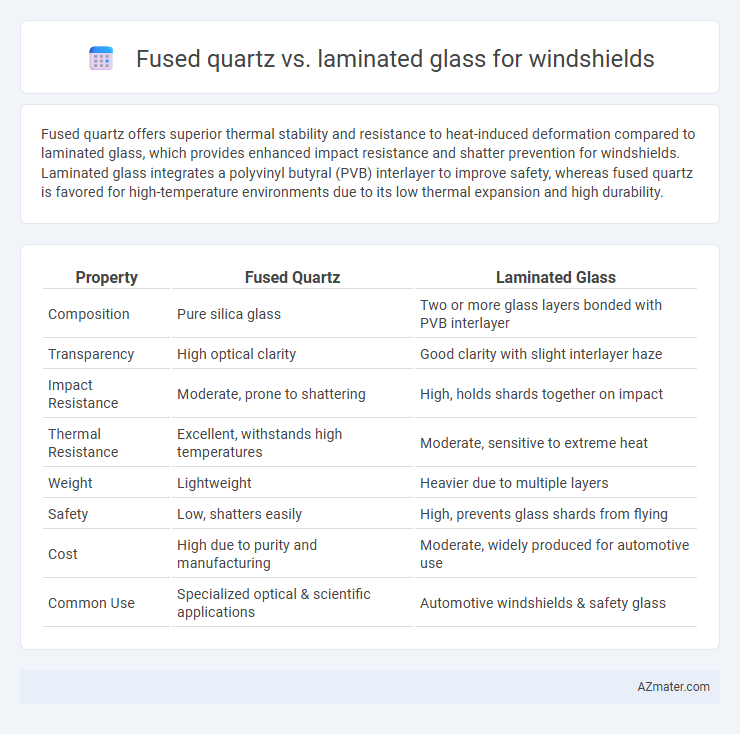
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and resistance to heat-induced deformation compared to laminated glass, which provides enhanced impact resistance and shatter prevention for windshields. Laminated glass integrates a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer to improve safety, whereas fused quartz is favored for high-temperature environments due to its low thermal expansion and high durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silica glass | Two or more glass layers bonded with PVB interlayer |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Good clarity with slight interlayer haze |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, prone to shattering | High, holds shards together on impact |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands high temperatures | Moderate, sensitive to extreme heat |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Safety | Low, shatters easily | High, prevents glass shards from flying |
| Cost | High due to purity and manufacturing | Moderate, widely produced for automotive use |
| Common Use | Specialized optical & scientific applications | Automotive windshields & safety glass |
Introduction: Fused Quartz vs Laminated Glass
Fused quartz and laminated glass serve different purposes in windshield applications, with fused quartz offering exceptional thermal resistance and durability due to its high purity silica composition. Laminated glass, commonly used in vehicle windshields, consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. The choice between fused quartz and laminated glass hinges on factors such as heat resistance requirements and impact safety standards in automotive design.
Material Composition and Structure
Fused quartz windshield material consists of pure silica with a non-crystalline structure that offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. Laminated glass is composed of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering upon impact. The material composition of fused quartz ensures superior clarity and durability under extreme conditions, while laminated glass structure prioritizes safety and impact absorption for automotive applications.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Fused quartz windshields are produced by melting high-purity silica at temperatures exceeding 1700degC, resulting in a non-crystalline, homogeneous glass known for its exceptional thermal stability and optical clarity. Laminated glass manufacturing involves layering two or more glass sheets with a polymer interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which is then subjected to heat and pressure to bond the layers securely, enhancing impact resistance and safety. The fundamental difference lies in fused quartz's single-material high-temperature melting process versus laminated glass's multi-layer assembly with polymer bonding under controlled thermal and pressure conditions.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity and transparency due to its low thermal expansion and high purity, reducing distortion and improving visibility in automotive windshields. Laminated glass, while providing enhanced safety with its polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, often exhibits slightly reduced optical clarity caused by the multiple layers and potential for minor imperfections. For applications prioritizing maximum transparency and minimal optical distortion, fused quartz outperforms laminated glass, particularly in high-precision automotive windshield manufacturing.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Fused quartz offers exceptional impact resistance and durability due to its high tensile strength and thermal stability, making it highly resistant to cracking under stress or extreme temperatures. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced shatter resistance by absorbing and dispersing impact forces, preventing shards from causing injury. While fused quartz excels in high-impact, heat-resistant applications, laminated glass remains the industry standard for automotive windshields due to its superior ability to maintain structural integrity upon impact.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional thermal stability and heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC without deformation, making it ideal for high-heat applications in windshields. Laminated glass, typically composed of layers of glass and polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offers moderate heat resistance but can delaminate or warp at temperatures above 150degC. Fused quartz windshields provide superior performance under extreme thermal stress compared to laminated glass, ensuring enhanced durability and safety in high-temperature environments.
UV Protection Capabilities
Fused quartz offers superior UV protection due to its high purity silica composition, effectively blocking nearly all ultraviolet radiation and preventing damage to the vehicle's interior and occupants. Laminated glass incorporates a PVB or EVA interlayer that absorbs a significant portion of UV rays but typically allows more UV transmission compared to fused quartz. For enhanced UV protection in windshields, fused quartz outperforms laminated glass in filtering harmful ultraviolet light and reducing potential health risks from prolonged sun exposure.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Fused quartz windshields are significantly more expensive than laminated glass due to high manufacturing costs and limited production scale, making them less feasible for mass-market vehicles. Laminated glass is widely available and cost-effective, produced extensively with established supply chains, ensuring easy replacement and repair. The cost difference can be up to several times, with laminated glass typically priced between $100 to $400, while fused quartz options may exceed $1000 due to its enhanced durability and thermal resistance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Fused quartz offers superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability, making it environmentally durable and less prone to degradation compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass enhances safety by preventing shattering and retaining its structure upon impact, reducing injury risk during accidents. Environmental impact favors fused quartz due to its longer lifespan and recyclability, whereas laminated glass often requires specialized disposal processes because of its interlayer materials.
Applications and Future Trends in Windshield Technology
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for advanced automotive windshields requiring durability under extreme temperatures. Laminated glass, integrating plastic interlayers, ensures enhanced impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering, widely used in conventional vehicle windshields. Future trends focus on integrating smart technologies such as augmented reality displays and improved sensor embedding, with materials like fused quartz expected to play a critical role due to their optical clarity and robustness.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com