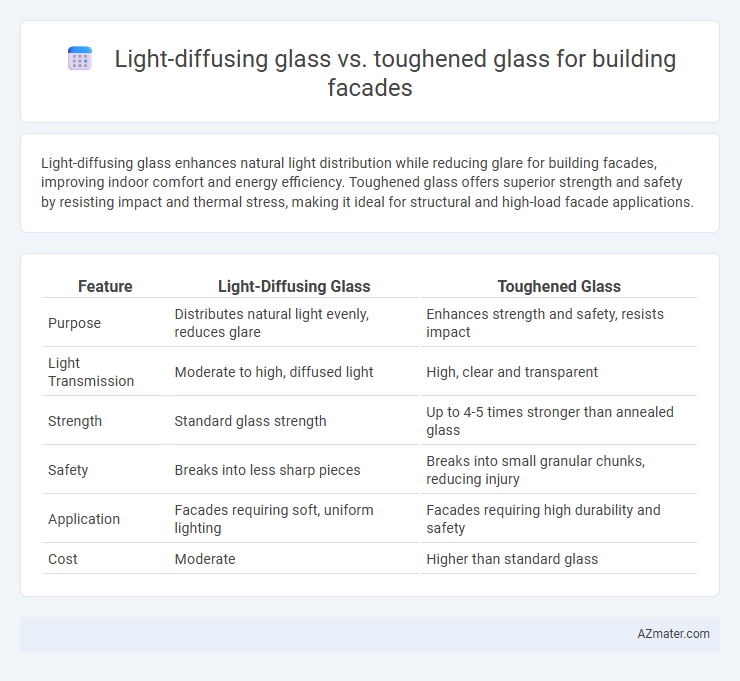
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural light distribution while reducing glare for building facades, improving indoor comfort and energy efficiency. Toughened glass offers superior strength and safety by resisting impact and thermal stress, making it ideal for structural and high-load facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light-Diffusing Glass | Toughened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Distributes natural light evenly, reduces glare | Enhances strength and safety, resists impact |
| Light Transmission | Moderate to high, diffused light | High, clear and transparent |
| Strength | Standard glass strength | Up to 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass |
| Safety | Breaks into less sharp pieces | Breaks into small granular chunks, reducing injury |
| Application | Facades requiring soft, uniform lighting | Facades requiring high durability and safety |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than standard glass |
Understanding Light-Diffusing Glass
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by scattering natural light to reduce glare and create a uniform illumination, improving visual comfort and energy efficiency. This glass type utilizes embedded micro-structures or additives to diffuse sunlight while maintaining translucency, unlike toughened glass which prioritizes impact resistance and safety. Understanding light-diffusing glass involves recognizing its role in optimizing daylight distribution without compromising structural integrity, making it ideal for facades requiring balanced natural lighting and aesthetic appeal.
What is Toughened Glass?
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is designed to withstand higher impacts and thermal stresses, making it ideal for building facades requiring enhanced durability and safety. Unlike light-diffusing glass, which focuses on scattering light to reduce glare and improve natural illumination, toughened glass emphasizes structural integrity and resistance to breakage.
Key Differences: Light-Diffusing vs Toughened Glass
Light-diffusing glass scatters natural light to reduce glare and create a uniform illumination inside buildings, enhancing comfort and energy efficiency in facades. Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, undergoes thermal or chemical treatment to increase its strength and safety, making it resistant to impact and thermal stress in architectural applications. While light-diffusing glass optimizes daylight distribution, toughened glass primarily provides structural integrity and safety in building facades.
Aesthetic Impact on Building Facades
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by creating a soft, uniform illumination that visually reduces harsh shadows and glare, contributing to a modern and elegant aesthetic. Toughened glass offers a sleek, clear appearance with increased structural integrity, allowing for expansive transparent surfaces that emphasize sharp lines and open views. Combining these glass types strategically can balance aesthetic warmth with architectural strength, elevating the overall facade design.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facade thermal performance by evenly distributing solar heat and reducing glare, resulting in improved indoor temperature regulation and lower cooling loads. Toughened glass offers high strength and safety but typically lacks the specialized thermal control properties of light-diffusing glass, potentially leading to higher solar heat gain and increased energy consumption. The choice between the two influences facade insulation efficiency, with light-diffusing glass providing better thermal comfort and energy savings in climates with intense sunlight.
Safety and Strength Considerations
Toughened glass offers high impact resistance and shatters into small, blunt pieces, enhancing safety in building facades by reducing injury risk during breakage. Light-diffusing glass, while providing excellent natural light dispersion and aesthetic appeal, may not match the strength and impact resistance of toughened glass, requiring additional reinforcement in safety-critical applications. Choosing toughened glass ensures superior structural integrity and safety compliance for facades exposed to wind loads and accidental impacts.
Daylighting and Glare Control
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facades by scattering natural daylight evenly, reducing harsh shadows and minimizing glare, which improves occupant comfort and reduces reliance on artificial lighting. Toughened glass offers high strength and safety but lacks intrinsic light diffusion properties, often requiring additional coatings or films to control glare effectively. For optimal daylighting and glare control, light-diffusing glass provides superior performance in distributing light uniformly while toughened glass prioritizes durability and impact resistance.
Energy Efficiency Implications
Light-diffusing glass enhances building facade energy efficiency by evenly distributing natural light, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and minimizing glare-related cooling costs. Toughened glass, known for its strength and thermal resistance, improves energy performance by providing superior insulation and withstanding environmental stress without compromising facade integrity. Combining both glass types can optimize daylight utilization and thermal regulation, resulting in significant energy savings for building operations.
Cost Factors and Installation
Light-diffusing glass typically incurs higher material costs due to specialized manufacturing processes that enhance privacy and distribute natural light evenly. Toughened glass costs less but requires precise handling and installation techniques to maintain safety standards, often reducing labor expenses. Installation of light-diffusing glass may demand skilled labor and longer times, impacting overall project budget compared to the quicker installation of standardized toughened glass panels.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade
Light-diffusing glass enhances natural illumination by scattering sunlight evenly, reducing glare and improving indoor comfort, making it ideal for facades where balanced daylight is crucial. Toughened glass offers superior strength and safety, with high resistance to impact and thermal stress, suitable for facades requiring durability and compliance with building codes. Evaluating facade exposure, structural requirements, aesthetic goals, and energy performance needs ensures the right glass choice for optimal functionality and design.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Toughened glass for Building facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com