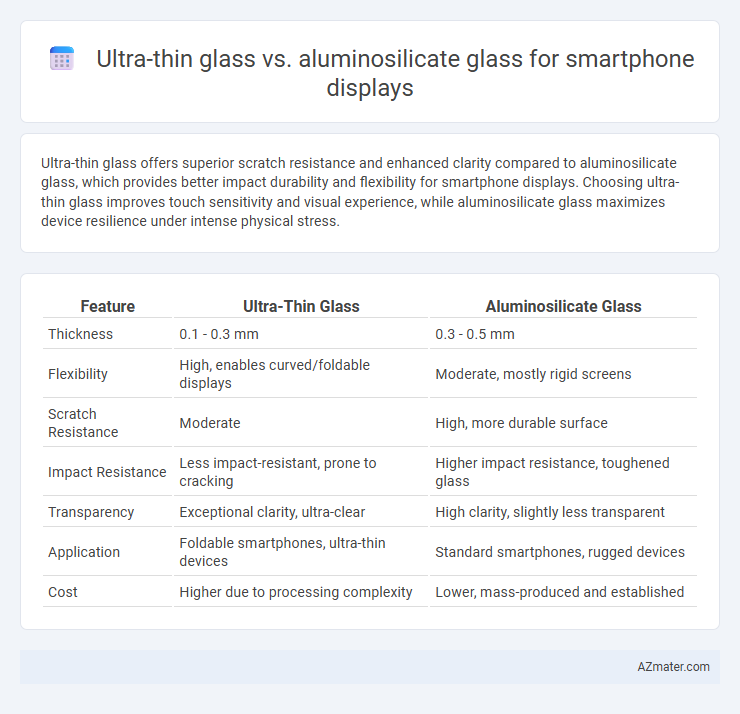
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass, which provides better impact durability and flexibility for smartphone displays. Choosing ultra-thin glass improves touch sensitivity and visual experience, while aluminosilicate glass maximizes device resilience under intense physical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Thin Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.1 - 0.3 mm | 0.3 - 0.5 mm |
| Flexibility | High, enables curved/foldable displays | Moderate, mostly rigid screens |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High, more durable surface |
| Impact Resistance | Less impact-resistant, prone to cracking | Higher impact resistance, toughened glass |
| Transparency | Exceptional clarity, ultra-clear | High clarity, slightly less transparent |
| Application | Foldable smartphones, ultra-thin devices | Standard smartphones, rugged devices |
| Cost | Higher due to processing complexity | Lower, mass-produced and established |
Introduction to Smartphone Display Glass Types
Ultra-thin glass offers superior flexibility and enhanced scratch resistance compared to traditional Aluminosilicate glass, making it ideal for curved and foldable smartphone displays. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its robust chemical composition and high tensile strength, provides excellent durability and impact resistance for standard flat screens. Both materials contribute to improved screen clarity and touch sensitivity, but ultra-thin glass leads in innovation for next-generation smartphone designs.
What is Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG)?
Ultra-Thin Glass (UTG) is a specialized form of glass engineered to be extremely thin, typically measuring between 30 to 100 microns, enhancing flexibility and durability for smartphone displays, especially foldable models. Unlike traditional Aluminosilicate glass, which is thicker and offers high scratch resistance, UTG combines the rigidity of glass with the pliability required for bending without compromising display clarity or touch responsiveness. Its ultra-thin profile allows manufacturers to create sleek, lightweight devices with improved screen resilience against scratches and impacts in foldable smartphones.
Understanding Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass, primarily composed of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offers exceptional strength and scratch resistance compared to ultra-thin glass, making it ideal for smartphone displays requiring durability and clarity. Its chemical composition improves thermal and mechanical properties, allowing it to withstand impact and reduce breakage risk, which is crucial for high-performance mobile devices. This glass type also provides superior resistance to environmental factors such as heat and corrosion, enhancing the lifespan of smartphone screens.
Mechanical Strength: UTG vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to aluminosilicate glass, offering enhanced resistance to scratches and impacts due to its uniform thickness and chemical composition. UTG's higher tensile strength and flexibility reduce the likelihood of cracks and fractures during drops, making it ideal for foldable and curved smartphone displays. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable, typically has lower fracture toughness and is more prone to damage under high stress or bending conditions.
Flexibility and Bendability Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers superior rigidity and scratch resistance but has limited flexibility compared to aluminosilicate glass, which demonstrates enhanced bendability and impact absorption due to its chemically strengthened composition. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in flexible smartphone displays, withstands repeated bending cycles without cracking, making it ideal for foldable device screens. The inherent flexibility of aluminosilicate glass supports advanced curved display designs, whereas ultra-thin glass is more prone to breakage under stress despite its thinness.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its high surface hardness and enhanced chemical strengthening processes, making it less prone to everyday abrasions compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass provides better impact resistance, thanks to its robust molecular structure that absorbs shocks and reduces crack propagation under sudden drops. Combining ultra-thin glass with aluminosilicate layers or coatings can optimize both scratch and impact resistance for smartphone displays.
Thickness and Weight Implications
Ultra-thin glass for smartphone displays typically measures between 30 to 100 microns in thickness, significantly slimmer than aluminosilicate glass which generally ranges from 100 to 200 microns. The reduced thickness of ultra-thin glass directly results in lighter device weight, enhancing portability without compromising structural integrity. Aluminosilicate glass, while thicker, offers robust scratch resistance and durability, but this added thickness increases overall device weight compared to ultra-thin glass options.
Optical Clarity and Display Quality
Ultra-thin glass offers superior optical clarity with higher light transmittance and reduced haze, enhancing display brightness and color accuracy compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable, often exhibits slightly lower transparency and can impact contrast and sharpness under direct sunlight. The enhanced optical properties of ultra-thin glass contribute to a more vivid and immersive smartphone display experience, crucial for 4K and HDR content viewing.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ultra-thin glass offers superior scratch resistance and higher optical clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass, but it demands more complex manufacturing processes that elevate production costs. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone displays like Corning Gorilla Glass, balances durability and affordability due to established, cost-efficient mass production techniques. Choosing between these materials depends heavily on the targeted device price point and production scalability, with aluminosilicate preferred for budget-friendly models and ultra-thin glass reserved for premium smartphones requiring enhanced aesthetics and robustness.
Future Trends in Smartphone Display Glass
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced durability and flexibility, enabling foldable and curved smartphone displays with higher scratch resistance compared to conventional aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass remains popular for its balance of strength, cost-efficiency, and damage resistance, but future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid materials combining ultra-thin glass with advanced coatings for improved clarity and impact absorption. Emerging innovations focus on integrating ultra-thin glass with next-generation OLED and MicroLED technologies to deliver ultra-slim, lightweight smartphones with superior tactile sensitivity and breakage resistance.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone display
 azmater.com
azmater.com