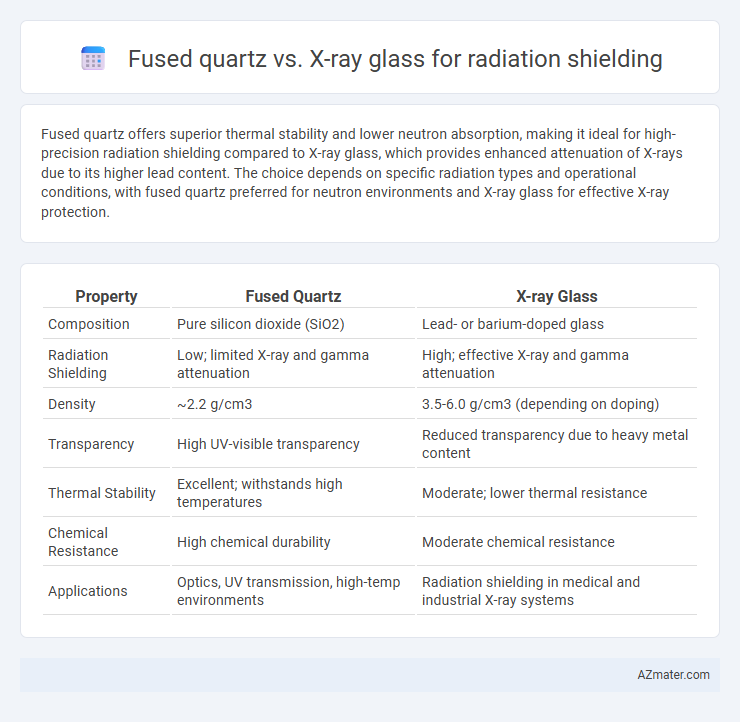
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and lower neutron absorption, making it ideal for high-precision radiation shielding compared to X-ray glass, which provides enhanced attenuation of X-rays due to its higher lead content. The choice depends on specific radiation types and operational conditions, with fused quartz preferred for neutron environments and X-ray glass for effective X-ray protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | X-ray Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Lead- or barium-doped glass |
| Radiation Shielding | Low; limited X-ray and gamma attenuation | High; effective X-ray and gamma attenuation |
| Density | ~2.2 g/cm3 | 3.5-6.0 g/cm3 (depending on doping) |
| Transparency | High UV-visible transparency | Reduced transparency due to heavy metal content |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent; withstands high temperatures | Moderate; lower thermal resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | High chemical durability | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Applications | Optics, UV transmission, high-temp environments | Radiation shielding in medical and industrial X-ray systems |
Introduction: Importance of Radiation Shielding Materials
Radiation shielding materials like fused quartz and X-ray glass are vital for protecting sensitive equipment and personnel from harmful ionizing radiation. Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature environments, while X-ray glass provides superior attenuation of X-ray and gamma radiation due to its heavy metal oxide content. Selecting the appropriate material depends on balancing factors such as radiation energy, material thickness, and mechanical properties to ensure effective and reliable shielding.
Overview of Fused Quartz in Radiation Shielding
Fused quartz offers excellent radiation shielding properties due to its high purity and low thermal expansion, making it resistant to radiation-induced damage and suitable for high-precision environments. Its ability to effectively absorb and block certain wavelengths of ionizing radiation, especially ultraviolet and X-rays, provides reliable protection in medical and scientific applications. Compared to X-ray glass, fused quartz maintains clarity and structural integrity under prolonged radiation exposure, ensuring durability and consistent performance.
Overview of X-ray Glass for Radiation Protection
X-ray glass for radiation protection is engineered with high lead oxide content to effectively absorb and attenuate X-ray and gamma radiation, making it ideal for medical and industrial shielding applications. Compared to fused quartz, X-ray glass offers superior density and radiation attenuation properties, reducing exposure while maintaining optical clarity. Its tailored composition allows for customization in thickness and lead concentration to meet specific radiation protection standards.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Fused quartz, primarily composed of highly pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with an amorphous, non-crystalline structure, offers excellent thermal stability and moderate radiation shielding due to its low atomic number elements. In contrast, X-ray glass contains heavy metal oxides such as lead oxide (PbO) or bismuth oxide (Bi2O3) integrated into a silica-based matrix, enhancing its density and significantly increasing attenuation of X-ray and gamma radiation. The material structure of X-ray glass, combining a dense, heavy metal-rich composition with a glassy network, provides superior radiation shielding performance compared to the more uniform but less dense fused quartz.
Radiation Attenuation Efficiency: Fused Quartz vs X-ray Glass
Fused quartz exhibits lower radiation attenuation efficiency compared to X-ray glass due to its predominantly silicon dioxide composition, which provides limited density for effective shielding. X-ray glass, often doped with heavy metal oxides like lead oxide or barium oxide, offers superior attenuation of X-rays and gamma rays by increasing photon absorption and scattering probabilities. The higher atomic number and density of X-ray glass enable significantly better radiation shielding performance, making it preferable for applications requiring enhanced protection against ionizing radiation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Fused quartz exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to standard X-ray glass, making it more resistant to cracking and deformation under high stress conditions commonly encountered in radiation shielding applications. Its durability is enhanced by a high melting point and low thermal expansion coefficient, ensuring long-term dimensional stability and resistance to thermal shock. In contrast, X-ray glass, while effective in attenuating radiation, typically has lower mechanical toughness and may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, maintaining stability against acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly suitable for harsh radiation shielding environments. X-ray glass, while effective in radiation attenuation, generally has lower chemical resistance and can degrade when exposed to corrosive substances over time. The environmental stability of fused quartz outperforms X-ray glass, with superior resistance to thermal shock and long-term environmental factors, ensuring durable performance in radiation shielding applications.
Transparency and Optical Properties in Shielding Applications
Fused quartz offers superior optical transparency across a broad spectrum, including ultraviolet to near-infrared wavelengths, making it ideal for radiation shielding applications requiring clear visibility. X-ray glass, while providing effective radiation attenuation due to its high lead content, generally exhibits lower transparency and may have distortion or color tinting that affects optical clarity. The choice between fused quartz and X-ray glass balances the need for maximal radiation shielding effectiveness with the demand for optical performance in precise imaging or viewing environments.
Cost-effectiveness and Availability
Fused quartz offers superior radiation shielding with high purity and thermal stability, but its cost is significantly higher compared to standard X-ray glass, making it less cost-effective for large-scale applications. X-ray glass provides adequate protection at a lower price point and is widely available, making it a practical choice for budget-sensitive projects. Availability of fused quartz is limited due to its specialized production process, whereas X-ray glass is more accessible through numerous suppliers globally.
Choosing the Right Material: Application-based Recommendations
Fused quartz offers superior transparency and thermal stability, making it ideal for optical applications requiring minimal radiation distortion, while X-ray glass provides enhanced radiation absorption due to higher lead content, suitable for medical and industrial shielded viewing windows. When selecting materials for radiation shielding, consider application-specific factors such as radiation type, intensity, and visibility requirements to balance protection with clarity. For high-dose X-ray environments, X-ray glass offers better attenuation, whereas fused quartz is preferable in environments demanding precise optical performance alongside moderate shielding.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs X-ray glass for Radiation shielding
 azmater.com
azmater.com