Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced safety and sound insulation for windows. Tempered glass is heat-treated to increase strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, offering superior impact resistance and safety in high-stress window installations.
Table of Comparison
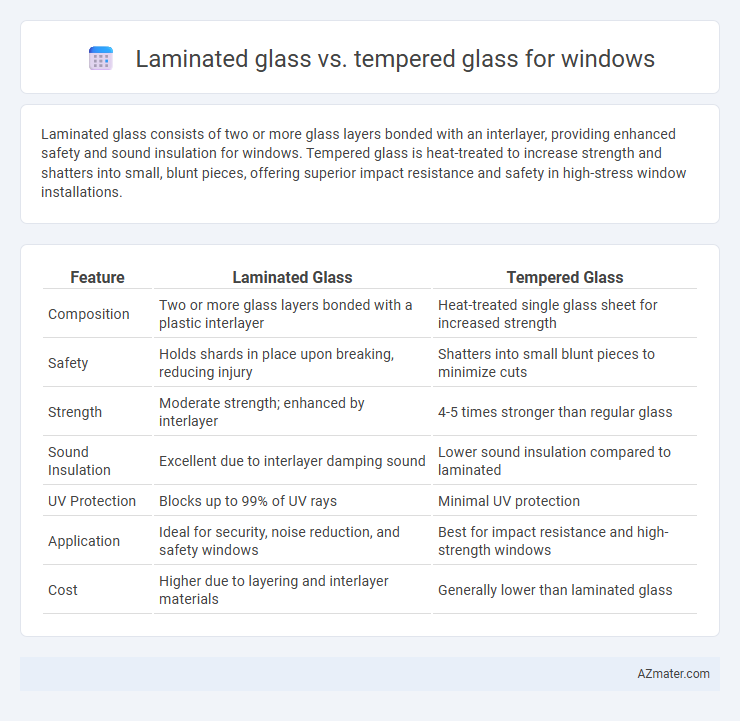
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer | Heat-treated single glass sheet for increased strength |
| Safety | Holds shards in place upon breaking, reducing injury | Shatters into small blunt pieces to minimize cuts |
| Strength | Moderate strength; enhanced by interlayer | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass |
| Sound Insulation | Excellent due to interlayer damping sound | Lower sound insulation compared to laminated |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of UV rays | Minimal UV protection |
| Application | Ideal for security, noise reduction, and safety windows | Best for impact resistance and high-strength windows |
| Cost | Higher due to layering and interlayer materials | Generally lower than laminated glass |
Introduction to Laminated and Tempered Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior safety by holding shards together upon impact, making it ideal for windows requiring enhanced security and sound insulation. Tempered glass is heat-treated to increase strength, shattering into small, blunt pieces when broken, which reduces injury risk and is commonly used for windows needing high impact resistance and thermal stability. Both types improve window durability but offer distinct benefits in safety, noise reduction, and structural integrity.
Understanding Laminated Glass: Structure and Properties
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances its strength and safety by holding the shards in place upon impact. This structure provides superior sound insulation, UV protection, and improved resistance to penetration compared to tempered glass. Laminated glass is favored for windows requiring enhanced security, support against breakage, and reduced risk of injury from shattered glass.
What is Tempered Glass? Key Characteristics
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is characterized by its ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing the risk of injury. This glass is commonly used in windows where enhanced durability and safety are essential, such as in automotive, architectural, and security applications.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded by an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance by holding shards in place upon breakage. Tempered glass is heat-treated to enhance strength, making it four to five times stronger than standard glass and resistant to sudden impacts. While tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces for safety, laminated glass maintains its integrity under high impact, making it ideal for security and safety-critical window applications.
Safety Features: Which Glass Offers Better Protection?
Laminated glass provides superior safety features for windows by holding shattered pieces together with an interlayer, preventing dangerous shards from dispersing during impact. Tempered glass, while stronger and designed to break into small, less harmful fragments, may still pose a risk of injury upon breaking. For enhanced protection against break-ins, accidents, and severe weather, laminated glass offers better overall safety performance in window applications.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Differences
Laminated glass outperforms tempered glass in acoustic insulation due to its interlayer that dampens sound transmission, making it ideal for noise reduction in windows. Thermal insulation is enhanced in laminated glass as the interlayer minimizes heat transfer, providing better energy efficiency compared to tempered glass. Tempered glass offers superior strength and impact resistance but lacks the soundproofing and thermal performance advantages inherent to laminated glass.
Security Benefits: Breakage and Intrusion Resistance
Laminated glass offers superior security benefits by holding together upon impact due to its interlayer, significantly reducing the risk of shattering and preventing easy access during break-ins. Tempered glass, though stronger than standard glass and resistant to thermal stress, breaks into small, blunt pieces that can still allow intrusion if force is applied. For enhanced breakage and intrusion resistance in windows, laminated glass provides a more reliable barrier against forced entry and accidental impacts.
Cost Analysis: Laminated vs Tempered Glass
Laminated glass typically costs 20-30% more than tempered glass due to its multi-layered structure and enhanced safety features. Tempered glass offers a more budget-friendly option, ideal for standard window applications, while laminated glass delivers superior sound insulation and impact resistance, justifying the higher price in high-security or noise-sensitive environments. Long-term savings with laminated glass arise from its durability and ability to remain intact when broken, reducing replacement frequency compared to tempered glass.
Best Applications for Each Glass Type
Laminated glass is ideal for areas requiring enhanced safety, sound insulation, and UV protection, making it perfect for skylights, skylight windows, and glass facades. Tempered glass excels in applications demanding high strength and impact resistance, such as side windows, shower doors, and sliding glass doors. Selecting laminated glass ensures durability and noise reduction, while tempered glass provides robust shatterproof performance in high-traffic or safety-critical zones.
How to Choose the Right Glass for Your Windows
Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and sound insulation by holding shards together upon impact, making it ideal for windows in high-traffic or security-sensitive areas. Tempered glass is stronger and more resistant to thermal stress, providing greater durability and safety through shattering into small, less harmful pieces when broken. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing safety needs, energy efficiency, and noise reduction, with laminated glass preferred for security and soundproofing, while tempered glass suits environments requiring high strength and heat resistance.
Infographic: Laminated glass vs Tempered glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com