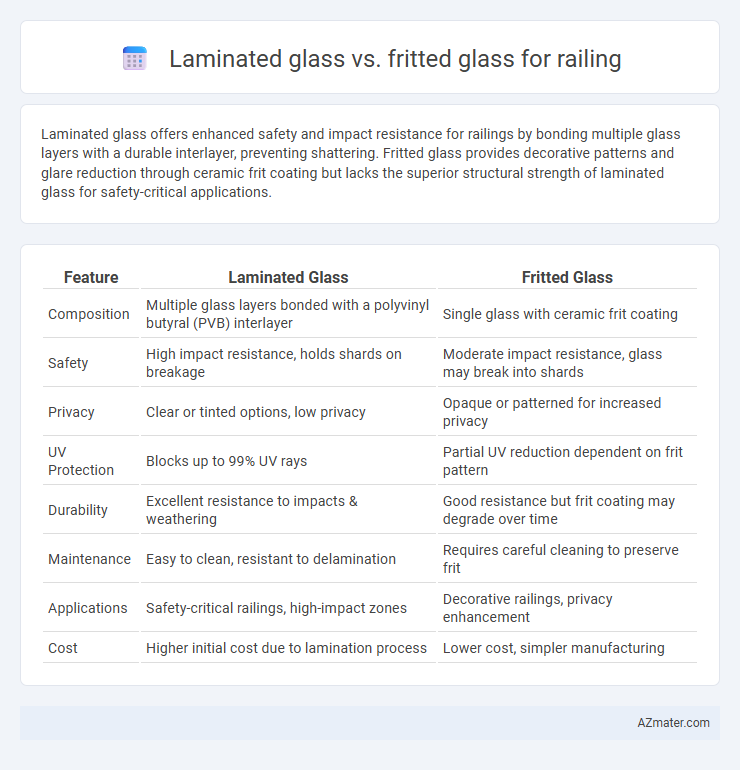
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and impact resistance for railings by bonding multiple glass layers with a durable interlayer, preventing shattering. Fritted glass provides decorative patterns and glare reduction through ceramic frit coating but lacks the superior structural strength of laminated glass for safety-critical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Fritted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Multiple glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer | Single glass with ceramic frit coating |
| Safety | High impact resistance, holds shards on breakage | Moderate impact resistance, glass may break into shards |
| Privacy | Clear or tinted options, low privacy | Opaque or patterned for increased privacy |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays | Partial UV reduction dependent on frit pattern |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to impacts & weathering | Good resistance but frit coating may degrade over time |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to delamination | Requires careful cleaning to preserve frit |
| Applications | Safety-critical railings, high-impact zones | Decorative railings, privacy enhancement |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to lamination process | Lower cost, simpler manufacturing |
Introduction to Glass Railings: Laminated vs Fritted
Laminated glass railings consist of multiple glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety and impact resistance ideal for secure barrier applications. Fritted glass features ceramic frit patterns fused onto the glass surface, offering both aesthetic appeal and additional privacy without compromising visibility. Choosing between laminated or fritted glass for railings depends on the balance between structural performance and design preferences in architectural projects.
What is Laminated Glass? Key Features
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), enhancing its strength and safety for railing applications. Its key features include high impact resistance, shatterproof properties that hold together upon breaking, and improved sound insulation, making it ideal for secure and durable railings. Laminated glass also offers UV protection and can be customized for various aesthetic finishes, ensuring both functional safety and design flexibility.
Understanding Fritted Glass: Properties and Applications
Fritted glass features a ceramic enamel pattern fused onto its surface through a high-temperature process that enhances durability and reduces glare, making it ideal for railing applications requiring safety and aesthetics. Its properties include increased thermal resistance, improved privacy, and reduced solar heat gain, contributing to energy efficiency in architectural designs. Commonly used in balcony and stair railings, fritted glass provides a non-slip surface and mitigates wind and noise, enhancing both functionality and visual appeal.
Safety Comparison: Laminated Glass vs Fritted Glass
Laminated glass offers superior safety for railings due to its interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury and maintaining structural integrity. Fritted glass, while providing aesthetic benefits and solar control through its ceramic frit patterns, lacks the same level of impact resistance and shatter containment as laminated glass. For environments prioritizing safety and durability, laminated glass is the preferred choice for railing applications.
Visual Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Laminated glass offers superior clarity and a seamless, smooth surface that enhances visual aesthetics by providing an unobstructed view ideal for modern railing designs. Fritted glass incorporates ceramic dots or patterns that offer versatile design options through various color, texture, and opacity choices, adding decorative elements while maintaining privacy and reducing glare. Both materials balance safety and style, with laminated glass emphasizing transparency and strength, and fritted glass prioritizing artistic expression and adaptive design features.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Laminated glass offers superior durability for railings due to its multiple layers bonded with a resilient interlayer that prevents shattering and enhances impact resistance. Fritted glass, coated with ceramic frit, provides excellent resistance to scratches and environmental wear but may require more frequent cleaning to maintain its opaque appearance. Maintenance of laminated glass is generally simpler since its smooth surface resists dirt buildup, whereas fritted glass demands careful cleaning to avoid damaging the fritted pattern and preserving its aesthetic integrity.
Light Transmission and Privacy Considerations
Laminated glass offers high light transmission, typically around 80%, allowing for clear visibility while providing enhanced safety through its interlayer that holds shards together if broken. Fritted glass reduces light transmission significantly, often by 20-40%, with ceramic patterns that increase privacy by obscuring direct views without compromising structural integrity. Choosing between laminated and fritted glass for railings depends on the desired balance between maximizing natural light and ensuring privacy in the space.
Cost Analysis: Laminated vs Fritted Glass Railings
Laminated glass railings typically incur higher initial costs due to multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers for enhanced safety and durability, whereas fritted glass offers a more affordable option by applying ceramic frit patterns directly onto single-pane glass for aesthetic and functional benefits. Maintenance expenses for laminated glass can be higher owing to potential delamination issues over time, while fritted glass usually requires less upkeep and resists staining and glare effectively. Evaluating long-term value, laminated glass provides superior impact resistance essential for safety-critical applications, justifying its premium price compared to the cost-effective fritted glass ideal for decorative railings.
Installation Processes and Structural Support
Laminated glass for railing involves bonding multiple glass layers with a polymer interlayer, offering enhanced strength and safety during installation, often requiring precise anchoring to ensure structural integrity. Fritted glass features ceramic-based patterns baked onto the surface, which does not alter the glass's structural support but demands careful handling and alignment to maintain aesthetic consistency and durability. Both types necessitate specialized mounting hardware compatible with their distinct properties for secure installation in railing systems.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Railing Project
Laminated glass offers superior safety and impact resistance for railing projects, making it ideal for areas requiring enhanced security and durability. Fritted glass provides aesthetic versatility with its decorative patterns and improved solar control, suitable for projects prioritizing design and energy efficiency. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing safety needs with architectural style and environmental factors in your railing installation.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Fritted glass for Railing
 azmater.com
azmater.com