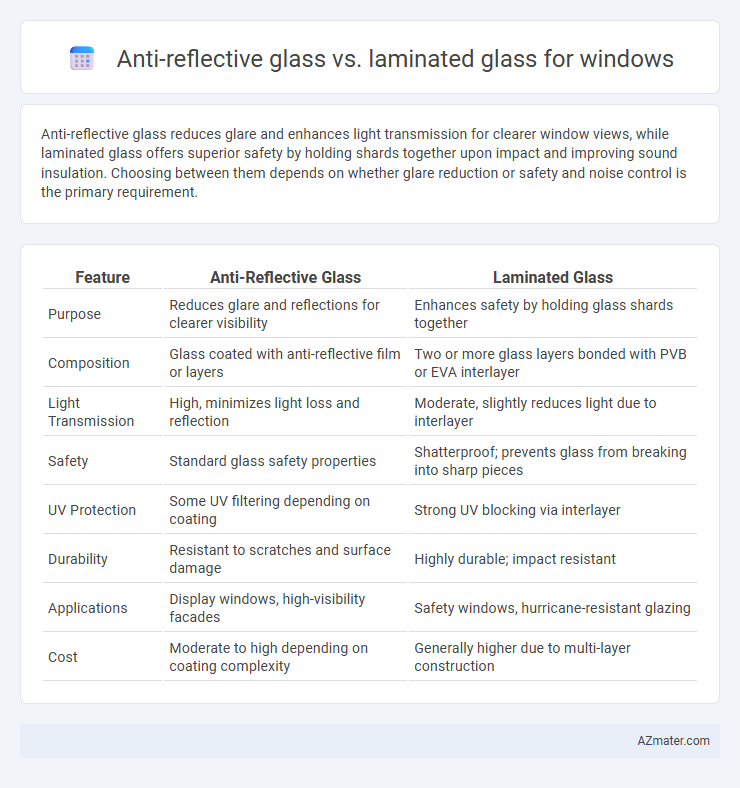
Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and enhances light transmission for clearer window views, while laminated glass offers superior safety by holding shards together upon impact and improving sound insulation. Choosing between them depends on whether glare reduction or safety and noise control is the primary requirement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Reflective Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces glare and reflections for clearer visibility | Enhances safety by holding glass shards together |
| Composition | Glass coated with anti-reflective film or layers | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB or EVA interlayer |
| Light Transmission | High, minimizes light loss and reflection | Moderate, slightly reduces light due to interlayer |
| Safety | Standard glass safety properties | Shatterproof; prevents glass from breaking into sharp pieces |
| UV Protection | Some UV filtering depending on coating | Strong UV blocking via interlayer |
| Durability | Resistant to scratches and surface damage | Highly durable; impact resistant |
| Applications | Display windows, high-visibility facades | Safety windows, hurricane-resistant glazing |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on coating complexity | Generally higher due to multi-layer construction |
Introduction to Anti-Reflective and Laminated Glass
Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and enhances clarity by minimizing surface reflections through specialized coatings, making it ideal for windows in high-light environments. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety, noise reduction, and UV protection for window applications. Both types of glass serve distinct purposes: anti-reflective glass improves visibility and aesthetics, while laminated glass focuses on security and durability.
Understanding Anti-Reflective Glass Technology
Anti-reflective glass technology uses nanostructured coatings to reduce surface reflections, enhancing light transmission and visibility through windows. This type of glass is designed to minimize glare and improve clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring high optical performance, such as display cases and architectural glazing. In contrast, laminated glass focuses on safety by bonding layers with interlayers that hold shards together upon impact, rather than reducing reflections.
What Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made from polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection. Unlike anti-reflective glass, which minimizes reflections and glare for better visibility, laminated glass primarily offers impact resistance and prevents shattering upon breakage, making it ideal for security and safety windows. The interlayer holds the glass fragments in place, reducing the risk of injury and improving durability in both residential and commercial applications.
Key Differences Between Anti-Reflective and Laminated Glass
Anti-reflective glass minimizes glare and enhances light transmission by using special coatings that reduce surface reflections, making it ideal for maximizing clarity and visibility in windows. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior safety, sound insulation, and UV protection by holding shards together when broken. Unlike laminated glass, anti-reflective glass prioritizes optical performance, while laminated glass focuses on structural strength and safety features for windows.
Light Transmission and Visibility Comparison
Anti-reflective glass offers superior light transmission, reducing glare and enhancing visibility by minimizing surface reflections, making it ideal for clear, unobstructed views. Laminated glass, while providing safety and sound insulation benefits, typically has lower light transmission due to the interlayer, which can slightly reduce clarity and visibility. For applications prioritizing maximum natural light and clear sightlines, anti-reflective glass outperforms laminated glass in maintaining high visibility and brightness indoors.
Safety and Security Considerations
Anti-reflective glass enhances visibility and reduces glare, but it offers limited impact resistance compared to laminated glass, which features a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage, significantly increasing safety. Laminated glass provides superior security by resisting forced entry and minimizing injury risk during accidents or natural disasters, making it ideal for high-risk areas. Choosing laminated glass improves protection against impact and intrusion, while anti-reflective glass prioritizes visual clarity without compromising basic structural integrity.
Acoustic Performance: Which Glass Reduces Noise Better?
Laminated glass offers superior acoustic performance compared to anti-reflective glass due to its interlayer that dampens sound vibrations, effectively reducing noise transmission through windows. The polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer in laminated glass absorbs and diminishes sound waves, making it an ideal choice for noise reduction in urban or high-traffic areas. While anti-reflective glass enhances visibility by minimizing glare, it lacks the soundproofing properties that laminated glass provides.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection
Anti-reflective glass significantly enhances energy efficiency by reducing glare and improving light transmission, thereby minimizing the need for artificial lighting and cooling. Laminated glass excels in UV protection, blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, which prevents interior fading and skin damage. Combining anti-reflective coatings with laminated glass offers an optimal solution for energy savings and superior UV defense in windows.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Long-Term Value
Anti-reflective glass typically involves higher upfront costs due to advanced coating technologies that reduce glare and improve visibility, making it a premium choice for energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal. Laminated glass, while generally more affordable initially, offers enhanced safety and sound insulation benefits that contribute to long-term durability and reduced maintenance expenses. When comparing investment and value, laminated glass provides cost-effective protection and lifespan advantages, whereas anti-reflective glass maximizes optical performance and potential energy savings over time.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windows
Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and enhances visibility by minimizing reflections, making it ideal for windows in offices, showrooms, and homes where natural light is prioritized. Laminated glass provides superior safety and sound insulation by bonding two panes with a plastic interlayer, preventing shattering and enhancing security. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing the need for clear views and aesthetics with safety and noise reduction requirements specific to your window's location.
Infographic: Anti-reflective glass vs Laminated glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com