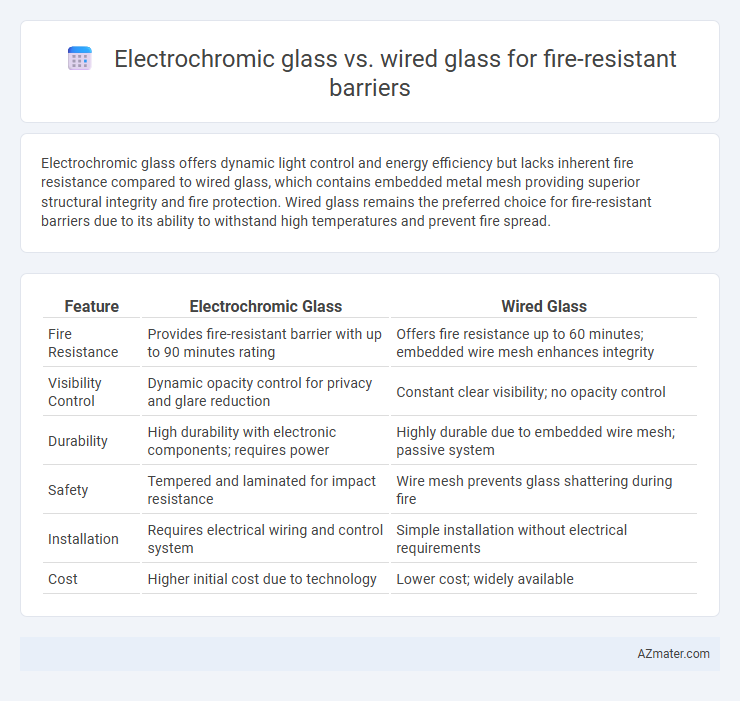
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and energy efficiency but lacks inherent fire resistance compared to wired glass, which contains embedded metal mesh providing superior structural integrity and fire protection. Wired glass remains the preferred choice for fire-resistant barriers due to its ability to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Provides fire-resistant barrier with up to 90 minutes rating | Offers fire resistance up to 60 minutes; embedded wire mesh enhances integrity |
| Visibility Control | Dynamic opacity control for privacy and glare reduction | Constant clear visibility; no opacity control |
| Durability | High durability with electronic components; requires power | Highly durable due to embedded wire mesh; passive system |
| Safety | Tempered and laminated for impact resistance | Wire mesh prevents glass shattering during fire |
| Installation | Requires electrical wiring and control system | Simple installation without electrical requirements |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to technology | Lower cost; widely available |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Barriers
Fire-resistant barriers are critical components in building safety, designed to prevent the spread of fire and smoke while maintaining structural integrity. Electrochromic glass offers dynamic opacity control with fire-resistance properties, enabling both visibility and thermal protection, whereas wired glass provides a traditional, reinforced solution with embedded wire mesh to resist breakage and contain flames. Selection depends on balancing aesthetic versatility, fire rating requirements, and compliance with fire safety codes such as NFPA 80 and ASTM E119.
What Is Electrochromic Glass?
Electrochromic glass is a smart glass technology that changes its tint when an electrical voltage is applied, enabling dynamic control of light and heat transmission while maintaining fire-resistant barrier properties. Unlike wired glass, which contains embedded wire mesh for structural integrity during fire exposure, electrochromic glass enhances energy efficiency and occupant comfort without compromising safety standards. This glass type integrates advanced coatings and materials to meet fire resistance ratings, making it a versatile choice for modern fire-rated glazing systems.
Understanding Wired Glass
Wired glass is a type of fire-resistant barrier known for its embedded metal mesh that helps maintain glass integrity during high-temperature exposure, preventing shattering and fire spread. Unlike electrochromic glass, which primarily offers light and privacy control through electrical tinting, wired glass provides superior fire protection by withstanding flames and heat for up to 45 minutes or more, meeting strict fire safety codes. Its durability and compliance with NFPA 80 and UL 972 standards make wired glass a reliable choice for fire-rated partitions in commercial and industrial buildings.
Fire Resistance Capabilities: Electrochromic vs Wired Glass
Electrochromic glass offers limited fire resistance, primarily providing thermal insulation and visibility control but failing to meet strict fire barrier standards. Wired glass, embedded with a metal mesh, meets high fire-resistant ratings by preventing glass breakage and maintaining barrier integrity during fire exposure. Fire-resistant wired glass typically withstands temperatures up to 1,200degF (650degC) for durations ranging from 20 to 90 minutes, outperforming electrochromic glass in fire containment applications.
Safety and Impact Resistance Comparison
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic opacity control, enhancing fire safety by reducing glare and heat transmission while maintaining visibility during emergencies. Wired glass, traditionally used for fire-resistant barriers, provides superior impact resistance through embedded wire mesh that prevents shattering and maintains structural integrity under thermal stress. In terms of safety, wired glass excels in impact resistance and fire containment, whereas electrochromic glass contributes to occupant comfort and energy efficiency but may require additional protective treatments to match wired glass's durability in fire scenarios.
Aesthetic and Functional Differences
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and privacy by changing transparency with an electric signal, enhancing aesthetic versatility in fire-resistant barriers. Wired glass features embedded metal mesh for structural integrity and fire resistance but limits design flexibility due to its opaque, industrial appearance. While electrochromic glass balances safety with modern, sleek visuals, wired glass prioritizes robust fire protection at the expense of visual appeal and adaptability.
Energy Efficiency and Light Control Features
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic energy efficiency by electrically tinting to regulate solar heat gain and reduce cooling costs, enhancing fire-resistant barriers without compromising visibility. Wired glass, while traditionally valued for its fire resistance and structural integrity, lacks light control and energy-saving capabilities, remaining static in performance. Integrating electrochromic technology in fire-resistant barriers optimizes daylight management and thermal insulation, providing a smart, energy-efficient alternative to conventional wired glass.
Cost Considerations and Installation
Electrochromic glass typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to wired glass due to advanced technology and integrated electronics, with prices influenced by factors like size and control systems. Wired glass offers a more budget-friendly option with simpler installation processes, requiring standard framing and minimal electrical integration, reducing labor expenses. Installation of electrochromic glass demands specialized expertise for electrical wiring and control setup, extending installation time and costs, whereas wired glass can be installed faster with conventional glazing contractors.
Code Compliance and Standards for Fire Barriers
Electrochromic glass and wired glass both serve as fire-resistant barriers, but their compliance with fire safety codes varies significantly. Wired glass meets ASTM E119 and NFPA 80 standards for fire resistance and is widely accepted for use in fire-rated assemblies due to its ability to withstand high temperatures without breaking. Electrochromic glass, while offering dynamic shading and energy efficiency benefits, must be specifically rated and tested under UL 972 or similar fire performance standards to ensure code compliance, often limiting its use in certified fire barriers.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire-Resistant Applications
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control and enhanced energy efficiency, making it suitable for modern fire-resistant barriers where visibility and aesthetics matter alongside safety. Wired glass provides superior fire resistance by preventing glass breakage and maintaining barrier integrity under high temperatures, complying with stringent fire code requirements. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing fire safety standards, mechanical performance, and design preferences specific to the application environment.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Wired glass for Fire-resistant barrier
 azmater.com
azmater.com