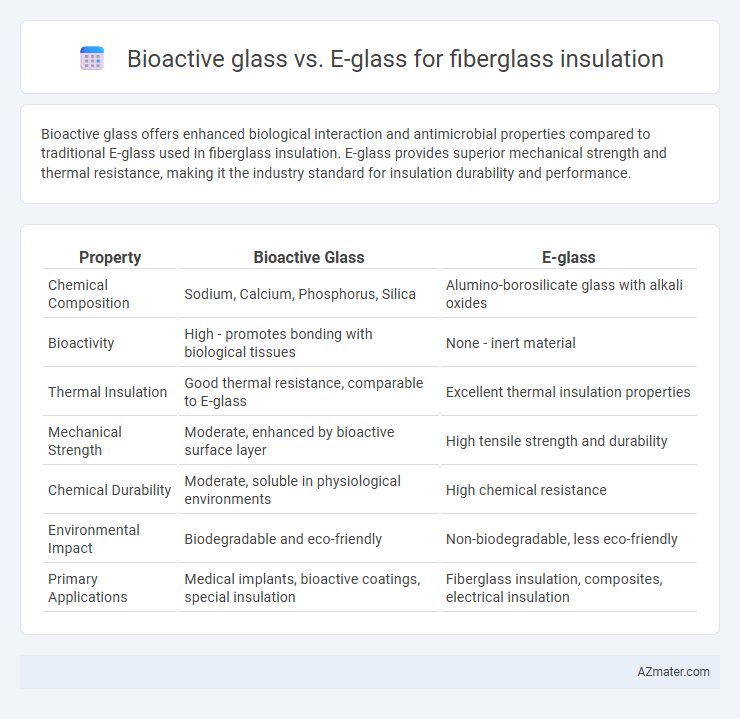
Bioactive glass offers enhanced biological interaction and antimicrobial properties compared to traditional E-glass used in fiberglass insulation. E-glass provides superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making it the industry standard for insulation durability and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioactive Glass | E-glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Sodium, Calcium, Phosphorus, Silica | Alumino-borosilicate glass with alkali oxides |
| Bioactivity | High - promotes bonding with biological tissues | None - inert material |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal resistance, comparable to E-glass | Excellent thermal insulation properties |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, enhanced by bioactive surface layer | High tensile strength and durability |
| Chemical Durability | Moderate, soluble in physiological environments | High chemical resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, less eco-friendly |
| Primary Applications | Medical implants, bioactive coatings, special insulation | Fiberglass insulation, composites, electrical insulation |
Introduction to Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation primarily utilizes E-glass, a silica-based glass fiber known for its high tensile strength, thermal resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for building insulation. Bioactive glass, while commonly used in medical applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to bond with living tissue, is not typically employed in insulation materials because its properties do not enhance thermal or acoustic insulation performance. E-glass fibers dominate the fiberglass insulation market, offering durability and energy efficiency essential for residential and commercial construction.
Overview of E-glass: Properties and Applications
E-glass, a widely used type of fiberglass, is composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate glass with excellent tensile strength, electrical insulation properties, and chemical resistance. Its thermal stability and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for applications such as insulation, reinforcement in composites, and structural materials in aerospace and automotive industries. The material offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to bioactive glass, which is primarily used for biomedical purposes rather than insulation.
What is Bioactive Glass? Composition and Characteristics
Bioactive glass is a type of glass-ceramic material primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), calcium oxide (CaO), sodium oxide (Na2O), and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), designed to interact biologically with surrounding tissues. Its unique characteristics include the ability to bond with bone and promote tissue regeneration through the formation of hydroxycarbonate apatite layers when exposed to bodily fluids. Unlike E-glass, used in fiberglass insulation for its mechanical strength and thermal resistance, bioactive glass exhibits bioactivity and biocompatibility, making it suitable for medical applications rather than traditional insulation purposes.
Thermal Performance: Bioactive Glass vs E-glass
Bioactive glass exhibits enhanced thermal insulation properties compared to conventional E-glass, with lower thermal conductivity values contributing to superior energy efficiency in fiberglass insulation applications. The unique molecular structure of bioactive glass promotes better heat resistance and thermal stability under fluctuating temperature conditions. This results in improved overall thermal performance, making bioactive glass a promising material for advanced insulation solutions.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Bioactive glass offers enhanced mechanical strength due to its unique composition that promotes rigidity and durability, making it more resistant to stress and deformation compared to traditional E-glass. E-glass fibers provide good tensile strength and flexibility, but bioactive glass outperforms in long-term structural integrity under mechanical loads. This superior strength makes bioactive glass a preferable choice for high-performance fiberglass insulation applications requiring enhanced durability and mechanical resilience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass offers enhanced environmental benefits over traditional E-glass in fiberglass insulation due to its ability to support biodegradability and reduce landfill waste. E-glass, a common fiberglass material, involves energy-intensive production of silica and aluminum oxides, contributing to a higher carbon footprint. Utilizing bioactive glass in insulation promotes sustainability by integrating eco-friendly raw materials and facilitating possible recycling or safe degradation at end-of-life stages.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bioactive glass in fiberglass insulation offers enhanced biocompatibility, reducing skin irritation and respiratory risks compared to traditional E-glass. Its composition often includes elements that promote healing and minimize toxicity, making it safer for installers and occupants. E-glass, while effective for thermal insulation, can cause irritation and respiratory issues due to its fine glass fibers and potential airborne particles during installation.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Bioactive glass in fiberglass insulation offers superior moisture resistance compared to traditional E-glass, significantly reducing water absorption and mold growth risk. The enhanced chemical stability of bioactive glass improves long-term durability by resisting degradation in humid environments. E-glass, while cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under moisture exposure, leading to reduced insulation performance and lifespan.
Cost Analysis and Material Availability
Bioactive glass generally incurs higher production costs compared to E-glass due to its specialized composition and manufacturing processes tailored for biomedical applications, making it less cost-effective for standard fiberglass insulation use. E-glass benefits from widespread availability and established manufacturing infrastructure, resulting in lower material costs and easier procurement for insulation projects. The cost advantage and material accessibility of E-glass make it the preferred choice for large-scale fiberglass insulation, while bioactive glass remains a niche option with limited commercial supply.
Future Trends in Fiberglass Insulation Technology
Bioactive glass offers promising advancements in fiberglass insulation by enhancing thermal performance and incorporating environmentally friendly, recyclable materials compared to traditional E-glass fibers. Innovations in nanotechnology and bioactive additives are driving future trends, enabling insulation products with improved durability, moisture resistance, and antimicrobial properties. Research emphasizes sustainable production processes and multifunctional insulation solutions to meet evolving energy efficiency standards and building regulations.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs E-glass for Fiberglass insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com