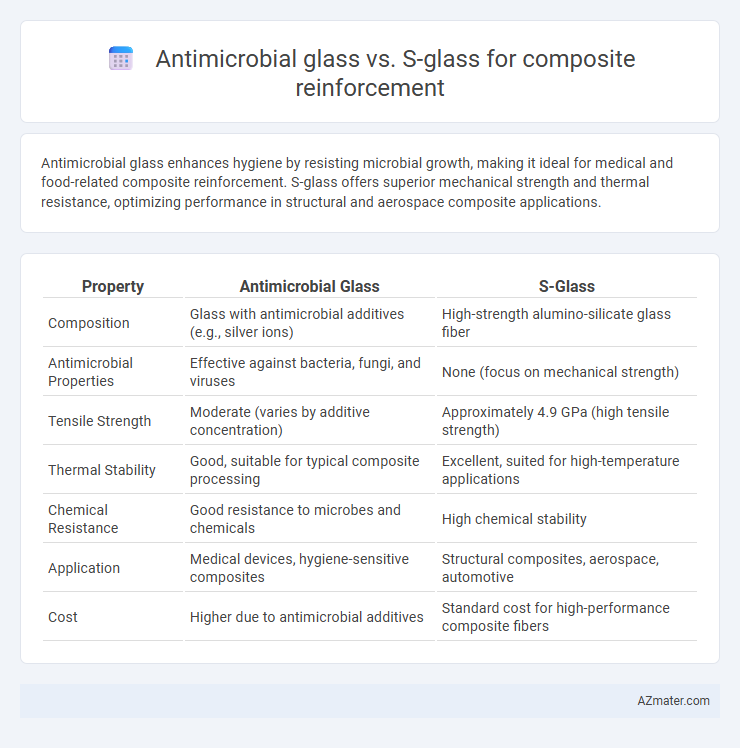
Antimicrobial glass enhances hygiene by resisting microbial growth, making it ideal for medical and food-related composite reinforcement. S-glass offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, optimizing performance in structural and aerospace composite applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Antimicrobial Glass | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glass with antimicrobial additives (e.g., silver ions) | High-strength alumino-silicate glass fiber |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Effective against bacteria, fungi, and viruses | None (focus on mechanical strength) |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (varies by additive concentration) | Approximately 4.9 GPa (high tensile strength) |
| Thermal Stability | Good, suitable for typical composite processing | Excellent, suited for high-temperature applications |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to microbes and chemicals | High chemical stability |
| Application | Medical devices, hygiene-sensitive composites | Structural composites, aerospace, automotive |
| Cost | Higher due to antimicrobial additives | Standard cost for high-performance composite fibers |
Overview of Composite Reinforcement Materials
Antimicrobial glass and S-glass are key materials used in composite reinforcement, offering distinct advantages for structural applications. Antimicrobial glass incorporates agents that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing durability and hygiene in composite products, while S-glass, known for its high tensile strength and thermal resistance, provides superior mechanical performance in demanding environments. Both materials improve composite reinforcement by increasing strength, durability, and environmental resistance, with antimicrobial glass adding a functional benefit in sectors requiring contamination control.
Introduction to Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass incorporates chemical agents such as silver or copper ions that inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing the hygiene and durability of composite materials. It offers superior resistance to microbial colonization compared to traditional S-glass, which primarily provides mechanical strength and heat resistance. The integration of antimicrobial glass in composites improves long-term performance in medical, marine, and construction applications by reducing biofouling and contamination risks.
What is S-Glass?
S-Glass is a high-strength, high-modulus glass fiber primarily used for composite reinforcement due to its superior tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to standard E-glass. It offers enhanced durability and improved mechanical properties, making it ideal for aerospace, military, and industrial applications where performance and damage tolerance are critical. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which focuses on inhibiting microbial growth, S-Glass is engineered specifically for structural integrity and load-bearing efficiency in composite materials.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Antimicrobial glass exhibits enhanced resistance to microbial growth and chemical degradation, making it highly suitable for hygienic applications in composite reinforcement, whereas S-glass provides superior tensile strength and thermal stability, essential for high-performance structural components. The antimicrobial glass typically offers moderate stiffness and durability, while S-glass features higher modulus of elasticity and impact resistance, optimizing it for aerospace and automotive composites. Both materials differ significantly in their interfacial bonding characteristics with resin matrices, influencing composite longevity and mechanical performance.
Antimicrobial Mechanisms in Reinforcement
Antimicrobial glass incorporates metal ions such as silver or copper that disrupt microbial cell membranes and inhibit biofilm formation, enhancing the longevity and hygiene of composite reinforcements. In contrast, S-glass primarily offers superior mechanical strength without inherent antimicrobial properties, relying on physical durability rather than microbial inhibition. The integration of antimicrobial mechanisms within glass fibers significantly reduces bacterial colonization, making antimicrobial glass a preferred choice in composite reinforcement for medical and hygiene-critical applications.
Mechanical Performance: Antimicrobial Glass vs S-Glass
Antimicrobial glass demonstrates comparable tensile strength and modulus to traditional S-glass, with enhanced resistance to microbial degradation that preserves composite integrity over time. S-glass offers superior stiffness and high impact resistance crucial for load-bearing applications but lacks the infection control properties of antimicrobial glass. The integration of antimicrobial agents in glass fibers slightly modifies mechanical properties, yet maintains performance within acceptable engineering parameters for long-term composite reinforcement.
Durability and Longevity in Composite Structures
Antimicrobial glass enhances composite reinforcement by reducing microbial degradation, thereby improving durability and extending the service life of composite structures in harsh environments. S-glass offers superior mechanical strength and resistance to chemical attack, contributing to long-term stability under high stress and corrosive conditions. Combining antimicrobial properties with S-glass reinforcement results in composites that maintain structural integrity and longevity, especially in applications exposed to microbial and chemical challenges.
Applications in Industry and Healthcare
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced resistance to microbial growth, making it ideal for healthcare environments where infection control is critical, such as in surgical instruments and hospital equipment. S-glass provides superior tensile strength and thermal stability, benefiting aerospace, automotive, and industrial composite reinforcements that demand high mechanical performance and durability. Industries requiring both hygiene and mechanical robustness increasingly integrate antimicrobial coatings with S-glass composites to optimize safety and structural integrity.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Antimicrobial glass incorporates biocidal agents that reduce microbial growth, enhancing hygiene and safety in composite applications, making it ideal for medical and food-related environments. S-glass provides superior mechanical strength and impact resistance but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, requiring additional coatings for microbial protection. Environmentally, antimicrobial glass can reduce the need for chemical disinfectants, lowering environmental impact, whereas S-glass is more energy-intensive to produce and recycle.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Reinforcement
Antimicrobial glass in composite reinforcement provides enhanced durability and resistance to microbial degradation, crucial for medical and marine applications. Future trends indicate increased integration of nanotechnology to improve antimicrobial efficacy and mechanical performance while maintaining biocompatibility. Innovations focus on hybrid composites combining S-glass fibers' high tensile strength with antimicrobial coatings to create multifunctional materials with superior longevity and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs S-glass for Composite reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com