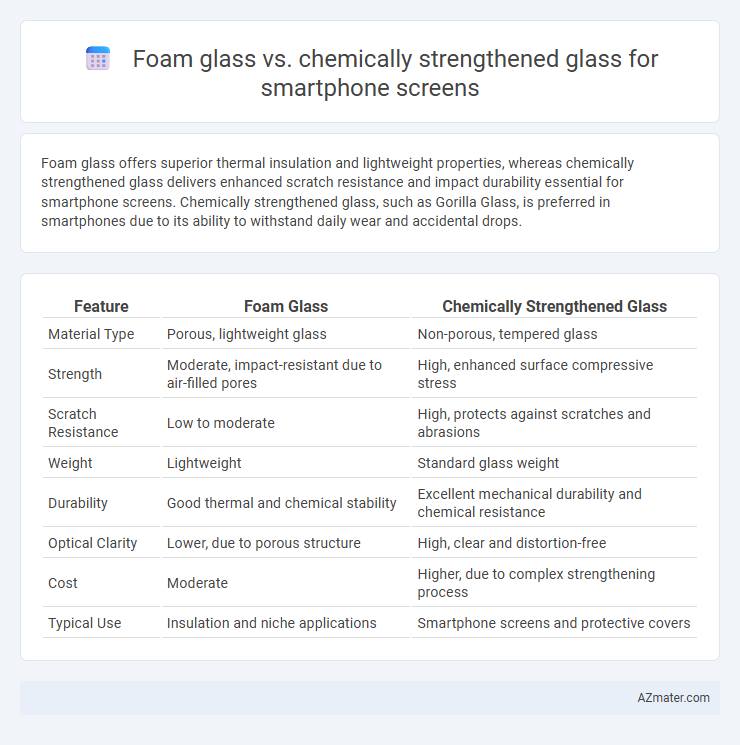
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, whereas chemically strengthened glass delivers enhanced scratch resistance and impact durability essential for smartphone screens. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, is preferred in smartphones due to its ability to withstand daily wear and accidental drops.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Glass | Chemically Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous, lightweight glass | Non-porous, tempered glass |
| Strength | Moderate, impact-resistant due to air-filled pores | High, enhanced surface compressive stress |
| Scratch Resistance | Low to moderate | High, protects against scratches and abrasions |
| Weight | Lightweight | Standard glass weight |
| Durability | Good thermal and chemical stability | Excellent mechanical durability and chemical resistance |
| Optical Clarity | Lower, due to porous structure | High, clear and distortion-free |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher, due to complex strengthening process |
| Typical Use | Insulation and niche applications | Smartphone screens and protective covers |
Overview of Smartphone Screen Materials
Foam glass and chemically strengthened glass serve distinct roles in smartphone screen technology, with chemically strengthened glass being the prevalent choice due to its enhanced durability and scratch resistance provided by ion exchange processes. Foam glass, primarily used in insulation and lightweight construction, lacks the structural integrity and optical clarity required for smartphone displays. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, offers superior impact resistance and maintains touchscreen sensitivity, making it ideal for modern smartphones.
Introduction to Foam Glass Technology
Foam glass technology utilizes a lightweight, porous structure created by heating glass with foaming agents, resulting in exceptional thermal insulation and mechanical strength. In contrast, chemically strengthened glass enhances smartphone screens by ion-exchanging smaller ions with larger ones on the surface, significantly increasing scratch resistance and durability. Foam glass's unique cellular composition offers distinct advantages in cushioning and impact absorption compared to the dense, rigid nature of chemically strengthened glass commonly used in smartphone displays.
Understanding Chemically Strengthened Glass
Chemically strengthened glass for smartphone screens undergoes an ion-exchange process, replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions on the glass surface, which induces compressive stress and enhances durability against scratches and impacts. Unlike foam glass, which is primarily used for insulation due to its cellular structure and low density, chemically strengthened glass maintains optical clarity and touch sensitivity crucial for display performance. The superior mechanical strength and resistance to damage make chemically strengthened glass the preferred material for modern smartphone screen protection.
Key Material Properties: Foam vs Chemically Strengthened Glass
Foam glass offers lightweight and excellent thermal insulation properties with high compressive strength but lacks the scratch resistance and optical clarity required for smartphone screens. Chemically strengthened glass, typically aluminosilicate glass, provides superior hardness, scratch resistance, and enhanced mechanical strength due to ion-exchange processes, making it ideal for durable and transparent smartphone displays. The choice depends on the need for impact resistance and clarity, where chemically strengthened glass outperforms foam glass in maintaining screen integrity and user experience.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, undergoes an ion-exchange process that significantly enhances its surface compressive stress, resulting in superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to foam glass. Foam glass, characterized by its cellular structure, provides lightweight cushioning and thermal insulation but lacks the high tensile strength and surface hardness required for smartphone screen protection. Therefore, chemically strengthened glass remains the preferred choice for smartphone screens due to its optimized balance of strength, toughness, and resistance to everyday wear and tear.
Scratch and Impact Resistance Analysis
Foam glass offers superior impact resistance due to its cellular structure that absorbs shock effectively, making it less prone to shattering upon drops. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, excels in scratch resistance with a compressive stress layer that prevents surface cracks and scratches from everyday use. While foam glass provides enhanced durability against impacts, chemically strengthened glass remains the benchmark for maintaining a clear, scratch-free smartphone screen.
Optical Clarity and Display Performance
Foam glass, with its porous structure, generally offers lower optical clarity compared to chemically strengthened glass, which is designed to maintain high transparency and minimal light distortion for smartphone screens. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes ion-exchange processes that enhance surface durability while preserving excellent display brightness and color accuracy. Foam glass's light scattering properties reduce display sharpness, making chemically strengthened glass the preferred choice for superior optical clarity and optimal display performance in smartphones.
Weight, Thickness, and Design Flexibility
Foam glass offers superior lightweight properties and increased thickness tolerance, making it ideal for robust smartphone cases without compromising durability. Chemically strengthened glass excels in ultra-thin profiles and provides exceptional design flexibility due to its ability to resist scratches and impacts while maintaining a sleek appearance. Weight reduction is more significant with foam glass, whereas chemically strengthened glass focuses on combining thinness with mechanical resilience for high-performance smartphone screens.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Foam glass offers a lower material cost and simpler manufacturing process compared to chemically strengthened glass, making it attractive for budget smartphone screens. Chemically strengthened glass requires complex ion-exchange treatments that increase production time and expenses but provides superior scratch resistance and durability. The choice between foam glass and chemically strengthened glass hinges on balancing material costs with performance needs in high-volume smartphone manufacturing.
Future Trends in Smartphone Screen Materials
Foam glass offers enhanced impact resistance and lightweight properties, making it a promising material for future smartphone screens focused on durability and portability. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, continues to evolve with improved scratch resistance and higher tensile strength, supporting thinner and more flexible displays. Innovations combining foam glass's cellular structure with chemical strengthening techniques could drive next-generation screens that maximize both toughness and design versatility in upcoming smartphones.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Chemically strengthened glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com